Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now



Copyright infringement not intended
Context: Two foreign nationals were arrested by the Central Bureau of Narcotics (CBN) Preventive and Intelligence team for supplying cocaine and synthetic substances in commercial quantities.
Central Bureau of Narcotics (CBN)
About
Organization
Responsibilities
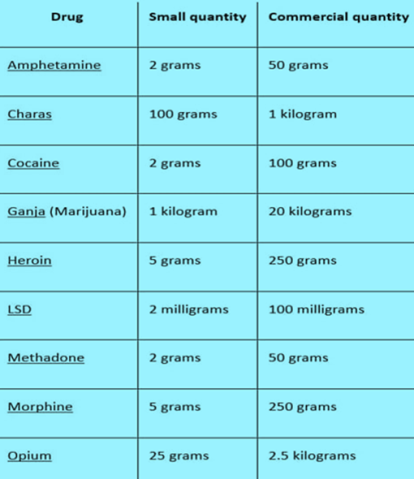
Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act, 1985
About
Punishments
Must Read Articles:
Drug abuse in India: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/drug-abuse-in-india
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. Drug misuse is one of the biggest public health issues of our day. It not only damages the addict but also his family, community, and the country as a whole and encourages antisocial behaviour like theft, crime, and violence. In this context, describe the causes of the rising drug problem in Indian states and the necessity of stringent legislation and interstate cooperation. |
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1911518
© 2024 iasgyan. All right reserved