Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now



Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
Acidification of Water Bodies
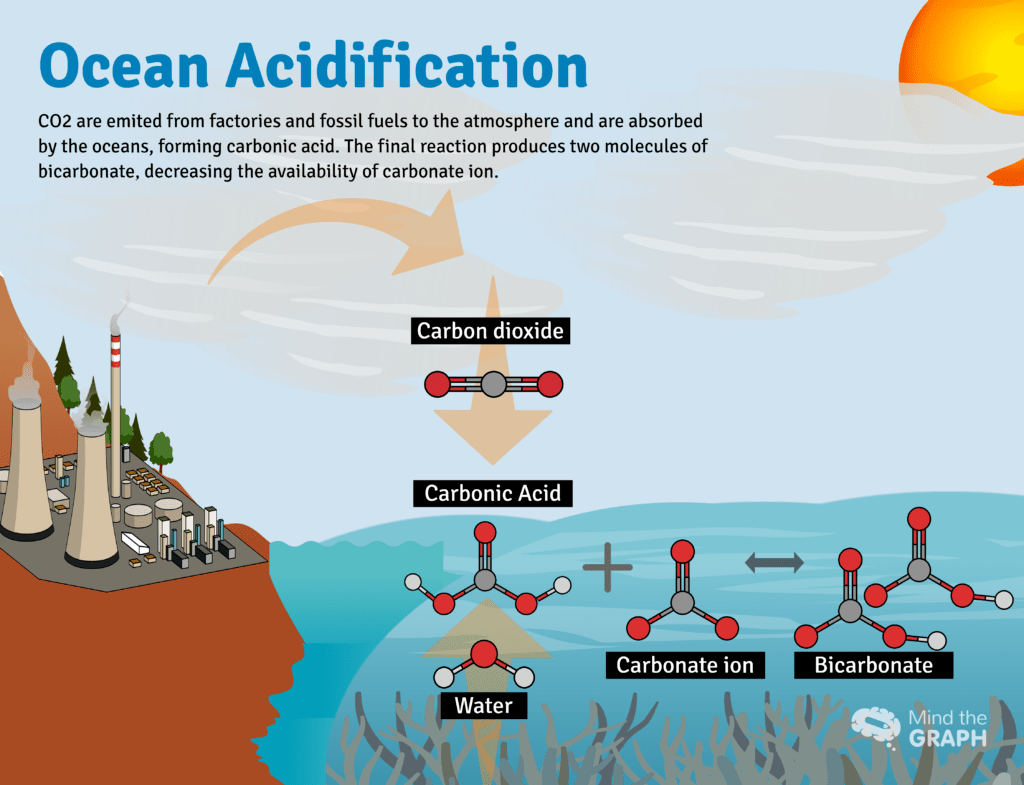
Impact of Ocean Acidification
Decreasing the quality of oceanic water
Affecting the marine life:

Affecting the coral reefs:
Affecting the vegetation of the marine ecosystem:
Behavioral changes of water animals:
Effects on the shellfish:
Food sources are declining
Way Ahead
Bottomline
© 2024 iasgyan. All right reserved