Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now



The Constitution of India begins with a Preamble. It contains the ideals, objectives and basic principles of the Constitution. The salient features of the Constitution have evolved directly and indirectly from these objectives which flow from the Preamble. It spells out the basic philosophy contained in the body of the Indian Constitution.
Reading through the Preamble, one can see the purpose that it serves, namely, the declaration of
(1) the source of the constitution
(2) a statement of its objectives
(3) the date of its adoption.
The Preamble, in brief, explains the objectives of the Constitution in two ways:
It is because of this, the Preamble is considered to be the key to the Constitution.
Besides serving as an introduction to the Constitution, it serves many other purposes like :

The objectives, which are laid down in the Preamble, are:
1. Description of Indian State as Sovereign, Socialist, Secular, Democratic Republic. (Socialist, Secular added by 42nd Amendment, 1976).
2. Provision to all the citizens of India i.e.,
a) Justice social, economic and political.
b) Liberty of thought, expression, belief, faith and worship.
c) Equality of status and opportunity.
d) Fraternity assuring dignity of the individual and unity and integrity of the nation.
Although it appears at the very beginning of our Constitution, it didn't come into existence in the same order. Rather, it was the last piece of Drafting adopted by the Constituent Assembly at the end of the first reading of the Constitution.
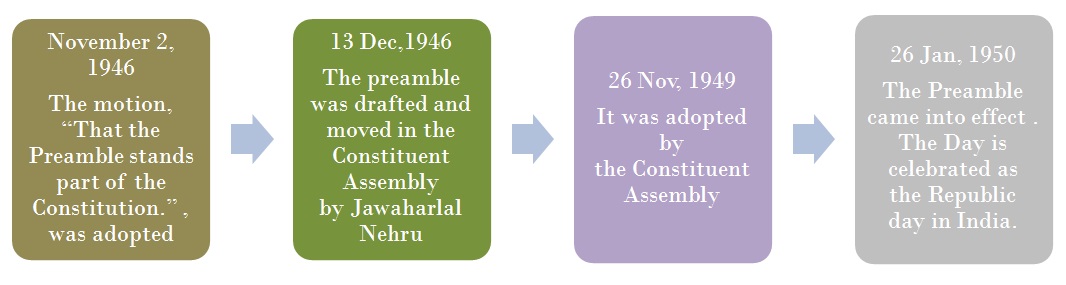
The preamble to the Indian Constitution is a very important part of the Constitution itself. However, the most discussed about topic remains
"Whether it is an Integral Part of the Constitution ?" and "Whether it can be amended like any other part of the Indian Constitution ?"
It has been highly a matter of arguments and discussions in past whether Preamble should be treated as a part of the constitution or not. The basic question beneath the debate is, whether or not a citizen of a nation to which he is subject to can challenge in the court of law if in case his rights have been infringed which were mentioned in the Preamble.
To have an answer to this question, we need to take into account the interpretation of the Supreme Court in two important cases.
Kesavanada Bharati v. the State of Kerala
The majority held that since the Preamble is the part of the Constitution it can be amended but subject to this condition that the “basic feature” in the Preamble cannot be amended. The Preamble declares that the people of India resolved to constitute their country into the Sovereign Democratic Republic.
An amending power cannot be interpreted so as to confer power on the Parliament to take away any of these fundamental characteristics of policy.
Subscribe to our Polity Mock Series HERE.
A Preamble indicates only the general purposes for which the people ordained and established the Constitution. It cannot be regarded and has never been regarded as the source of any substantive power conferred on the Government or any of its departments.
A Preamble provides significant help in the interpretation of the Constitution when words actually are ambiguous. Under such circumstances it is the key to open the minds of the makers of the Act. But if the language of the Article is sufficiently clear, it is not to be interpreted in the light of the Preamble in preference to the obvious meaning thereof.
The objectives in the Preamble are just a part of the basic structure of the Constitution and nothing more than that. So, Preamble cannot be amended so as to destroy the objectives, but also cannot be used as a law to judge people on.
Click HERE to Subscribe our Test Series on Indian Polity for UPSC CSE 2021.
© 2024 iasgyan. All right reserved