Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- There has been an increase in the number of earthquakes from January to November 2023 compared to the last three years, Union Minister of Earth Sciences Kiren Rijiju told the Lok Sabha on December 6, 2023.
- However, experts have questioned the government’s information on the causes of the increase in earthquakes.
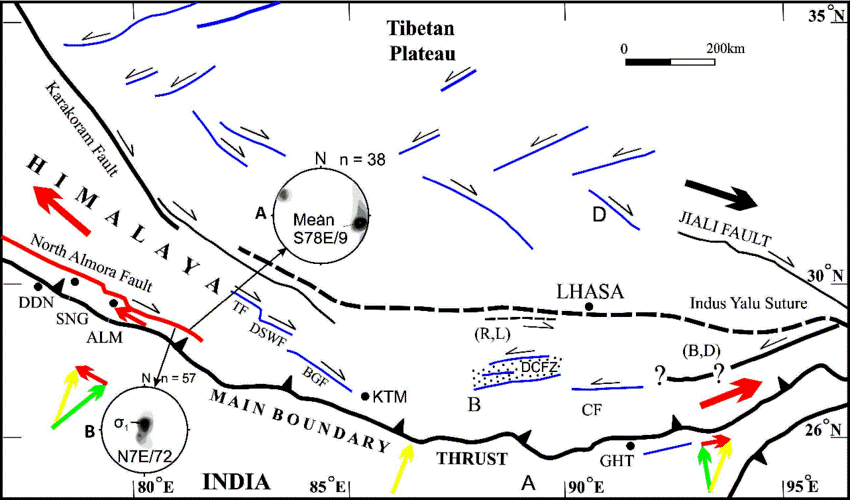
About Almora Fault
- It is a geological fault that runs through Western Nepal and into India's Uttarakhand area.
- It is located in the Himalayan fault zone on the Main Boundary Thrust (MBT).
- In Kumaon, Uttarakhand, there are two thrusts: the South Almora Thrust and the North Almora Thrust.
- MBT (Main Boundary Thrust): This is a prominent Himalayan fault that separates the Lesser Himalayas from the Sub-Himalayas.
- The Main Himalayan Thrust (MHT) is a décollement under the Himalaya Range.
- This thrust fault follows a NW-SE strike, reminiscent of an arc, and gently dips about 10 degrees towards the north, beneath the region.
- It is the largest active continental megathrust fault in the world.
More about the News
Background Seismicity and Recent Spike
Consistent Background Seismicity:
- The Earth Sciences Minister emphasized the consistent level of background seismic activity in the regions under consideration, indicating normal earthquake occurrences.
Recent Earthquake Surge:
- Despite the persistent background seismicity, specific locations in north India and Nepal suffered a surge in seismic occurrences, which was linked in part to the activation of the Almora fault.
The Almora Fault's Role in Earthquake Occurrences
Significant Earthquakes:
- In recent seismic activity, the Almora fault, a critical geological structure in the western Himalayas, has played a critical role.
Key Mainshocks and Their Magnitudes:
- Notable earthquakes were observed on January 24 (5.8 magnitude), October 3 (6.2 magnitude), and November 3 (6.4 magnitude), all of which were associated to the Almora fault.
Geological Significance:
- The fault line is located near active faults in the Himalayan region, where the Indian plate subducts beneath the Eurasian Plate, resulting in frequent seismic occurrences.
.jpg)
Impact and Concerns
Geographical Impact:
- The seismic occurrences had a wide-ranging impact, with tremors felt throughout a large area.
- For example, the January 24 Nepal earthquake was felt powerfully in Delhi, Uttar Pradesh, and Uttarakhand.
Concerns about safety and preparedness:
- The recent activation of the Almora fault has sparked worries about area safety measures and earthquake preparedness.
Efforts at Mitigation and Safety Measures
Initiatives of the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS):
- The BIS has played a major part in the release of the Seismic Zoning Map of India, categorising locations into distinct danger zones (II to V), and providing standards for the construction of earthquake-resistant structures.
Interventions by the National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA):
- To improve preparedness and response capacities in seismic zones, the NDMA is actively adopting preventative measures including earthquake exercises, awareness programs, and incident management tactics.
Lessons and Continued Vigilance
Aftermath and Aftershocks:
- More than 382 aftershocks were recorded in the aftermath of the earthquakes, particularly the severe November 3 quake with a magnitude of 6.4.
- It emphasized the importance of maintaining vigilance and adhering to safety protocols in seismically active areas.
Regional Security and Current Concerns:
- The latest seismic incidents highlight the ongoing concern for regional safety and the importance of ongoing work in earthquake preparedness and risk reduction techniques.

Conclusion
- The Earth Sciences Minister's statement emphasized the heightened seismic activity in specific places caused by the activation of the Almora fault.
- By emphasizing the significance of geological structures such as the Almora fault and the subsequent impact on safety, the minister emphasizes the importance of proactive measures, guidelines, and initiatives aimed at mitigating earthquake risks and improving preparedness in earthquake-prone areas.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Explain the process of earthquake generation due to faulting, and discuss the various types of faults that play a significant role in seismic activities.
|




