HOW TO PRACTICE MAPS FOR UPSC
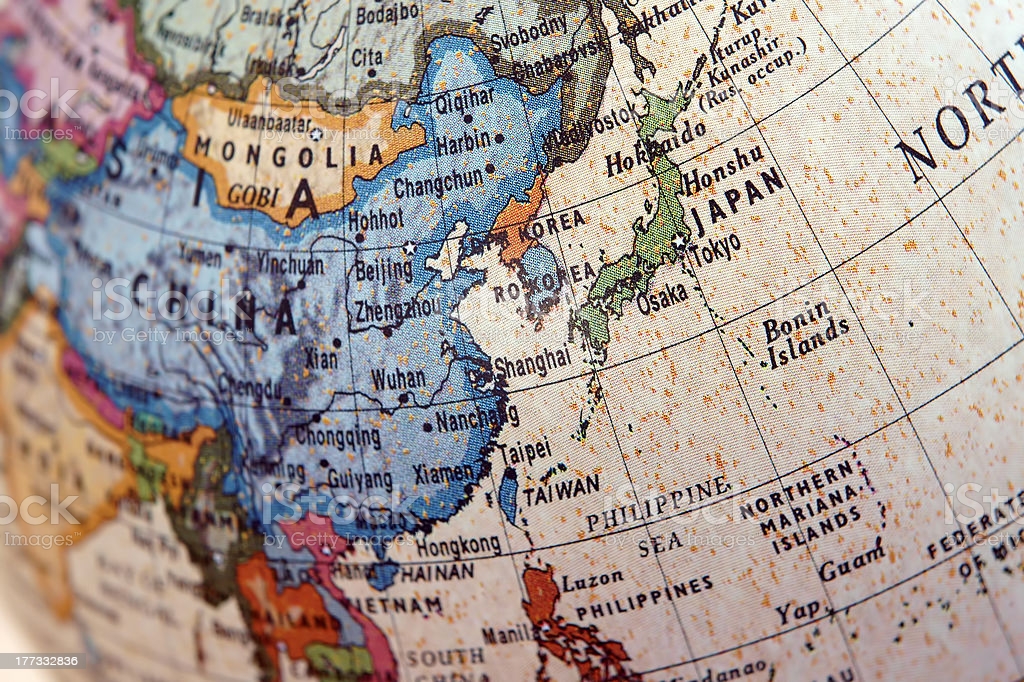
Every year a number of map-based questions are asked in UPSC CSE Prelims examination. And it is often perplexing for aspirants to figure out where to begin! This article gives you a few pointers on how to prepare the atlas effectively in order to tackle the map-based questions in UPSC examination.
India - Political
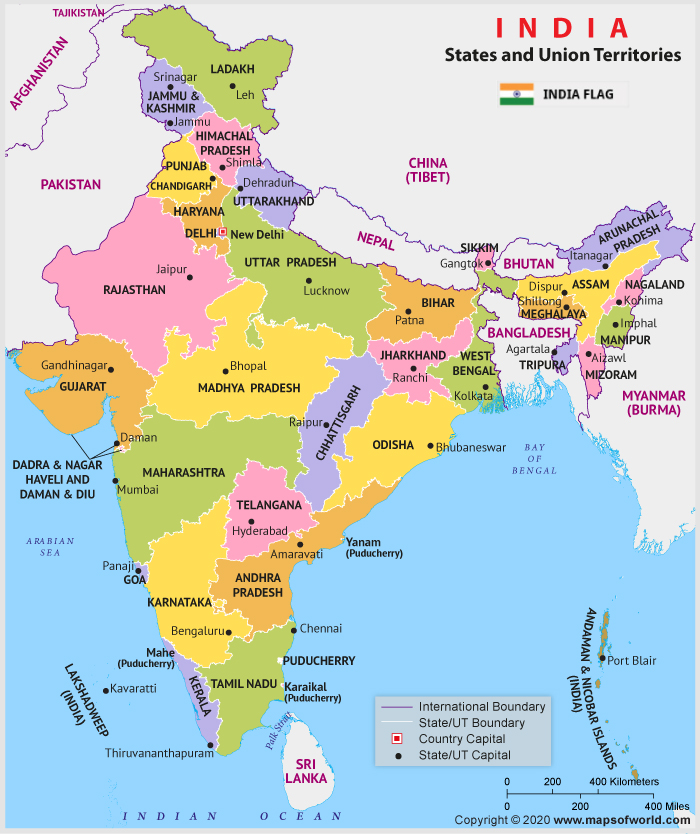
International Borders
- Make a note of all the countries which are in India’s neighbourhood.
- Now, jot down the name of India states which are sharing border with these countries. Also, keep a record of minute details.
For example: How many international borders a particular state is sharing?
Which state shares the longest international land border of a particular country? etc.
- Identify the eastern, western, northern, and southern extents of India.
States
- Make a note of the following:
- which states share boundaries with which other and how many states.
- Major cities of the states and their important details. For example, whether it lies along a riverbank.
