Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now



Copyright infringement not intended
Context
EOS-01
What is an Earth Observation Satellite?
Copyright infringement not intended
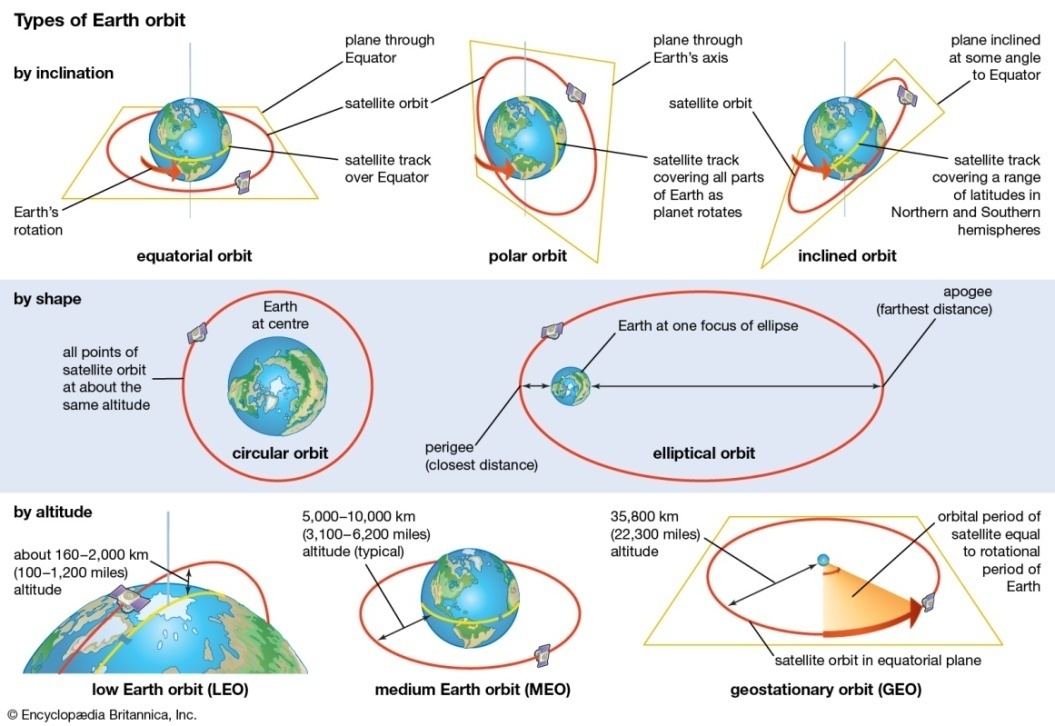
Types of Earth observation satellites
What are the applications of Earth Observation Satellites?
How earth observational satellites collect data
ISRO's Earth Observational Satellites
ISRO’s EOS Series Satellites
The details of the satellites included in the EOS series are as follows:

Copyright infringement not intended
|
Launch Vehicle |
Orbit Type |
Application |
|||
|
Feb 14, 2022 |
Earth Observation |
||||
|
Aug 12, 2021 |
GSLV-F10 / EOS-03 |
GTO |
Earth Observation |
||
|
Nov 07, 2020 |
PSLV-C49/EOS-01 |
LEO |
Disaster Management System, Earth Observation |
||
|
Dec 11, 2019 |
628 Kg |
LEO |
Disaster Management System, Earth Observation |
||
|
Cartosat-3 |
Nov 27, 2019 |
SSPO |
Earth Observation |
||
|
May 22, 2019 |
615 Kg |
LEO |
Disaster Management System, Earth Observation |
||
|
Nov 29, 2018 |
SSPO |
Earth Observation |
|||
|
Jan 12, 2018 |
710 Kg |
SSPO |
Earth Observation |
||
|
Jun 23, 2017 |
712 kg |
SSPO |
Earth Observation |
||
|
Feb 15, 2017 |
714 kg |
PSLV-C37 / Cartosat -2 Series Satellite |
SSPO |
Earth Observation |
|
|
Dec 07, 2016 |
1235 kg |
SSPO |
Earth Observation |
||
|
Sep 26, 2016 |
371 kg |
SSPO |
Climate & Environment |
||
|
INSAT-3DR |
Sep 08, 2016 |
2211 kg |
GSO |
Climate & Environment, Disaster Management System |
|
|
Jun 22, 2016 |
737.5 kg |
PSLV-C34 / CARTOSAT-2 Series Satellite |
SSPO |
Earth Observation |
|
|
Jul 26, 2013 |
2060 Kg |
Ariane-5 VA-214 |
GSO |
Climate & Environment, Disaster Management System |
|
|
Feb 25, 2013 |
407 kg |
SSPO |
Climate & Environment, Earth Observation |
||
|
Apr 26, 2012 |
1858 kg |
SSPO |
Earth Observation |
||
|
Oct 12, 2011 |
1000 kg |
PSLV-C18/Megha-Tropiques |
SSPO |
Climate & Environment, Earth Observation |
|
|
RESOURCESAT-2 |
Apr 20, 2011 |
1206 kg |
SSPO |
Earth Observation |
|
|
Jul 12, 2010 |
694 kg |
SSPO |
Earth Observation |
||
|
Sep 23, 2009 |
960 kg |
SSPO |
Climate & Environment, Earth Observation |
||
|
RISAT-2 |
Apr 20, 2009 |
300 kg |
SSPO |
Earth Observation |
|
|
Apr 28, 2008 |
690 Kg |
PSLV-C9 / CARTOSAT – 2A |
SSPO |
Earth Observation |
|
|
IMS-1 |
Apr 28, 2008 |
83 kg |
SSPO |
Earth Observation |
|
|
Jan 10, 2007 |
650 kg |
SSPO |
Earth Observation |
||
|
May 05, 2005 |
1560 kg |
SSPO |
Earth Observation |
||
|
Oct 17, 2003 |
1360 kg |
SSPO |
Earth Observation |
||
|
The Technology Experiment Satellite (TES) |
Oct 22, 2001 |
PSLV-C3 / TES |
SSPO |
Earth Observation |
|
|
May 26, 1999 |
1050 kg |
SSPO |
Earth Observation |
||
|
Sep 29, 1997 |
1250kg |
SSPO |
Earth Observation |
||
|
Mar 21, 1996 |
920 kg |
SSPO |
Earth Observation |
||
|
Dec 28, 1995 |
1250 kg |
Molniya |
SSPO |
Earth Observation |
|
|
Oct 15, 1994 |
804 kg |
SSPO |
Earth Observation |
||
|
Sep 20, 1993 |
846 kg |
LEO |
Earth Observation |
||
|
IRS-1B |
Aug 29, 1991 |
975 kg |
Vostok |
SSPO |
Earth Observation |
|
Jul 13, 1988 |
150 kg |
Earth Observation, Experimental |
|||
|
Mar 17, 1988 |
975 kg |
Vostok |
SSPO |
Earth Observation |
|
|
Apr 17, 1983 |
41.5 kg |
LEO |
Earth Observation |
||
|
Bhaskara-II |
Nov 20, 1981 |
444 kg |
C-1 Intercosmos |
LEO |
Earth Observation, Experimental |
|
May 31, 1981 |
38 kg |
LEO |
Earth Observation |
||
|
Bhaskara-I |
Jun 07, 1979 |
442 kg |
C-1Intercosmos |
LEO |
Earth Observation, Experimental |
Important Links: https://www.iasgyan.in/blogs/types-of-orbits-explained
https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/eos-03
https://pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=1814390
© 2024 iasgyan. All right reserved