Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now



Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
Bond
What determines the price of a bond in the open market?
|
· The primary market is where securities are created. Here securities are issued by companies for the first time. New stocks and bonds are offered to the public via an initial public offering (IPO). The secondary market, on the contrary, refers to exchanges such as BSE or New York Stock Exchange or Nasdaq where stocks are traded. |
What is Bond Yield?
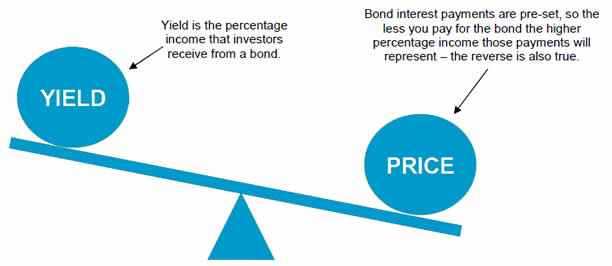
Details of Bond Yield
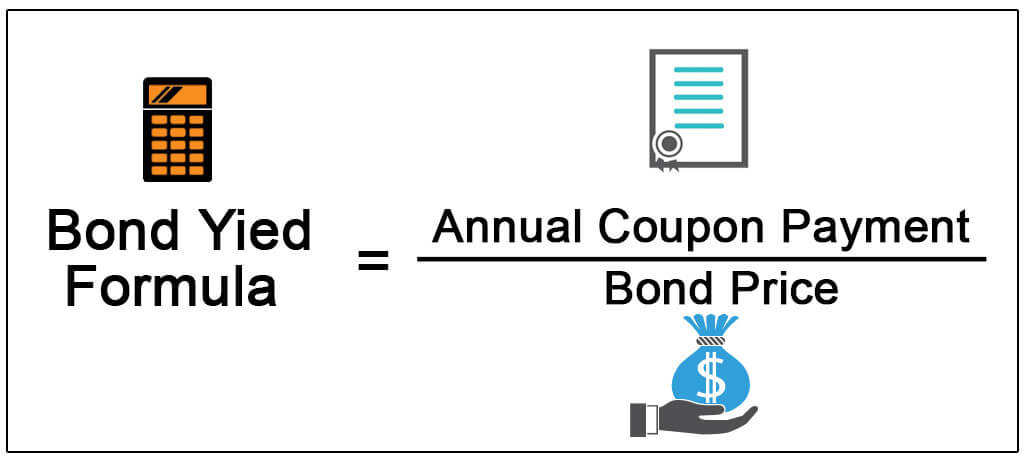
Bond Yield versus Price
|
Example from Market Perspective Let’s say a bond’s face value is Rs 1,000 on which an investor can earn 5%. This means that the coupon is 5% and an investor who buys the bond and holds it till maturity will get Rs 50 every year over the tenure of the bond. Now the price of the bond drops in the market to Rs 980. That means the current yield is Rs 50 divided by Rs 980 = 5.10%. Later, the price of the bond rises to Rs 1,030. That means the current yield is Rs 50 divided by Rs 1,030 = 4.85%. As the price of the bond fell, its yield increased. Because yield is a function of price, changes in price result in bond yields moving in the opposite direction. There are two ways of looking at bond yields - current yield and yield to maturity. |
When do Bond Yields Fall?