- Arrange important cities from East to West and North to South.
- cities and regions which are in news recently. For example:
Rajasthan’s Bhilwara was in news during the COVID-19 Lockdown (Bhilwara Model)
Latitudes and Longitudes
- Observe the Latitudes and longitudes passing through India. For instance, make a note of the states through which the Tropic of Cancer or the Standard Time Meridian is passing.
- Also, observe the various cities, water bodies in terms of longitudes and latitudes passing close to them.

India - Physical
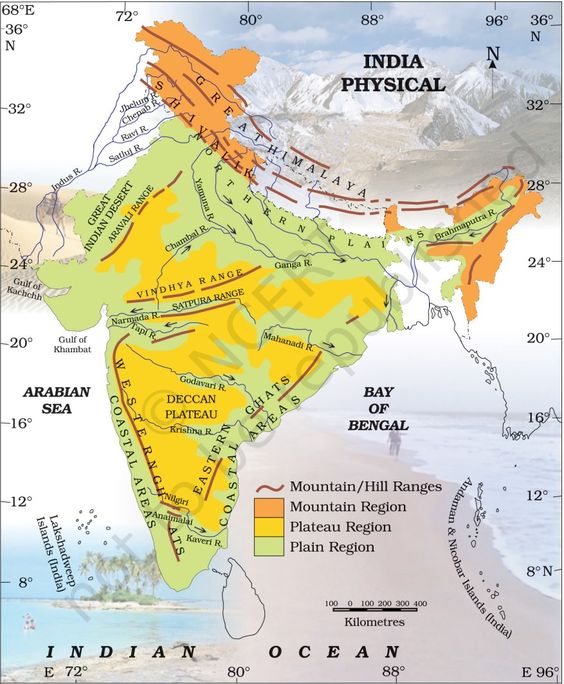
Mountain Ranges
- Study important peaks and mountains of India based on various regions. For example Himalayan Mountains --- further, ranges in greater Himalayas, lesser Himalayas and Shiwaliks.
- List down all the important glaciers in the Himalayan region.
- Similarly, study mountain ranges in the North-East India, Central India.
- Ranges in the Pensinsular region; Eastern Ghats and Western Ghats.
- Also, locate the important peaks like Doddabeta, Anaimudi, Kanchenjunga etc.
- Please, remember the east-west & north-south chronology of various mountain ranges and peaks.
- Make a note of important mountain passes such as Nathu La, Shipki La, Bomdi La, Lipu Lekh, etc.
- Observe the various passes and gaps lying within the geographical spread of such mountain ranges.
Rivers
- The best way to study a river is to note down its Source/Origin, course of flow, its tributaries and distributaries and finally its mouth (where the river meets the sea).
- Study rivers in three major divisions: Himalayan Rivers, Rivers of North-East and Peninsular Rivers.
- Remember the left and right bank Tributaries of rivers using mnemonics. Also, remember whether the rivers are east-flowing or west-flowing
- Focus on rivers which are in news.
- Jot down the names of important dams and the rivers on which they are built. (Only important ones and that are in news).
- Make of note of important falls and their respective rivers in India.
- North-South and East-West chronology of rivers is also important.
Plateaus
- Study the major Plateaus of Central and Peninsular India.
- For example: The Central Highland, The Bundelkhand Upland, The Malwa Plateau, The Baghelkhand, The Chotanagpur Plateau, The Meghalaya Plateau, The Deccan Plateau etc.
- Arrange the various plateaus from West to East and North to South.
- Also, observe whether a particular plateau is a source of some river or not. Example: Damodar originates in Chandwa on the Chota Nagpur Plateau. Narmada emerges from Amarkantak Plateau.
Soils and Rainfall
- Identify the group of states which represent the various categories of soils in India.
Example: Black soil is spread across Gujarat, Maharashtra, Karnataka, and Madhya Pradesh on the Deccan lava plateau. Locate these states on map.
- Classify states into groups based on the rainfall they receive and locate them on a map.
- Observe isotherms and their position in India’s map.
Lakes
- Make a state-wise list of important lakes in India and locate them on a map.
- Arrange them in chronology. Also, keep a track of lakes with unique features and those which are in news.
For example: Wular lake is the largest freshwater lake in India.
Lonar lake is one of the four basaltic impact structures of the Earth.
Natural Vegetation
- Locate the various forests on the map of India based on spatial distribution.
- Also, jot down the important flora and fauna of the region. This technique is studying through building links.
Other important locations
Identify locations of important wetlands, Ramsar sites, nuclear power stations; minerals like iron ore, coal; world heritage sites, pilgrimage sites, ports, National Parks etc.
Also, locate the Islands and their physical features: i.e Andaman and Lakshwadweep Island. Please remember the various lines and channels in these regions.
Example: The Ten Degree Channel separates the Andaman Islands and Nicobar Islands from each other in the Bay of Bengal.
