
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- The Rs 5-trillion domestic Fast-Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG) market is undergoing a gradual recovery from the prevailing slowdown, according to insights gleaned from industry experts and sector analysts.
NielsenIQ Data: Rural Resilience and Urban Challenges
- NielsenIQ reports a rural resurgence in the December 2023 to February 2024 period, surpassing urban markets in volume growth by 150-200 basis points.
- However, March 2024 figures are awaited.
Factors Driving Growth:
- The growth spurt is attributed to price adjustments by FMCG companies, leveraging favorable commodity costs.
- Industry experts anticipate challenges ahead due to recent inflationary trends in commodity prices, which may necessitate a delicate balance between pricing and volume strategies to safeguard margins.
Analyst Perspectives:
- Analysts caution that rural growth may be temporary, stemming from a low base, and may require time to stabilize.
- Kantar predicts continued market sluggishness till September 2024 due to global economic slowdown, election impacts, and weather uncertainties affecting agricultural output.
- While rural resilience offers a glimmer of hope for FMCG market recovery, sustained growth hinges on navigating inflationary pressures and addressing lingering urban market challenges amidst a backdrop of economic uncertainties.
FMCG SECTOR IN INDIA
Consumer-Driven Expansion and Price Dynamics:
- The FMCG sector in India expanded significantly, driven by consumer demand and increased prices, particularly for essential goods.
Employment Contribution and Revenue Growth Forecast:
- FMCG sector provides substantial employment, with around 3 million people employed, comprising 5% of total factory employment in India.
- Expected revenue growth of 7-9% in 2022-23, attributed to various growth drivers including government initiatives, rural market expansion, new products, and e-commerce growth.
Importance of Resilience for Sustainable Growth:
- Resilience is emphasized as a crucial factor across manufacturing, daily operations, retail, logistics, consumer insights, and communication to withstand challenges and create long-term value.
- India’s FMCG sector experienced a 7.5% volume growth in the April-June 2023 quarter, driven by rural revival and increased modern trade.
Contribution to India's Economy and Market Dynamics:
- FMCG sector is India's fourth-largest, expanding due to rising disposable income, youth population, and brand awareness.
- Household and personal care products constitute 50% of FMCG sales, making it a significant contributor to India's GDP.
India's Demographic Advantage and Government Support:
- India's large middle-class population and median age of 27 make it a crucial market for FMCG companies.
- Government initiatives promoting financial inclusion and social safety nets further support the sector's growth trajectory.
Key Growth Drivers and Market Segmentation:
- Growing awareness, accessibility, and evolving lifestyles are primary growth drivers.
- While the urban segment remains significant (accounting for 65% of revenue share), rural and semi-urban segments are experiencing faster growth, with FMCG products contributing significantly to rural spending.
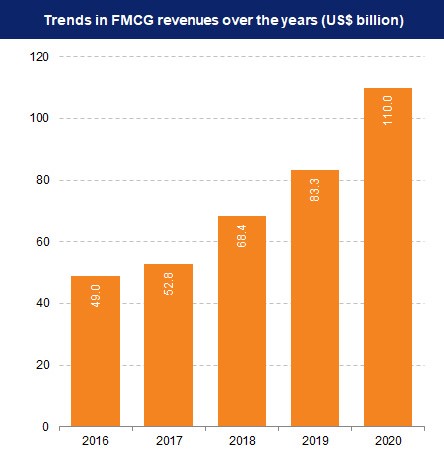
FMCG Market Size and Performance:
- Revenue Growth: FMCG market reached US$ 167 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 27.9% through 2021-27, reaching nearly US$ 615.87 billion.
- Segment Contribution: In 2022, urban segment contributed 65% to FMCG sales, while rural India contributed over 35%, with expectations of rural demand recovery aided by good harvest and government spending in FY24.
- Sector Performance: The sector experienced 8.5% revenue growth and 2.5% volume growth last fiscal year, with significant value growth in the January-June 2022 period and Q2 2022.
Growth in Indian Food Processing Market:
- Market Size: Indian food processing market reached US$ 307.2 billion in 2022 and is projected to reach US$ 547.3 billion by 2028, with a CAGR of 9.5% during 2023-2028.
- Government Initiative: The Union government approved a new PLI scheme for the food processing sector, with a budget outlay of Rs. 109 billion (US$ 1.46 billion), providing incentives until 2026-27.
