Context
The findings of the State of the Climate in Latin America and the Caribbean in 2022 report, released by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO).
Details
- The State of the Climate in Latin America and the Caribbean in 2022 report by the World Meteorological Organization highlights the increasing severity of climate change impacts in the region.
- The major impacts include rising temperatures, changing rainfall patterns, extreme weather events, glacier melting, sea level rise, and cascading effects on various sectors.
Temperature and Warming Trends
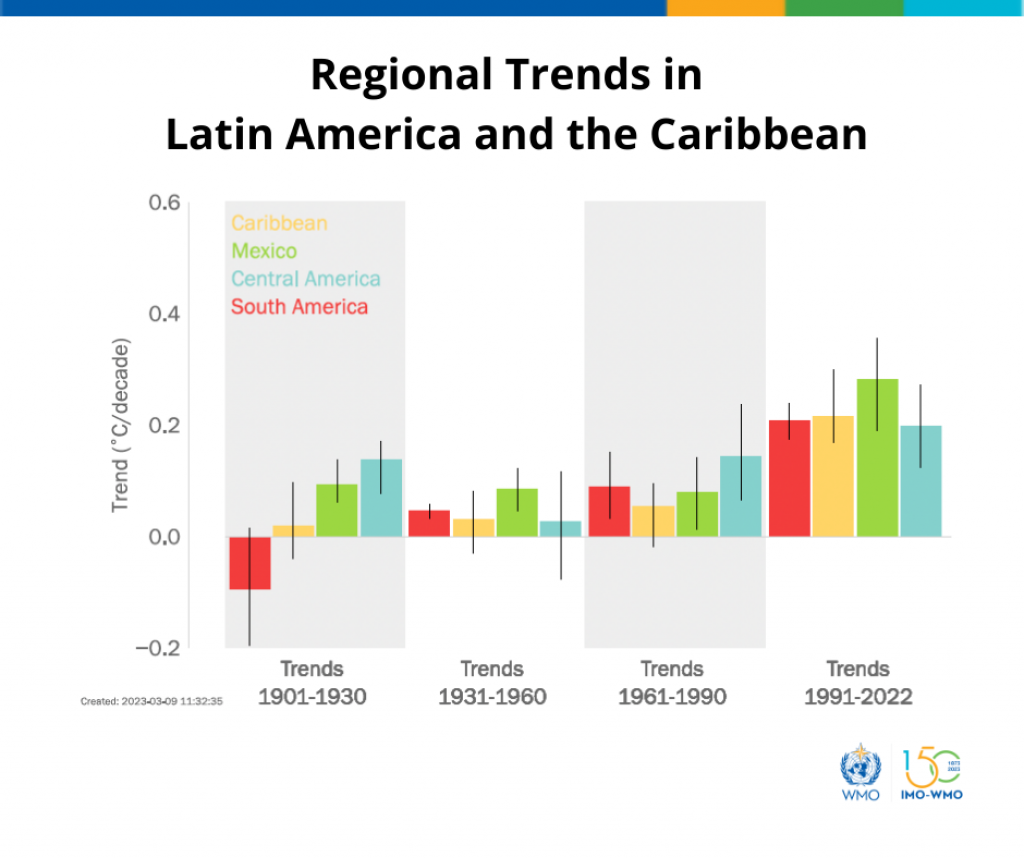
- The region has experienced a warming trend, with an average temperature increase over the past three decades.
- Between 1991 and 2022, the region exhibited a warming trend of 0.2°C per decade, with higher rates observed in Mexico and the Caribbean.
- These three decades have witnessed the highest rate of warming since 1900.
