Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Introduction
Hyperautomation is the advanced version of the automation process in the industry. This new technology eliminates the need for employees to monitor and perform specific operations. The idea is to use this future technology to replace human workers to reduce the limitation and errors in the process.
Companies started using automation processes in the last decade, but research and development have taken it to a different level in recent times.
What is Hyperautomation Technology?
Hyper-automation combines various advanced technologies such as Machine Learning and Artificial intelligence, together with Robotic Process Automation.
This technology aims to fully augment human capabilities by building intelligent robotic systems that can do anything a normal human can. These systems are designed to think, reason, compute and collaborate. In essence, it provides an improvement in the human factor in any endeavor. It enables machines to work alongside people in every walk of life.
Features of Hyperautomation
One of the most important features of the emerging breed of hyper-automated systems is intelligent software or self-programming code that runs on routers and nodes.
The logic engine of the computer then processes this programming code and executes the desired operation.
Additionally, Hyper-automation technology features include:
The other interesting feature of this future technology is that it will enable real-time execution across wide-ranging applications.
The other interesting feature of this future technology is that it will enable real-time execution across wide-ranging applications.
Some Real-Life Examples of Hyperautomation
One example of hyperautomation is the automated credit card approval process. Financial institutions get thousands of credit card applications every day. While traditional automation helps with pre-filling forms and validating fields, hyperautomation takes it to the next level. The hyperautomation framework communicates with different systems and retrieves customer data such as credit balance and debt. It automatically performs background checks on the customer. Then the hyperautomation framework approves or rejects the application based on the data it retrieved and the pre-set rules. Thus, hyperautomation makes the credit card issue incredibly faster.
Customer service is another real-life example where hyperautomation augments the human workforce. When a customer service executive gets a call, the hyperautomation pulls up various details about the customer from different systems and makes the task of the customer service executive easier.
