
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
A project aimed at restoring seagrass meadows in the Baltic Sea, particularly off the coast of Kiel in northern Germany.
Details
- Scuba divers off the coast of Kiel, northern Germany, involved in a new project to restore seagrass meadows.
- Seagrass meadows act as natural carbon sinks, but they have declined due to worsening water quality.
- The SeaStore Seagrass Restoration Project aims to train citizens to restore seagrass meadows autonomously.

Benefits of Seagrass Meadows
- Seagrasses store more carbon dioxide (CO2) per square mile than forests on land, acting as vital carbon sinks.
- They support fisheries and protect coastlines from erosion.
Loss of Seagrass Areas in Europe
- Europe has lost one third of its seagrass areas between the 1860s and 2016, contributing to carbon release and global warming.
The SeaStore Seagrass Restoration Project
- Led by Angela Stevenson from GEOMAR Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research.
- First initiative allowing citizens to restore seagrass meadows autonomously.
- A weekend course for divers and land volunteers to learn planting techniques.
- 2,500 plants were planted during the first course in July.
The Vision and Challenges
- The ultimate goal is to re-green the Baltic Sea through large-scale restoration.
- Research on seagrass resilience to temperature rises.
- Efforts to breed more heat-resistant seagrass strains.
- Experimenting with alternative methods of restoration using seeds.
Laborious Restoration Process
- Current approach requires a large number of divers planting shoots for an extended period.
- Estimated half a million divers, working for an entire year, needed to restore lost seagrass in the Baltic Sea along Germany's coast.
- Despite efforts, it would only account for a small fraction of German emissions.
Future Possibilities
- The team is exploring new technologies for artificial carbon removal.
- Advocating for nature-based solutions to carbon storage through seagrass meadows.
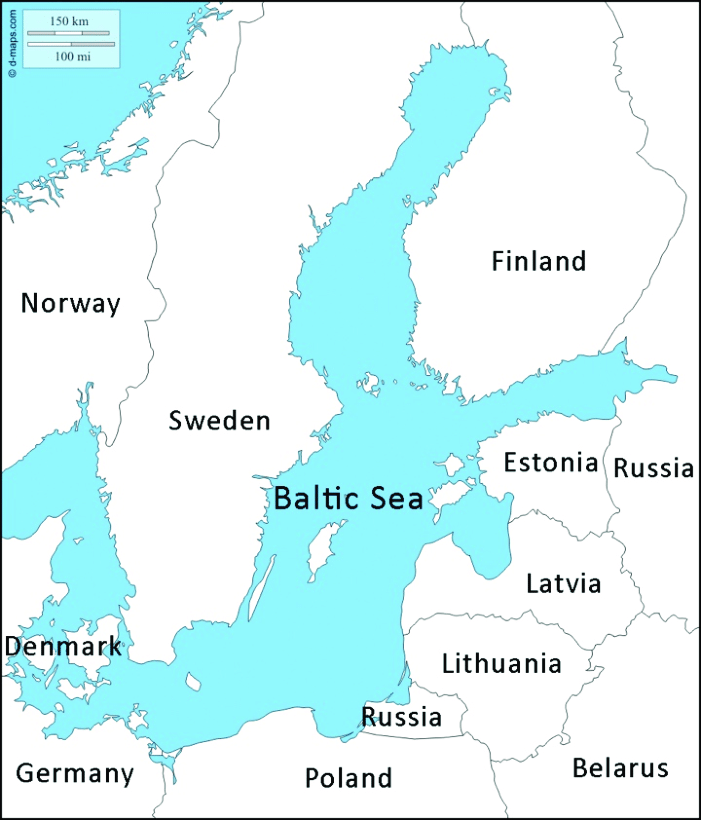
About Baltic Sea
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
- The Baltic Sea is a brackish inland sea located in Northern Europe.
- It is surrounded by several countries, including Sweden, Finland, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Germany, and Denmark.
- The sea connects with the North Sea through the narrow Danish Straits, including the Great Belt, the Little Belt, and the Oresund.
Geography and Extent
- The Baltic Sea covers an area of approximately 377,000 square kilometers.
- It is relatively shallow, with an average depth of about 55 meters and a maximum depth of around 459 meters in the Stockholm Archipelago.
- The coastline of the Baltic Sea is characterized by numerous bays, islands, and peninsulas.
Ecology and Environment
- The Baltic Sea is unique due to its brackish nature, resulting from a mix of fresh and saltwater.
- The sea is home to diverse marine ecosystems, including seagrass meadows, rocky shores, and sandy bottoms.
- However, it faces significant environmental challenges, including eutrophication, caused by excessive nutrient runoff from agriculture and urban areas, leading to harmful algal blooms and oxygen depletion in some areas.
Shipping and Trade
- The Baltic Sea has been a vital waterway for shipping and trade for centuries.
- Several major ports, such as Hamburg, Gdansk, Stockholm, and Helsinki, are located along its coast, facilitating international trade and commerce.
- The sea is also used for ferry services, connecting various Baltic countries and facilitating passenger transportation.
Marine Resources and Fisheries
- The Baltic Sea supports valuable fisheries, including herring, cod, salmon, and sprat, which are essential for the region's food security and economy.
- Overfishing and environmental degradation pose threats to fish stocks and sustainable fisheries management.
Tourism and Recreation
- The Baltic Sea attracts tourists and visitors from neighboring countries and beyond.
- Coastal regions offer opportunities for various recreational activities, such as sailing, boating, fishing, and beach vacations.
- The sea's archipelagos and coastal landscapes are popular destinations for nature enthusiasts and outdoor enthusiasts.
Environmental Conservation and Cooperation
- The Baltic Sea region is a hub for international cooperation and initiatives to address environmental challenges.
- Countries in the region work together to combat pollution, improve water quality, and promote sustainable resource management through organizations like the Helsinki Commission (HELCOM).
Historical and Cultural Significance
- The Baltic Sea has played a crucial role in the history and culture of the countries surrounding it.
- It has been a trade route, a site of naval battles, and a source of inspiration for literature, art, and folklore.
- The sea's maritime heritage is preserved through museums, historical sites, and traditional practices.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q) Discuss how international cooperation among Baltic Sea countries further enhances its preservation. (150 words).
|
https://theprint.in/environment/in-baltic-sea-citizen-divers-restore-seagrass-to-fight-climate-change/1686901/

https://epaper.thehindu.com/ccidist-ws/th/th_delhi/issues/45368/OPS/G8SBHRJQ4.1+GBUBHRNNU.1.html