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Extreme Weather Events
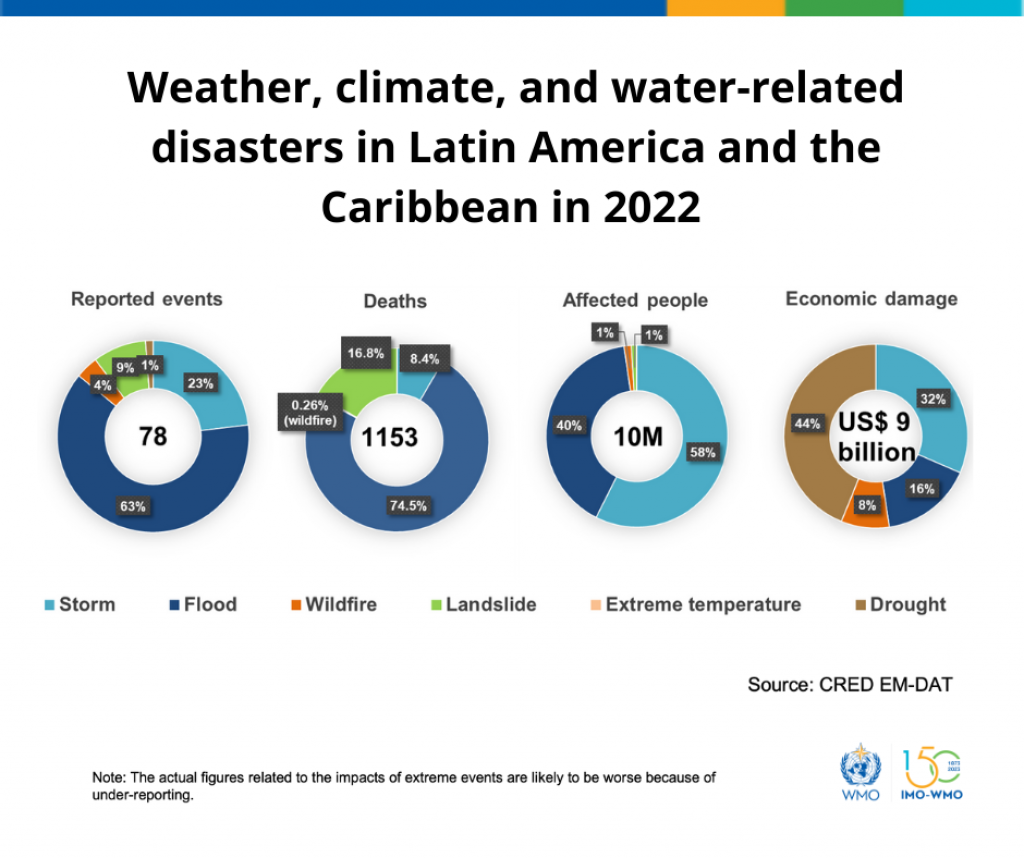
- The region has experienced a range of extreme weather events, including heatwaves, droughts, wildfires, tropical cyclones, floods, and landslides.
- Long and intense heat waves were recorded in southern South America during January, November, and December.
- Severe droughts affected Chile and the Paraná–La Plata Basin in southeastern South America, impacting agriculture and cereal production.
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Wildfires and Carbon Emissions
- Increased temperatures and low moisture levels led to widespread wildfires in South America.
- Argentina and Paraguay experienced a significant increase in wildfire hotspots, contributing to the highest carbon dioxide emissions from wildfires in the past 20 years.
- In the Amazonas state of Brazil, emissions from wildfires during July to October reached a record high in the past two decades.
Flooding, Landslides, and Tropical Storms
- The region witnessed extreme rainfall events leading to flooding and landslides.
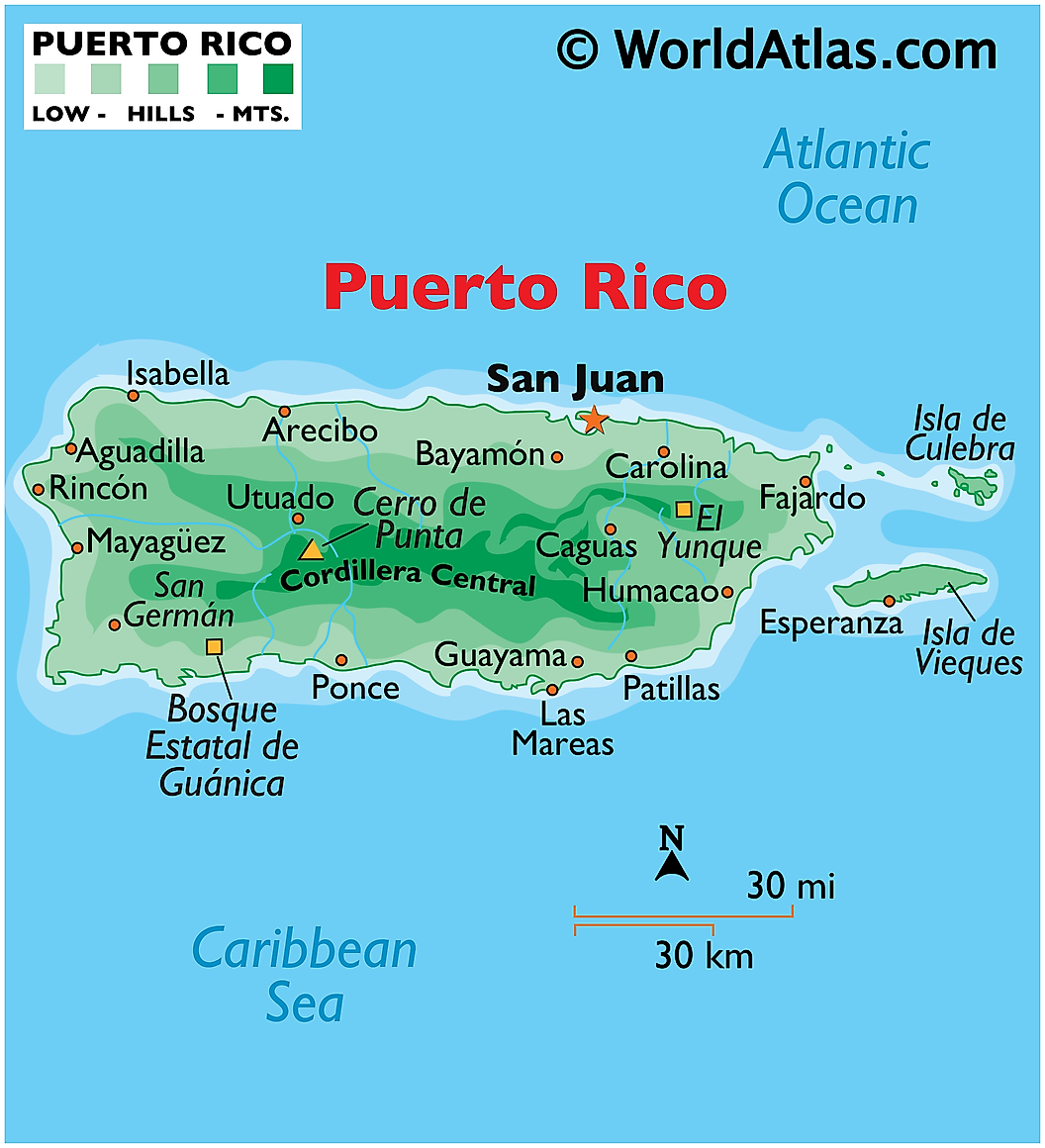
- Puerto Rico recorded its highest-ever daily rainfall, resulting in fatalities and significant damage.
- The impact of tropical storms and hurricanes contributed to flooding and agricultural damage in various countries, including Cuba and Jamaica.
Glacier Melting and Sea Level Rise
- Glaciers in the Andes mountain range showed a declining trend in ice mass due to increasing temperatures and decreasing snowfall.
- In the tropical Andes, glaciers lost ice mass at a rate of -96 m water equivalent per year between 1990 and 2021.
- Sea levels along the coasts of Latin America and the Caribbean rose at a rate higher than the global average, posing risks to coastal communities and ecosystems.
Economic Losses and Adaptation Challenges