History
The term “hyperautomation” was first used by noted mathematician Alan Turing in 1931. He came up with an idea to link computer hardware and human brains to make the latter able to do almost any task necessary to solve any problem.
After the development of the electronic computer, many other developments have come in the form of software specifically meant for manipulating data sets.
Afterwards, these programs are increasingly used in research and business activities, leading to hyper automation.
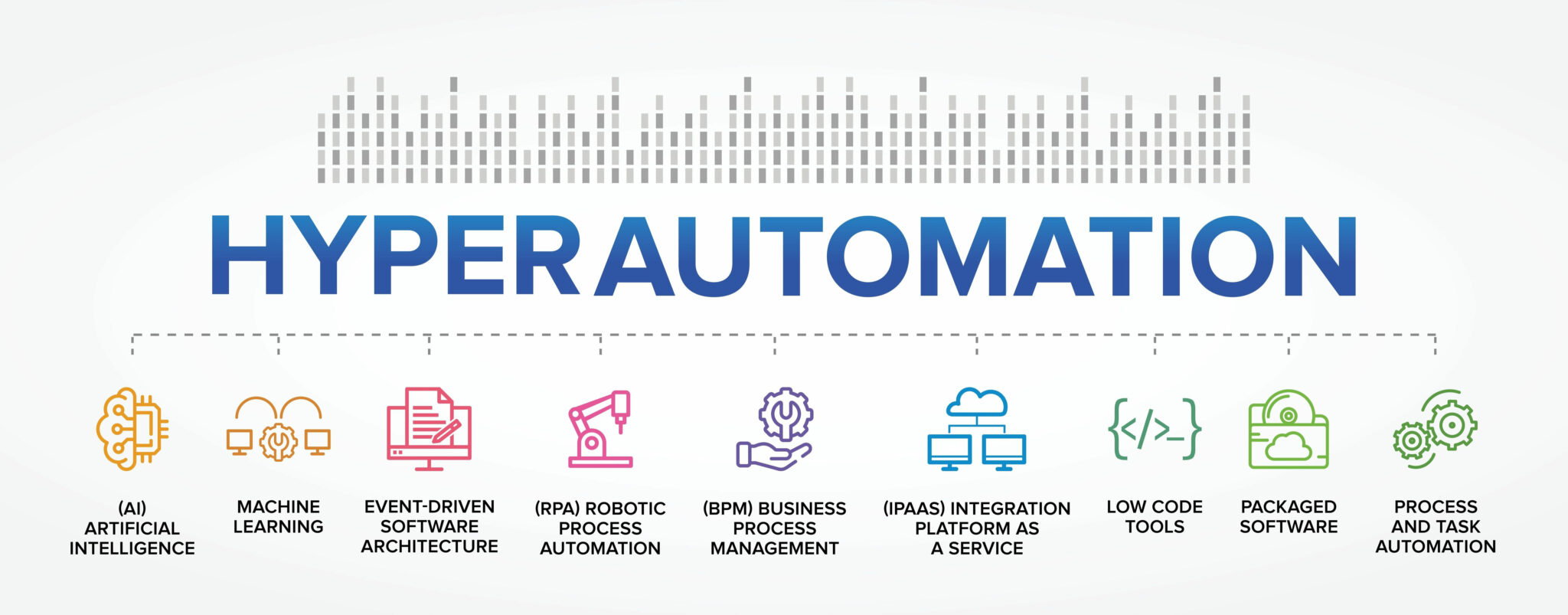
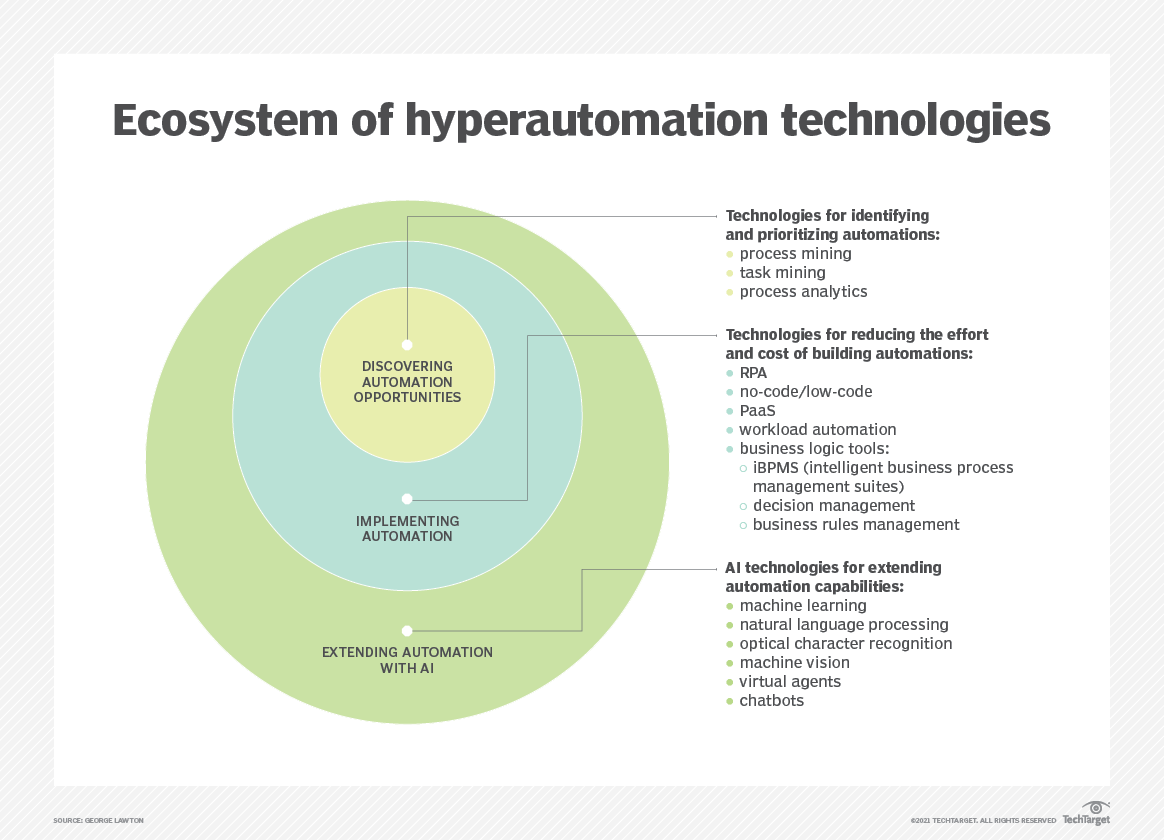
Technologies that Facilitate Hyperautomation
Hyperautomation is a complex process that combines many cutting-edge technologies. Here are different technologies facilitating hyperautomation:
Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
Robotic process automation uses computer programs known as software robots to automate structured and repetitive tasks. For example, in manual data entry, an employee looks at the forms submitted by customers and types in that data into a spreadsheet. If the input forms are standardized, a software program can mimic the actions of the employee by retrieving information from the relevant fields in the form and filling out the spreadsheet. This is an example of robotic process automation. Robotic process automation is not as simple as writing a piece of code to accomplish a simple task. It uses technologies like artificial intelligence to understand external events and change accordingly.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are widely understood technologies in their classic context. In hyperautomation, robotic process automation is used in conjunction with artificial intelligence and machine learning techniques. When an organization ventures to implement hyperautomation, it has to deal with large volumes of unstructured data, such as emails, chats, text messages, and purchase orders. Artificial intelligence techniques are used to process unstructured data.
Another application of artificial intelligence in hyperautomation is pattern recognition. Hyperautomation analyses the data and makes decisions without manual intervention. For example, hyperautomation uses artificial intelligence to analyze insurance claims and, based on the models, detect fraudulent claims.
Big Data
Big Data is a set of technologies that make it possible to store, analyse and manage huge amounts of data produced by devices in order to identify patterns and create optimal solutions.
