Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
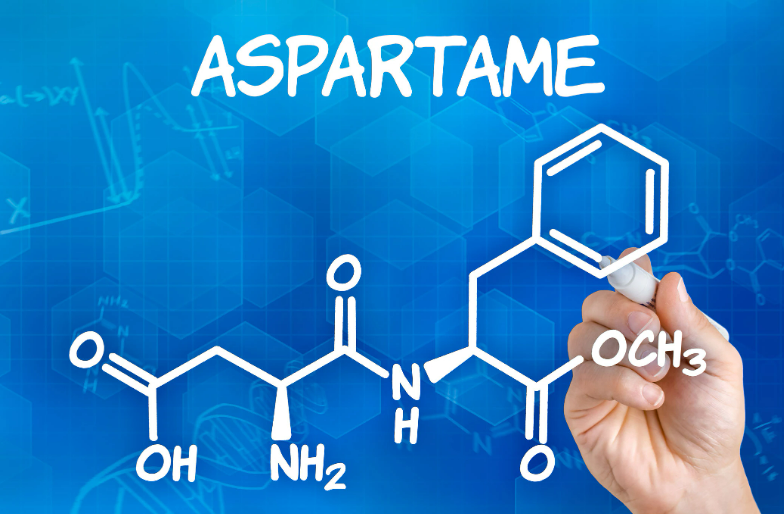
Aspartame
About
Chemical Composition
Discovery
Characteristics
Usage
Is aspartame dangerous?
Aspartame will be listed in July as "possibly carcinogenic to humans" for the very first time by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), that is WHO’s cancer research arm. The IARC along with the Joint Organization Expert Committee on Food Additives (JEFCA) are currently reviewing the effects and safety of aspartame.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. The term Aspartame is often in the news. What is Aspartame? 1. An Anti-caking agent. 2. An Artificial Sweetener. 3. An Emulsifier. 4. A Food Preservative. Correct Answer: 2. An Artificial Sweetener. |
© 2024 iasgyan. All right reserved