Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


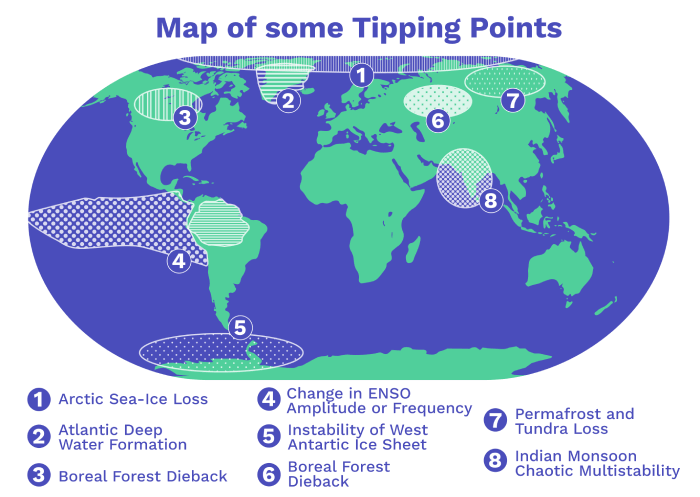
Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: https://climatescience.org/advanced-climate-climate-tipping-points
Context: Climate tipping points are critical thresholds in the Earth's climate system, beyond which natural systems can undergo irreversible and disastrous changes. These changes can lead to more warming and have cascading effects on the planet.
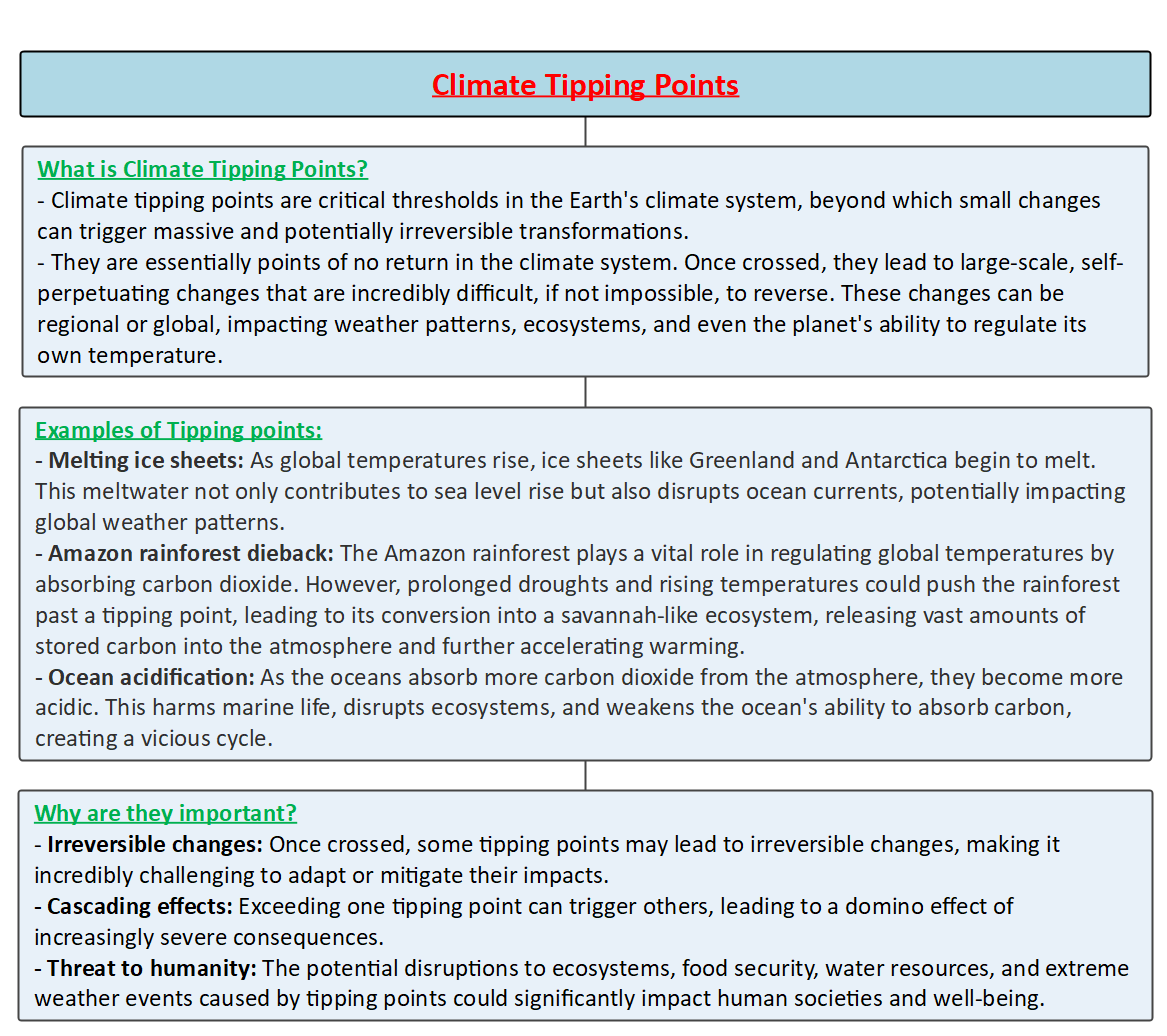
Climate Tipping Points
Key Characteristics
Examples of Climate Tipping Points
Consequences of Tipping Points
Factors Contributing to Tipping Points
Addressing Tipping Points
Challenges and Uncertainties
Way Forward
Reduce Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Invest in Adaptation and Resilience
Support Research and Monitoring
International Cooperation
Education and Advocacy
Community Engagement
Policy and Regulation
Innovation and Technology
Conclusion
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. Which of the following is NOT a potential strategy to mitigate the risk of climate tipping points? A) Rapidly reducing greenhouse gas emissions to achieve net-zero emissions B) Developing technologies to capture and store atmospheric carbon dioxide C) Investing in adaptation measures to prepare for the impacts of climate change D) Geoengineering interventions to manipulate the Earth's climate system Answer: D Explanation: While all the options listed have potential roles, geoengineering (option D) is a highly controversial and risky approach with uncertain consequences. It's not considered a mainstream mitigation strategy due to its potential for unintended side effects. |
|
Q. How will the impacts of climate tipping points be distributed unevenly across different regions, populations, and socioeconomic groups? What ethical considerations should guide our response, ensuring justice and equity in the face of these potential thresholds? Answer Structure: ●Define what climate tipping points are and why they are important for understanding the impacts of climate change. ●Provide some examples of climate tipping points that have been identified or projected by scientific research, such as melting ice sheets, permafrost thawing, or forest dieback. ●Explain how these tipping points can have uneven effects on different regions, populations, and socioeconomic groups, depending on their exposure, vulnerability, and adaptive capacity. ●Discuss the ethical implications of these uneven impacts, such as the responsibility of high-emitting countries to mitigate and support low-emitting countries, the rights of indigenous peoples and marginalized communities to participate in decision-making, and the need for intergenerational justice and equity. ●Conclude by summarizing the main points and suggesting some possible actions or policies that could address the challenge of climate tipping points fairly and effectively. |
© 2024 iasgyan. All right reserved