Cobots
Cobots are the prime example of collaborative robotics, in other words, robots that share tasks with human workers and are revolutionising production processes.
Chatbots
Chatbots are systems based on AI, ML and Natural Language Processing (NLP) that can hold a conversation in real time with a human being using text or speech.
What Are the Benefits of Hyperautomation?
Increased Efficiency
Automation increases the efficiency of the workforce. Organizations who still use manual processes may create bottlenecks, even when using simple automation. For example, in an automated business process, if at any stage, an employee should manually validate the results, it creates a bottleneck; hyperautomation removes this bottleneck by entirely eliminating the need for manual intervention.
Employee Satisfaction
In many organizations, employees need to perform repetitive, legacy tasks that could be easily automated. Employees might feel underwhelmed doing such tasks that do not offer intellectual stimulation. Hyperautomation takes away the stress of having to do repetitive, structured tasks, so employees can find time to do more valuable jobs, leading to better employee satisfaction.
Substitutes for Human Workers
Hyperautomation enables robots to work alongside humans in any industry. These robots can serve as assistants or substitutes for human workers in many situations.
There are instances when workers sit in front of the computer because they find it relaxing. Extended sitting can result in poor blood circulation, vision impairment, and other physical ailments. Therefore, hyperautomation technology is beneficial in this condition and can work well in eliminating such problems.
Create a Digital Twin of the Organization
A digital twin of an organization is the digital replica of its business processes. Take, for example, the case of a supplier who gets a request for a quote via mail. An employee manually creates the quote and sends it to the customer then the customer sends a purchase order, which the supplier fulfills. With hyperautomation, all these processes are automated, and the automated pipeline behaves just like a particular business process. With a digital replica, organizations can derive real-time, continuous insights about their business processes, opening up a huge opportunity for the business and process streamlining.
Elimination of Human Error
When an employee performs repetitive tasks like filling a spreadsheet with financial data, there is a high chance of error. The software bots installed by the hyperautomation doesn’t make human errors. Once deployed, they perform as expected in normal scenarios.
Higher Production in Industries
Hyperautomation allows the company to achieve more production targets in a shorter time. Certain companies have started using these robots for tasks such as packaging and unpacking food items. These people can do their work more efficiently as they do not have to leave their desks to complete such tasks.
Additionally, these robots help to lift heavy loads in the industries. For instance, forklift robots allow the workers to move the heavy load without getting tired easily.
Reducing Operational Obstacles:
Hyperautomation can steer legacy systems and navigate through other functional barriers, pinpointing inefficiencies or obstacles in enterprise operations. Merging AI and RPA helps determine best optimization practices for automated processes, therefore providing the greatest impact points.
Transforming Live Agents to Digital Workers:
Strengthens workforce by deploying digital workers to collaborate with employees for increased productivity or extra assistance. These digital workers, built through hyperautomation tools, can also help consumers navigate knowledge bases, provide support services, and manage accounts.
Accelerating Compound Tasks:
Hyperautomation pioneers a speedy pathway for digital transformation and increases automated tasks that were previously dependent on human insight and input. By streamlining several internal systems, hyperautomation provides visibility into previously hidden interactions between functions, KPIs, and processes.
Increasing business agility
Organizations today must be able to adapt their processes to new market needs. Hyperautomation enables them to scale operations, respond to market changes, and pursue emerging opportunities.
Upskilling
Through hyperautomation a culture of upskilling and expert-level support can be created. With all mundane tasks being taken off their to-do list, employees can handle various activities and upskill in the process.
Integrations
Seamless integration between cloud and on-premise infrastructure improves communication and reduces lag. All systems will be able to access the centralized data, which means that they will be on the same page. This will help them improve their efficiency.
