Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


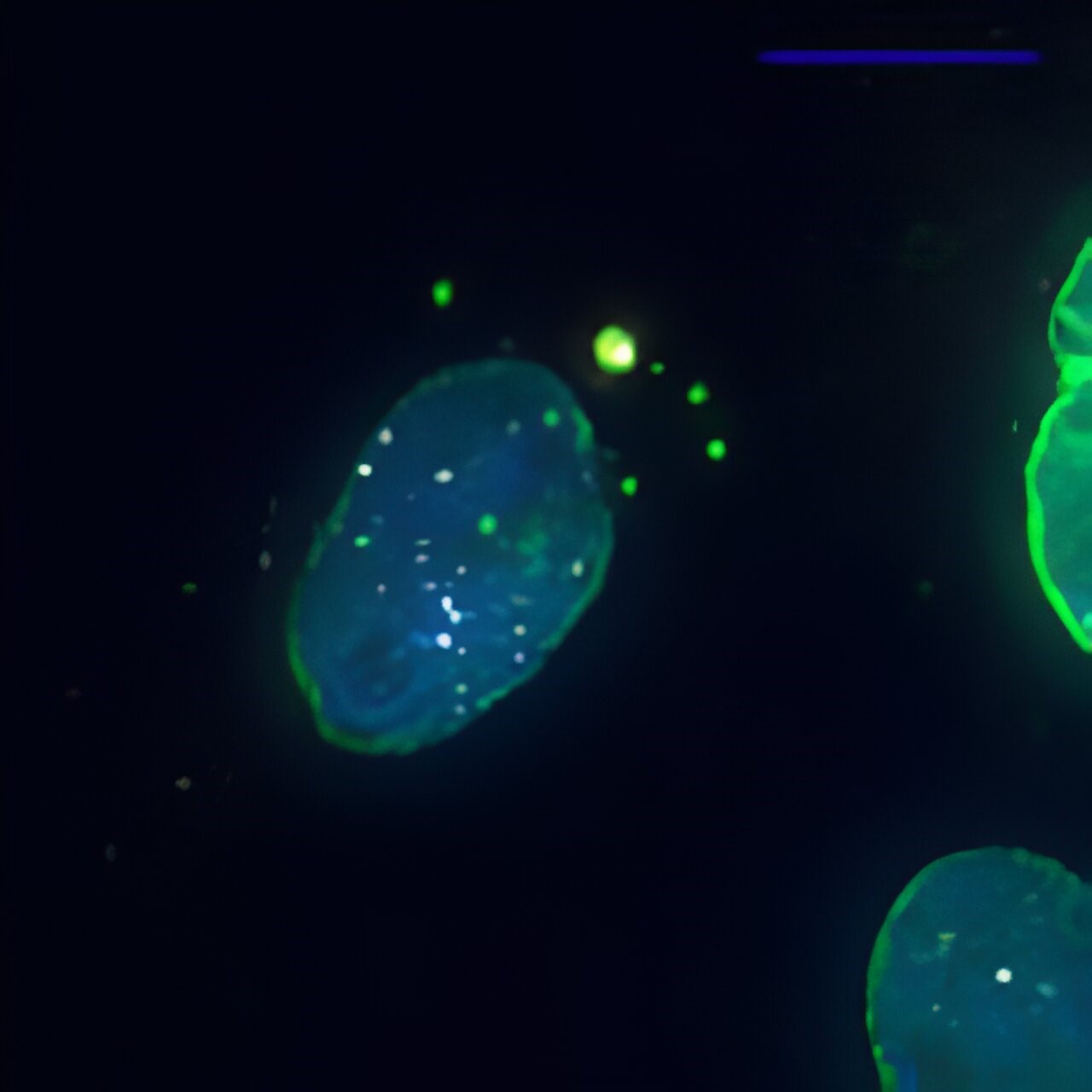
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
Researchers at ETH Zurich recently identified a previously unknown compartment in mammalian cells. They have named it the exclusome. It is made up of DNA rings known as plasmids.
Details
Composition of the Exclusome
The Role of the Cell Nucleus
Potential Functions of the Exclusome
Evolutionary Origins of the Exclusome
Comparing the Exclusome to the Nuclear Envelope
Unanswered Questions
Future Research
Conclusion
In summary, the exclusome represents a groundbreaking discovery in cell biology. Comprising DNA rings within the cell plasma, this organelle challenges conventional notions of DNA organization in eukaryotic cells. While its functions are still being explored, it may hold the key to understanding cellular immunological memory and its potential implications for autoimmune responses. Moreover, the exclusome's evolutionary significance and structural characteristics warrant further investigation, ensuring that the secrets of this intriguing organelle are fully unraveled.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. Explain the recent discovery of the "exclusome," a novel organelle in mammalian cells, and discuss its potential implications in the field of cell biology. How does it challenge conventional theories regarding DNA organization in eukaryotic cells, and what clues does it provide about the evolutionary history of cellular structures? (250 Words) |
© 2024 iasgyan. All right reserved