Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now



Its provisions are as follows:
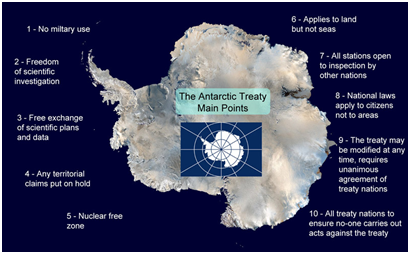
3.png)
|
The Indian Antarctic Program is a program under the control of the National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research, Ministry of Earth Sciences, Government of India. It was initiated in 1981 with the first Indian expedition to Antarctica. The program gained global acceptance with India's signing of the Antarctic Treaty and subsequent construction of the Dakshin Gangotri Antarctic research base in 1983, superseded by the Maitri base from 1989. The newest base commissioned in 2012 is Bharati. Under the program, atmospheric, biological, earth, chemical, and medical sciences are studied by India. |
© 2024 iasgyan. All right reserved