Disadvantages
There are also some potential disadvantages of hyper-automation. They are
Challenges of implementing Hyperautomation
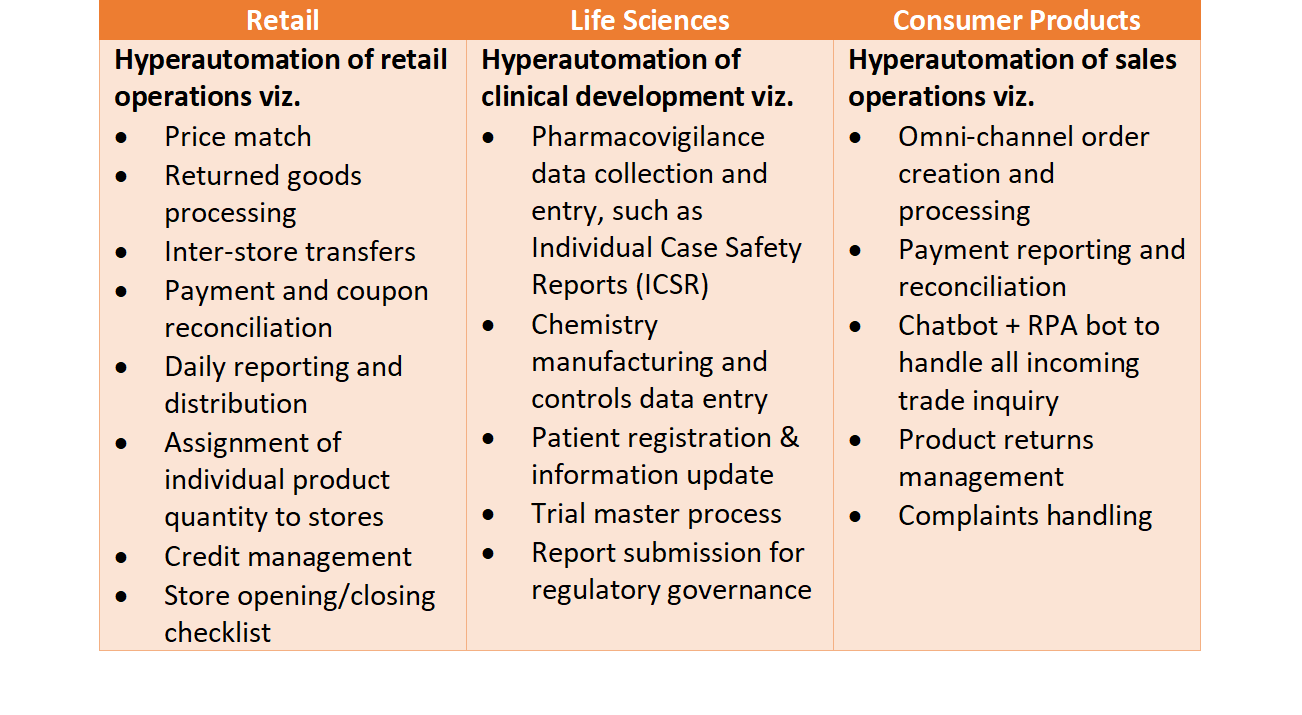
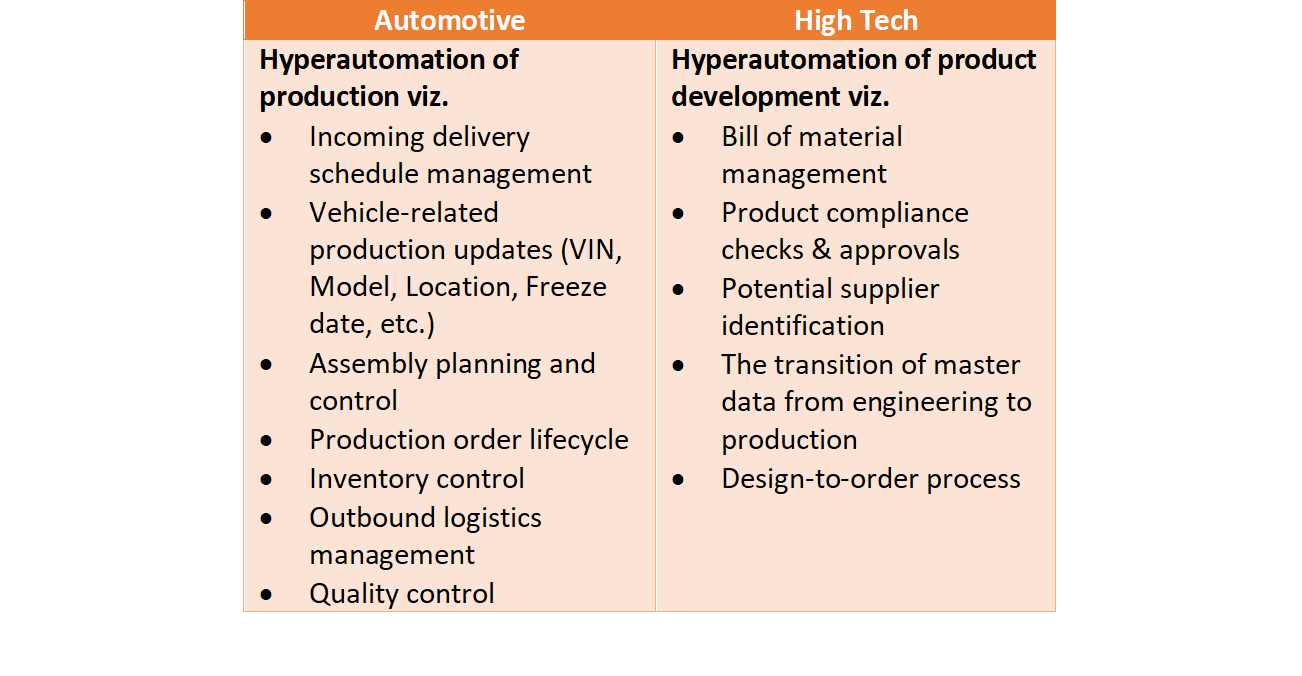
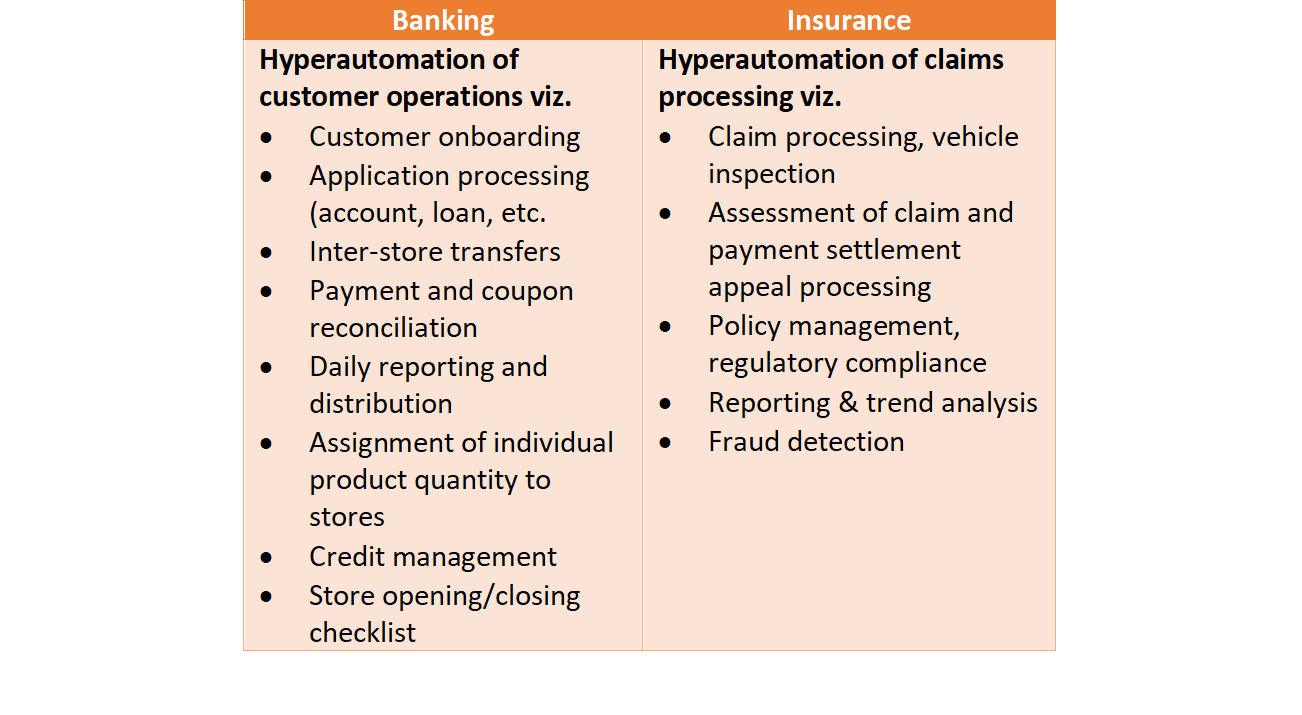
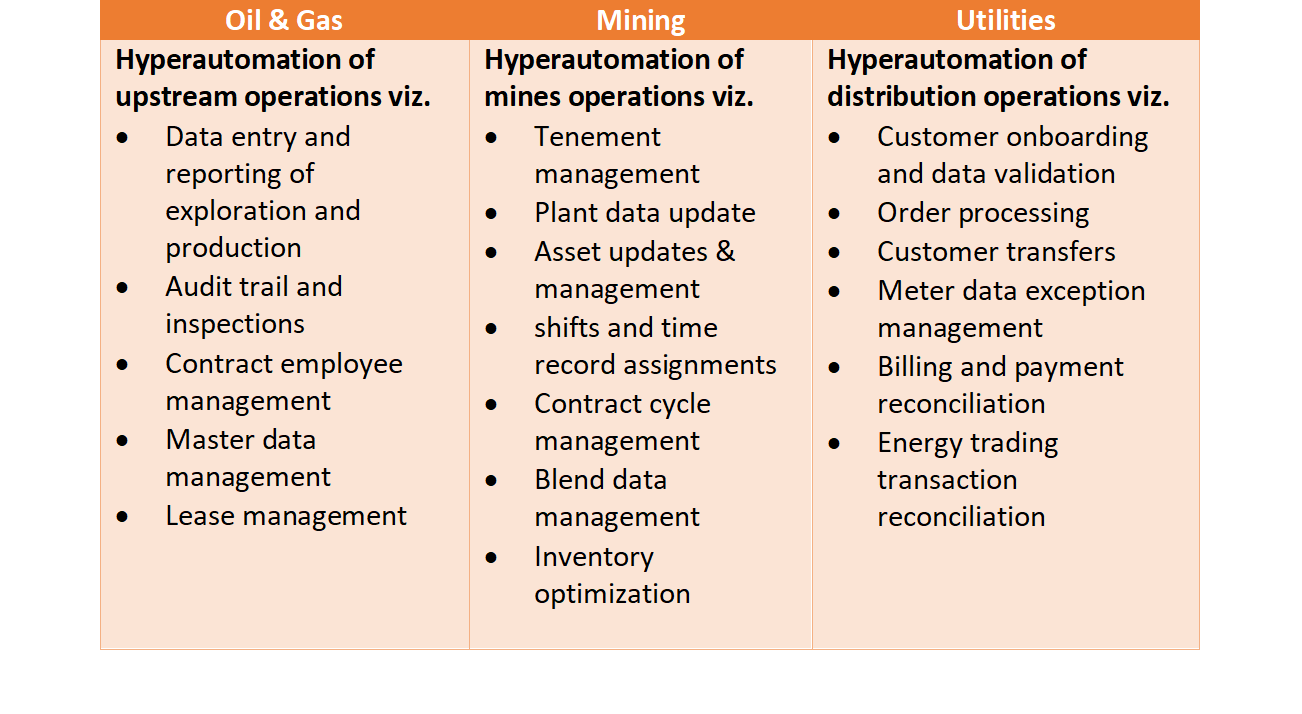
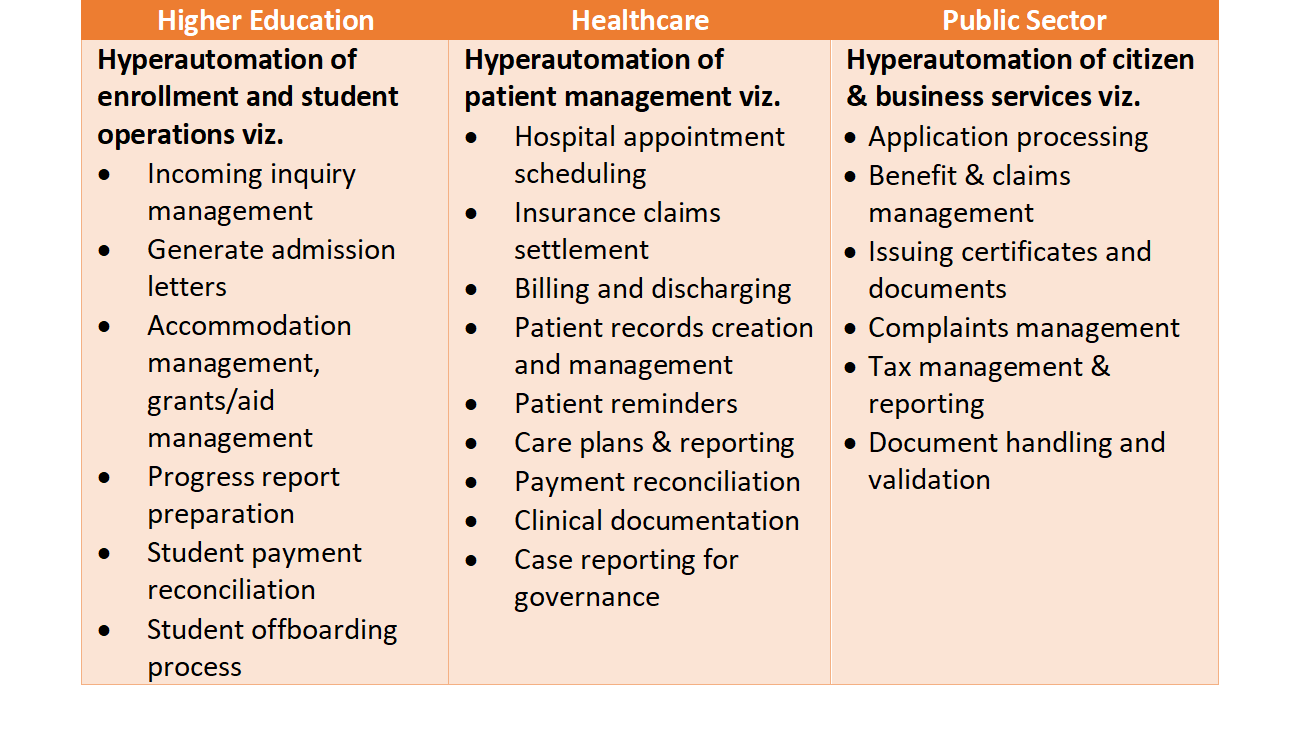
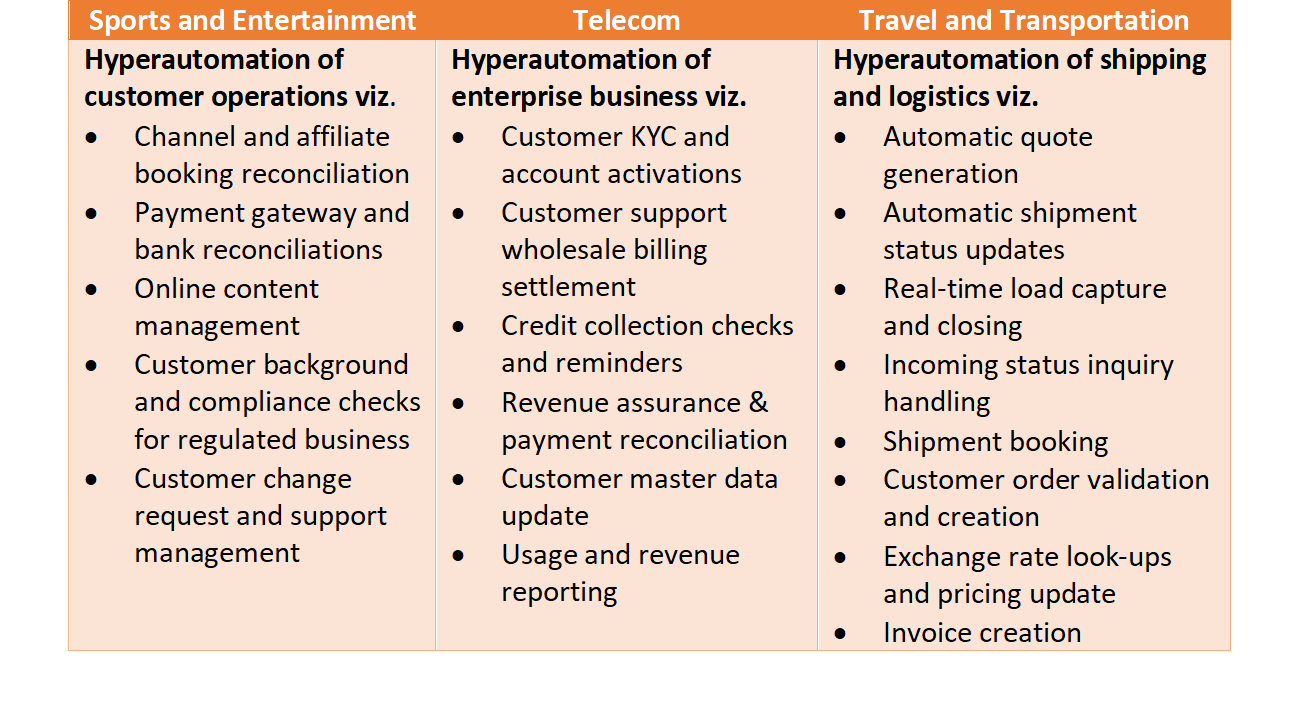
Hyperautomation Use Cases
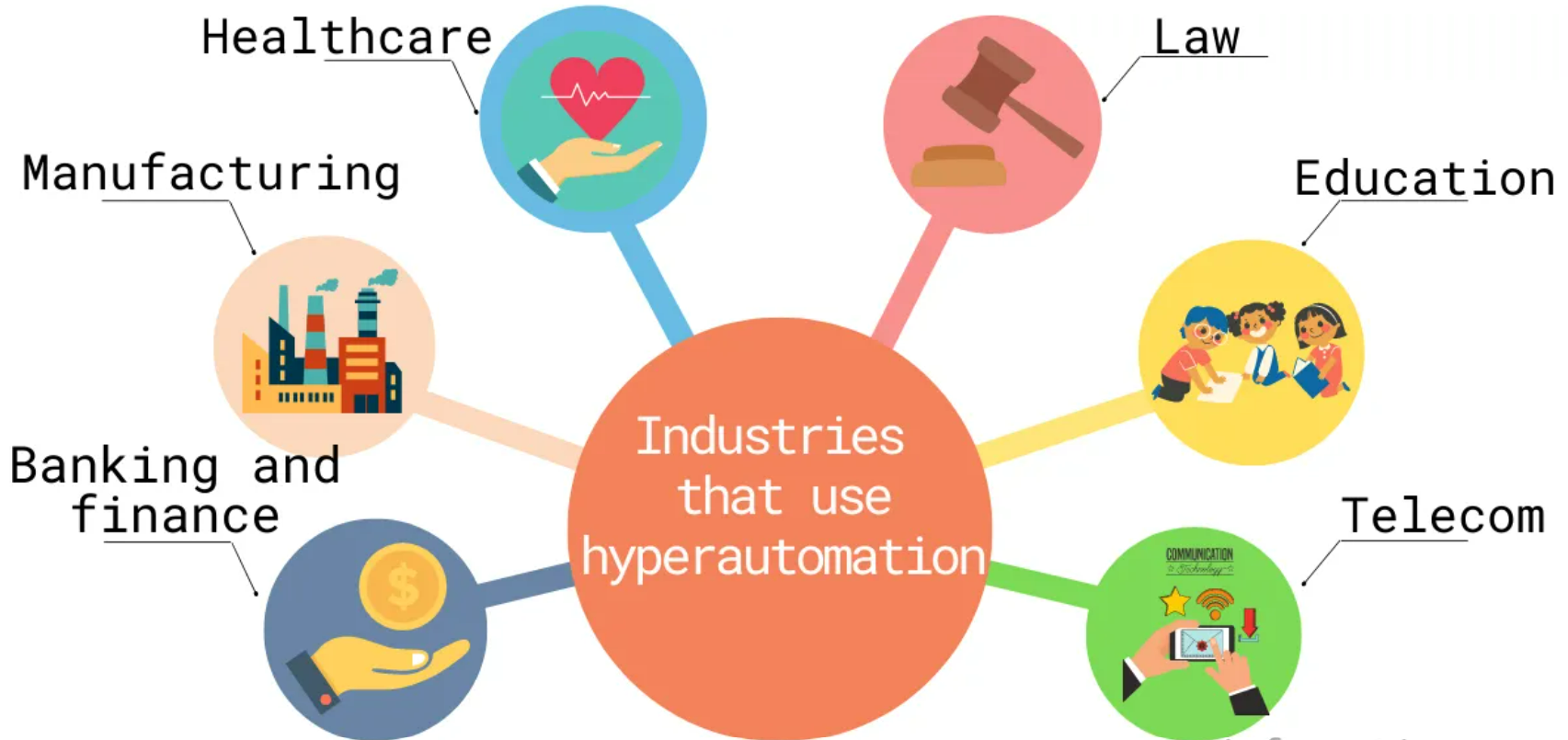
Healthcare:
Machine learning, AI and RPA provide immense value in improving processes in the healthcare industry. Using these tools together, hyperautomation enables organizations to save time, standardize processes, and reduce errors by automating repetitive tasks related to patient testing, medication reconciliation, patient registration, insurance verification, and more.
It also helps in the medical field by automating processing such as patient data entry, insurance claims, accumulating data, and giving beneficial output for more effective remedy plans.