- The region experienced significant economic losses due to climate-related hazards, with storm- and flood-related events being the most common.
- The impacts on agriculture, renewable energy production, and water resources affected the region's ability to mitigate and adapt to climate change.
- Decreased river flows in Brazil led to a decline in hydroelectric power generation and increased reliance on fossil fuels.
Priorities for Adaptation and Mitigation
- Key areas for climate change adaptation and mitigation in the region include agriculture, food security, and renewable energy.
- Persistent droughts' impacts on agricultural production and the untapped potential of solar and wind resources are highlighted.
About Latin America
- Latin America refers to the region in the Americas comprising countries in Central and South America, as well as parts of the Caribbean.
- It is known for its rich cultural diversity, natural beauty, and historical heritage.
Geographic Scope
- Latin America encompasses a vast area, stretching from Mexico in North America to the southern tip of South America.
- The region is bordered by the Pacific Ocean to the west and the Atlantic Ocean to the east.
Cultural Diversity
- Latin America is home to diverse cultures, languages, and traditions influenced by indigenous peoples, European colonization, and African heritage.
- Each country has its unique cultural identity, customs, and artistic expressions, including music, dance, literature, and cuisine.
Languages
- Spanish and Portuguese are the predominant languages in most Latin American countries.
- However, indigenous languages, such as Quechua, Guarani, and Mayan languages, are also spoken by significant populations.
Political Structure
- Latin America comprises various political systems, including democratic republics, constitutional monarchies, and socialist states.
- The region has seen political transitions, social movements, and efforts to address historical inequalities and human rights issues.
