Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
Details
Methodology and Study Findings
Role in Rewarding and Punishing Experiences
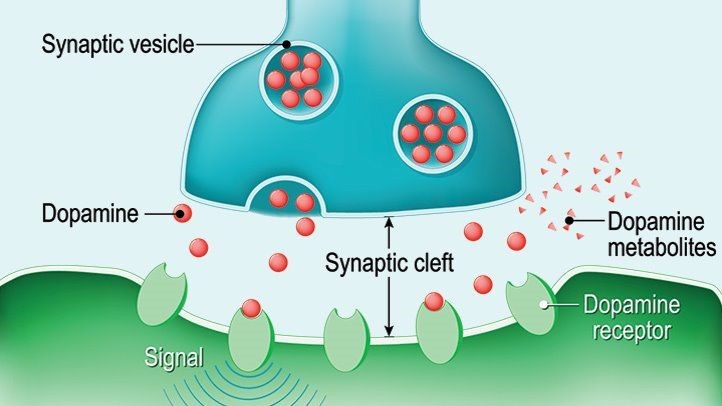
Understanding Dopamine
Synthesis and Pathways
Functions of Dopamine
Dopamine Receptors and Signaling
Implications in Health and Behavior
Conclusion
This groundbreaking research highlights dopamine's multifaceted role beyond its association with positive emotions. It unveils how dopamine contributes to the brain's ability to learn from both favorable and adverse events, potentially influencing decision-making processes and behavioral adaptations. Understanding dopamine's intricate mechanisms in encoding rewards and punishments can offer profound insights into human behavior and cognitive processes, contributing to advancements in neuroscience and decision sciences.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. Discuss the recent advancements in understanding dopamine's role in encoding reward and punishment prediction errors, as revealed by a study published in Science Advances. Elaborate on the implications of dopamine's involvement in learning from both positive and negative experiences, highlighting its significance in decision-making processes and behavioral adaptations. (250 Words) |
© 2024 iasgyan. All right reserved