One of the most prominent applications of this technology in the medical industry is tissue grafting. This process used to require the use of a needle and thread to graft the tissue into the patient.
Today, from applying the graft to its placement under the skin, the entire grafting process is made much more efficient and less painful for the patient because of hyperautomation.
Financial services:
The rise of alternative lending methods, fintechs, and challenger banks has made the financial services industry even more competitive. With hyperautomation, financial institutions can transform their operations and remain competitive by improving customer onboarding, streamlining compliance processes, and improving accuracy and speed.
Customer Service
As customer expectations and demands change, a business must find ways to adapt its operations to address customer concerns and enhance the customer experience. Integrating hyperautomation into customer service processes and systems can reduce manual tasks, sort queries, provide fast solutions, and streamline workflows.
In essence, hyperautomation mobilizes the power of organizations to connect employees, systems, and automation robots to collaborate for future business outcomes and goals.
Banking and finance:
These sectors operate where there are much data to deal with. Hyperautomation reduces the complexity by automating customer service tasks such as account opening and loan processing. In finance, it automates stock market analysis, financial report generation, and more.
Manufacturing:
In the manufacturing sector, it enables automation of machine monitoring, quality control, assembly line tasks, order fulfillment, and inventory management.
Law:
In legal processing, it automates the drafting of legal documents using natural language processing and also automates contract review and case management.
Education:
Automating student admissions and grade tracking by using RPA bots