World
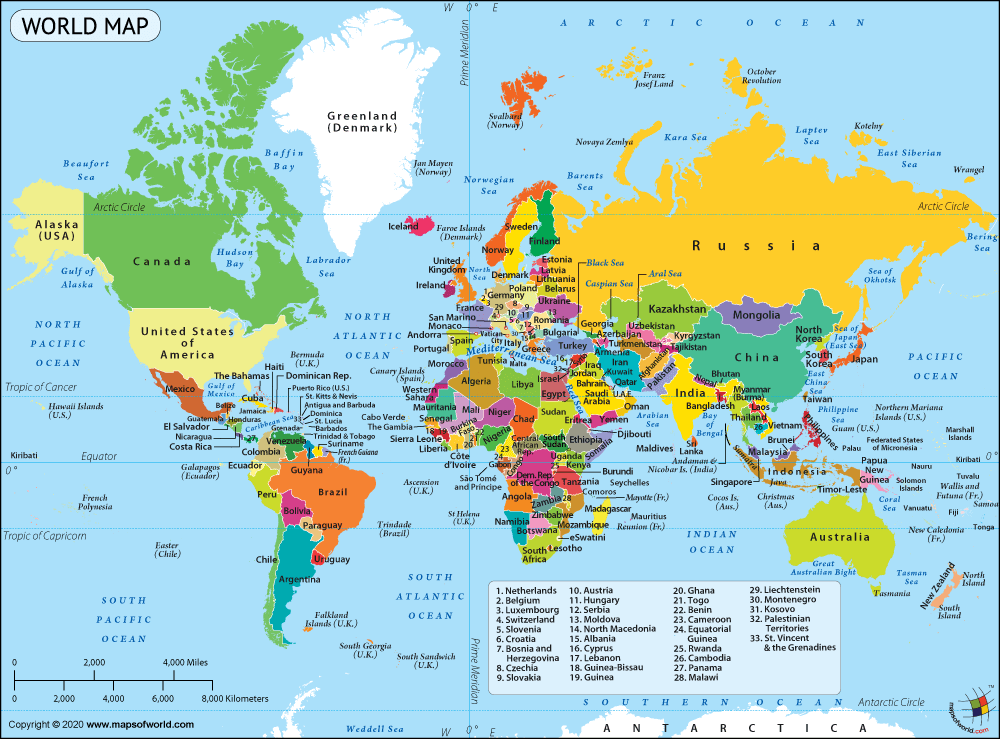
Latitude and Longitudes
- Note the countries through which lines of latitudes and longitudes pass.
For example Tropic of Cancer, Tropic of Capricorn, Arctic Circle, Equator.
Also, observe the International Date Line, Prime Meridian, and make a note of countries that fall on the two sides of the lines.
Locate the various lines: examples:
- Nine-dash line—is used by China and Taiwan, for their claims of the major part of the South China Sea.
- The 38th parallel north formed the border between North and South Korea prior to the Korean War.
Borders
- Prepare each of the continents one by one.
- Now, pick countries that are in Current Affairs and observe whether it is landlocked, which countries are sharing borders with it, and the water bodies it shares its borders with.
Physical Features
- Pick all-important mountain ranges, seas, lakes, rivers, volcanoes, plateaus, climatic regions, transport links, waterways, mineral resources regions, flora and fauna mentioned in your
- NCERTs
- Geography, history, economy books
- Current Affairs.
- Now, locate them on the map to have a fair idea.
Oceans and Water Bodies
- Use mnemonics to remember the names of countries sharing their borders with specific water bodies.
For example, the Caspian Sea is surrounded by T I R A K
Turkmenistan. Iran, Russia, Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan
- Remember the various divisions of oceans: Bermuda is a British Overseas Territory in the North Atlantic Ocean.
Current Affairs and Map
Keep a track of locations and physical features mentioned in recent news articles. Locate these regions on a map. For example: If Iraq is in news, you should be able to tell which country shares a border with which other countries in West Asia.
Some previous years Map-based questions:
Q) Which one of the following pairs of islands are separated from each other by the ‘Ten Degree Channel’? 2014
- Andaman and Nicobar
- Nicobar and Sumatra
- Maldives and Lakshadweep
- Sumatra and Java
Answer: a
Q) Consider these pairs
- Cardamom Hills Coromandel Coast
- Kaimur Hills Konkan Coast
- Mahadeo Hills Central India
- Mikir Hills North-East India
Which of the above pairs are correctly matched? 2014
- 1 and 2
- 2 and 3
- 3 and 4
- 2 and 4
Answer: c
Final words
Practice drawing rough sketches of maps and try locating important places/features on them because it will be highly useful in GS Mains papers. Map should be practiced as a recreation during free time and breaks. Maps should not be an extra burden for aspirants. Please, don’t try to mug up everything given in the world map as it is humanely not possible to remember everything and it won’t fetch easy marks either. Rather, make calculative and smart choices based on Current affairs and the static portion to figure out what to remember and what not. Try to make map-making a strength for your GS papers.
Happy Learning!