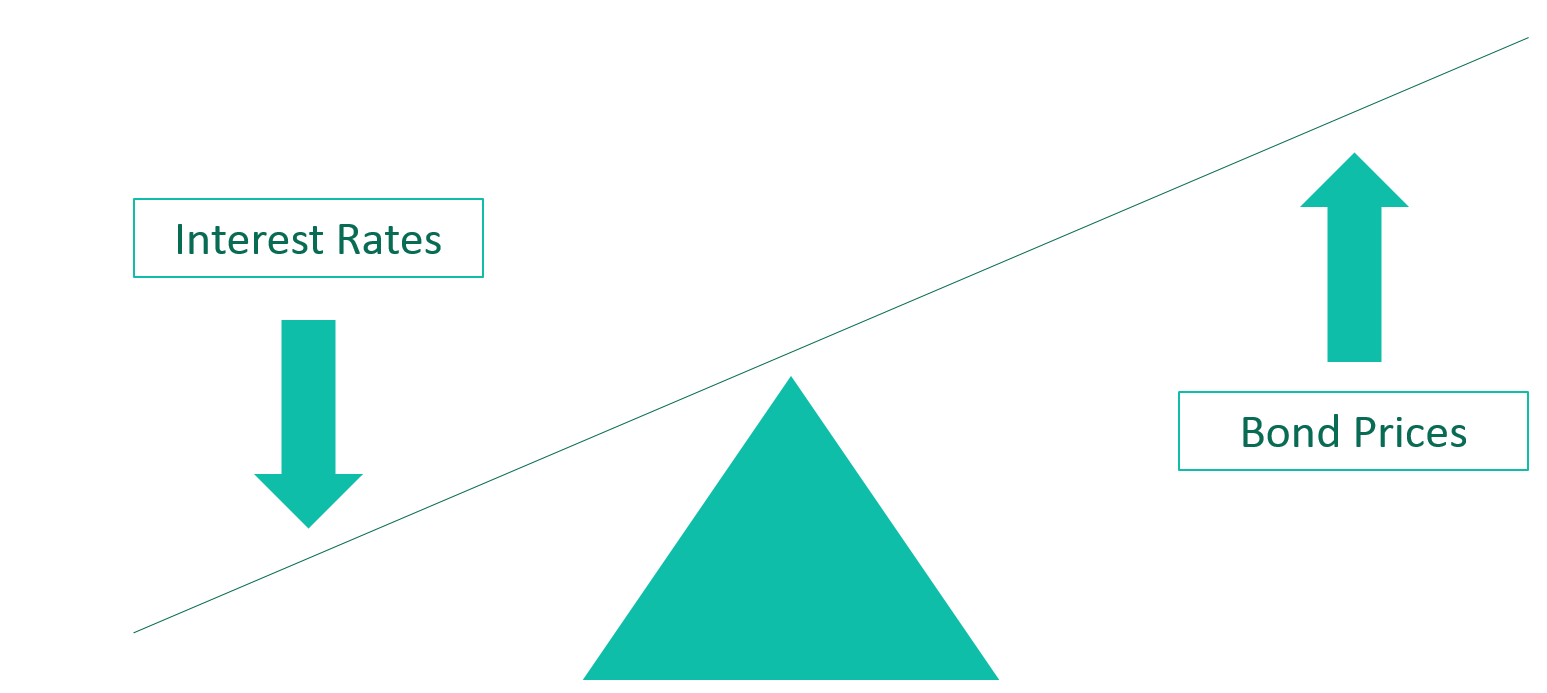
In a nutshell,
A bond's yield is based on the bond's coupon payments divided by its market price;
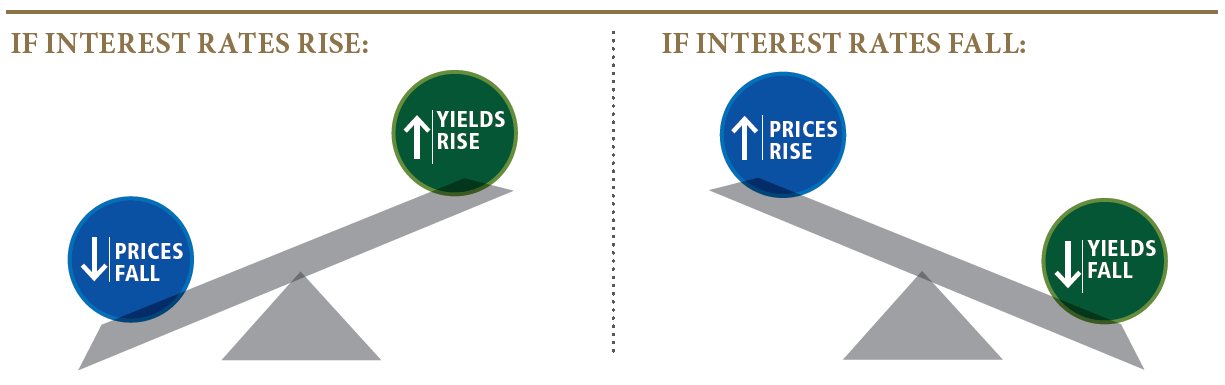
Interest Rates Versus Bond Prices
© 2024 iasgyan. All right reserved