Telecom:
Automating network repair and customer service tasks.
Military and Police:
Another application of this technology today is in the military and police industries. The application of hyper-automation has greatly reduced the time required to complete certain tasks, such as install new equipment, virtual military training, maintain security systems.
Conclusion
To summarise, the future may bring many new uses for these automated systems, which is effective as many advanced technologies are associating with the process. Moreover, they may become an important part of the manufacturing industry by taking over monotonous tasks that humans used to do. Therefore, hyperautomation may prove to be just the sort of machine that opens up many more doors. Hyperautomation allows the automation of activities that span multiple departments, systems, and job functions that previously required efforts that did not add value but limited creativity, cognition, and innovation in specific roles. The automation of mundane tasks free-up time for learning, upskilling, and focusing on value-added tasks maximising human potential and making a happier workforce.
CITATIONS
https://www.information-age.com/future-of-hyperautomation-in-2022-19107/
https://research.aimultiple.com/hyperautomation-examples/
https://orbograph.com/understanding-hyperautomation-for-banks-three-keys-to-success/
https://www.automationanywhere.com/rpa/hyperautomation
https://www.iberdrola.com/innovation/hyperautomation
https://www.techtarget.com/searchcio/definition/hyperautomation
https://www.tibco.com/reference-center/what-is-hyperautomation
https://www.mulesoft.com/resources/api/what-is-hyperautomation
https://quixy.com/blog/hyperautomation-what-why-and-how/
https://techarbiters.com/hyperautomation-key-features-advantages-and-future/
https://www.analyticsinsight.net/future-automation-belongs-hyperautomation/
© 2024 iasgyan. All right reserved