Economic Characteristics
- The economies of Latin America are diverse, ranging from emerging markets to developed economies.
- Key economic sectors include agriculture, mining, manufacturing, services, and tourism.
- The region faces challenges such as income inequality, poverty, and economic disparities among different social groups.
Natural Landscapes
- Latin America is known for its diverse and breathtaking natural landscapes.
- It includes the Amazon rainforest, the Andes Mountains, the Patagonian wilderness, the Atacama Desert, the Galapagos Islands, and the Caribbean beaches.
Biodiversity and Environmental Concerns
- Latin America is recognized for its extraordinary biodiversity, hosting a wide array of plant and animal species.
- Environmental conservation and sustainable development efforts are crucial to protect fragile ecosystems, combat deforestation, and address climate change challenges.
Historical Heritage
- Latin America has a rich historical heritage shaped by pre-Columbian civilizations, European colonization, and struggles for independence.
- Ancient ruins, colonial architecture, and archaeological sites, such as Machu Picchu and Chichen Itza, highlight the region's historical significance.
Social and Cultural Issues
- Latin America faces social challenges such as poverty, inequality, crime, and access to education and healthcare.
- Indigenous rights, gender equality, and cultural preservation are important issues that the region seeks to address.
Regional Organizations and Cooperation
- Latin American countries collaborate through regional organizations such as the Organization of American States (OAS), the Union of South American Nations (UNASUR), and the Community of Latin American and Caribbean States (CELAC).
- These organizations promote regional integration, cooperation, and dialogue on various political, economic, and social issues.

About Caribbean
- The Caribbean refers to a region of islands and coastal areas in the Caribbean Sea.
- It is known for its stunning beaches, vibrant cultures, and diverse ecosystems.
Geographic Scope
- The Caribbean is located in the western part of the Atlantic Ocean, southeast of North America and north of South America.
- It consists of more than 7,000 islands, including the Greater Antilles, Lesser Antilles, and the Bahamas.
Island Diversity
- The Caribbean islands vary in size, population, and political status.
- Major islands include Cuba, Jamaica, Hispaniola (shared by Haiti and the Dominican Republic), Puerto Rico, and Trinidad and Tobago.
Cultural Melting Pot
- The Caribbean is a cultural melting pot influenced by indigenous, African, European, and Asian traditions.
- Each island has its distinct cultural identity, including languages, music genres (such as reggae, calypso, and salsa), cuisine, and festivals.
Languages
- English, Spanish, French, Dutch, and Creole languages are commonly spoken across the Caribbean.
- Each island often has its own language variations and dialects.
Tourism and Beaches
- The Caribbean is renowned for its picturesque beaches, crystal-clear waters, and coral reefs.
- Tourism plays a vital role in the economies of many Caribbean countries, attracting visitors with opportunities for water sports, snorkeling, diving, and relaxation.
Biodiversity and Ecosystems
- The Caribbean is home to diverse ecosystems, including tropical rainforests, mangroves, coral reefs, and marine life.
- It boasts rich biodiversity with unique species, such as the Caribbean manatee, various bird species, and vibrant coral reef ecosystems.
Colonial History and Independence
- Many Caribbean islands were colonized by European powers, including Spain, Britain, France, and the Netherlands.
- The region has a history of struggle for independence, with some islands gaining sovereignty while others remain overseas territories or dependencies.
Hurricanes and Natural Disasters
- The Caribbean is prone to hurricanes, particularly during the Atlantic hurricane season (June to November).
- Major hurricanes have caused significant damage and loss of life in the region, prompting efforts for disaster preparedness and resilience.
Economic Activities
- Apart from tourism, the Caribbean economies depend on sectors such as agriculture (including sugar, bananas, and spices), fishing, manufacturing, and offshore financial services.
Regional Cooperation and Organizations
- Caribbean countries engage in regional cooperation through organizations such as the Caribbean Community (CARICOM) and the Organization of Eastern Caribbean States (OECS).
- These organizations aim to promote economic integration, sustainable development, and collaboration on regional issues.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q) Consider the following statements:
1. The majority of Latin American and Caribbean countries are democracies.
2. The region is home to a number of major mountain ranges, such as the Andes and the Sierra Madre.
Select the correct statement using the code below
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: B
|
https://www.downtoearth.org.in/news/climate-change/deluge-in-puerto-rico-drought-in-la-plata-wmo-paints-grim-picture-of-warming-latin-america-caribbean-90450








