Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now



Copyright infringement not intended
Context: The Government of National Capital Territory of Delhi (Amendment) Bill, 2023 was introduced in the Lok Sabha. The bill seeks to amend the Government of National Capital Territory of Delhi Act, 1991, which defines the powers and functions of the Lieutenant Governor (LG) and the elected government of Delhi. The bill has several implications for the governance of Delhi, which is a union territory with a special status under the Constitution of India.
Details
Key points about the bill
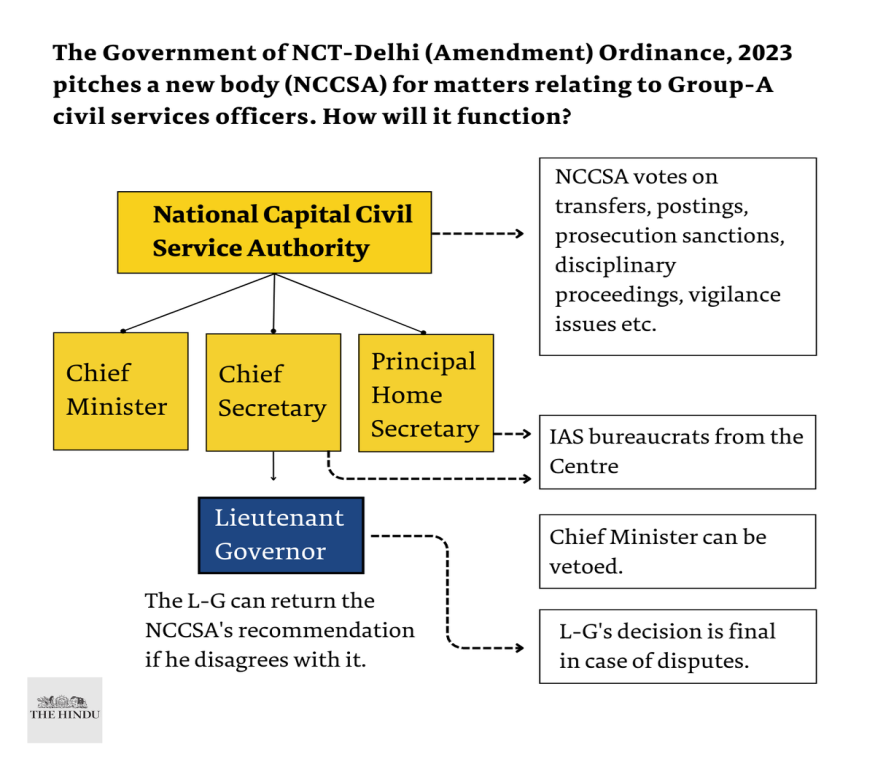
The bill seems to be an attempt to redefine the power dynamics between the Delhi government and the central government, particularly regarding the control over bureaucrats and administrative matters.
Must-Read Articles:
GOVERNMENT OF NATIONAL CAPITAL TERRITORY OF DELHI (AMENDMENT) ACT, 2021: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/government-of-national-capital-territory-of-delhi-amendment-act-2021
CENTRE ORDINANCE DESIGNATING L-G AS THE ADMINISTRATOR OF DELHI: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/centre-ordinance-designating-l-g-as-the-administrator-of-delhi
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. How does federalism operate under the Indian Constitution? What is the impact of federalism on India's governance and socio-political landscape? What are the main challenges faced in maintaining a federal structure, and how can the country move forward to strengthen and improve federalism in India? |
© 2024 iasgyan. All right reserved