Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
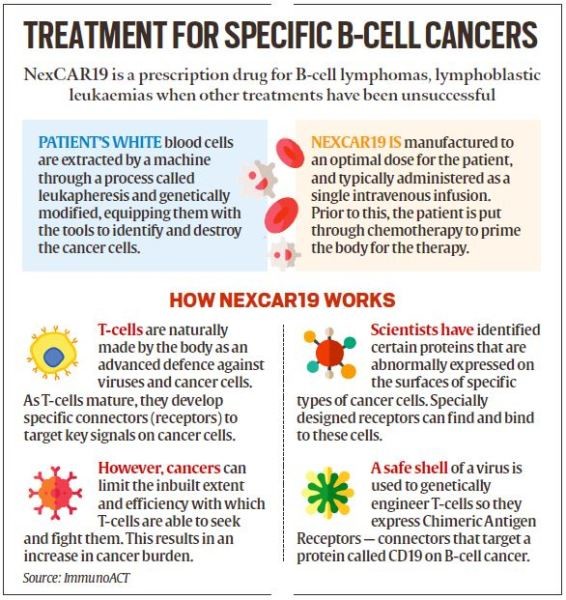
The Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO) this month granted market authorisation for NexCAR19, India’s first indigenously-developed CAR-T cell therapy, to ImmunoACT, a company incubated by IIT Bombay.
Details
About
- The therapy has gained attention for its ability to provide a potential cure and long-term benefit, differentiating it from traditional treatments like chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
- CAR-T (Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-cell) therapy involves modifying a patient's T-cells, a type of white blood cell, to recognize and attack cancer cells more effectively.
Mechanism of Action:
- The modified CAR-T cells are designed to target specific proteins, known as antigens, found on the surface of cancer cells.
- Once reintroduced into the patient's body, CAR-T cells recognize and bind to these cancer-specific antigens, leading to the destruction of cancer cells through the immune system's cytotoxic response.
Applications and Successes:
- CAR-T cell therapy has shown remarkable success in treating certain types of blood cancers, including acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL).
- It has provided a ray of hope for patients who have not responded to traditional treatments, offering the potential for long-term remission and improved quality of life.
Challenges and Limitations:
- Despite its successes, CAR-T cell therapy poses certain challenges, including potentially severe side effects like cytokine release syndrome (CRS) and neurotoxicity.
- High costs and the need for specialized infrastructure for production and administration remain significant barriers to widespread adoption.
Ongoing Research and Future Directions:
- Researchers are exploring the use of CAR-T cell therapy in treating various solid tumors and other types of cancers beyond blood cancers.
- Advancements in genetic engineering, as well as efforts to minimize side effects and improve the therapy's safety profile, are ongoing areas of research.

NexCAR19
- NexCAR19, India's first indigenous CAR-T cell therapy, has received market authorization from the Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO) for the treatment of B-cell lymphomas.
- Developed by ImmunoACT, a company incubated at IIT Bombay, this therapy is expected to be available in India at a significantly reduced cost compared to international alternatives.
Mechanism and Effectiveness:
- NexCAR19 is designed to target cancer cells expressing the CD19 protein, effectively eliminating them from the body.
- The therapy has shown promising results, with around 70% of patients exhibiting positive responses, particularly in cases of leukemia and lymphoma.
Pediatric Application and Ongoing Trials:
- While the therapy is currently approved for patients aged 15 years and older, ongoing trials at Tata Memorial Hospital are exploring its potential application in pediatric cases as well.
- The therapy's unique attributes have demonstrated reduced toxicities such as neurotoxicity and cytokine release syndrome, ensuring enhanced safety for patients.
Availability, Hospitals, and Cost:
- Plans are underway to make the therapy accessible to patients in various hospitals, including Tata Memorial Hospital, Nanavati, Fortis, and Jaslok, among others.
- The initial cost of the therapy is estimated to range between Rs 30-40 lakh, with efforts to reduce it to Rs 10-20 lakh in the future.
- Discussions with insurers and the government are ongoing to ensure potential coverage under national insurance schemes and private insurance policies.

Conclusion
India's foray into indigenous CAR-T cell therapy marks a significant advancement in the country's healthcare landscape, offering new hope and improved accessibility to cutting-edge cancer treatments for a wider patient population.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. Discuss the significance of CAR-T cell therapy in the context of cancer treatment, highlighting India's recent breakthrough in the development of indigenous CAR-T cell therapy. Examine the potential impact of this therapy on the accessibility and affordability of advanced cancer treatments in the country. (250 Words)
|