Digital Advertising Trends and E-commerce Growth:
- Digital Advertising: Expected to reach US$ 9.92 billion by 2023, with FMCG industry contributing 42% of total digital spend, driven by India's 780 million internet users and increasing digital consumption habits.
- E-commerce Expansion: Indian e-commerce market projected to grow from US$ 83 billion in 2022 to US$ 185 billion in 2026, with an annual gross merchandise value of US$ 350 billion by 2030, supported by a rising internet user base and digital transactions.
Projections for FMCG Market and Industry Dynamics:
- Market Growth: FMCG market in India expected to increase at a CAGR of 14.9% to reach US$ 220 billion by 2025, fueled by consumption-led growth and value expansion.
- Competition Landscape: Established FMCG giants facing competition from D2C-focused start-ups, with new-age brands achieving revenue milestones in shorter timeframes.
- Advertising Trends: Television advertising recorded healthy growth, with FMCG maintaining leadership position and e-commerce sector showing significant growth in ad volumes.
Government Initiatives for FMCG Sector Growth:
- Union Budget 2023–2024 Incentives: The budgetary provisions offer substantial incentives aimed at advancing food infrastructure research, development, and innovation. These measures are particularly encouraging for the FMCG sector's growth prospects, signaling the government's commitment to fostering innovation and modernization within the industry.
- New PLI Scheme for Food Processing Sector: With a significant budget outlay, the government has introduced a Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme tailored for the food processing sector. This initiative, spanning over six years, is poised to incentivize investments and bolster growth in the sector, thereby enhancing its competitiveness and capacity.
- Promotion of Millets and Research Excellence: Recognizing the health benefits of millets, the government has undertaken initiatives to promote their consumption and production. The declaration of the Indian Institute of Millet Research as a global center of excellence underscores the government's commitment to fostering knowledge exchange and innovation in this domain, further boosting the FMCG sector's prospects.
Performance and Investments:
- Investment Progress under PLI Scheme: The update on investments made under the PLI scheme highlights the industry's response to the government's incentives. The substantial investments signify confidence in the scheme's potential to drive sales and exports, thereby stimulating growth and employment within the sector.
- Completed Projects and Employment Generated: The completion and operationalization of numerous food processing projects, coupled with private investments and employment generation figures, underscore the tangible outcomes of government initiatives. These accomplishments not only enhance production capacity but also contribute to socio-economic development by creating employment opportunities.
- Tax Deductions and Excise Duty Waivers: The provision of tax deductions and excise duty waivers further incentivizes investment in agro-processing industries. By easing the financial burden on businesses, these measures facilitate the establishment of new ventures and encourage expansion, ultimately fostering a conducive environment for industry growth.
Support for Startups and Innovation:
- SETU Initiative and Incubation Centers: The allocation of funds for the SETU initiative and the establishment of incubation centers exemplify the government's focus on nurturing entrepreneurship and innovation. By providing resources and support to startups, these initiatives aim to catalyze technological advancements and enhance the competitiveness of the FMCG ecosystem.
- Partnership with Flipkart for Rural Empowerment: Collaborative efforts with leading e-commerce platforms such as Flipkart underscore the government's commitment to inclusive growth and rural empowerment. By leveraging digital platforms, local businesses and self-help groups can access larger markets, thereby enhancing their livelihoods and contributing to economic development in rural areas.
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and Retail Policies:
- FDI Incentives and Policies: The government's liberalization of FDI norms, particularly in the retail sector, reflects its efforts to attract foreign investments and stimulate growth. These policy reforms create opportunities for international players to contribute to the development of the FMCG market in India, fostering competition and innovation.
- New Consumer Protection Bill: The introduction of a comprehensive Consumer Protection Bill underscores the government's commitment to safeguarding consumer rights and ensuring accountability within the FMCG sector. By establishing mechanisms for redressal and enforcement, the bill aims to enhance consumer confidence and promote a fair and transparent marketplace.
Impact of GST and Logistics Transformation:
- GST Benefits for FMCG Industry: The implementation of GST has led to favorable tax revisions for various FMCG products, streamlining the tax structure and reducing compliance burdens. These reforms have improved cost efficiencies and price competitiveness, contributing to overall industry growth.
- Logistics Transformation under GST Model: The transition to the GST regime has prompted a transformation in logistics and warehousing practices within the FMCG sector. With streamlined processes and improved supply chain efficiencies, businesses are better equipped to meet consumer demands and expand their market reach, driving growth and innovation in the industry.
Recent Trends in the FMCG Sector:
- Impact of COVID-19: The FMCG industry faced challenges during the COVID-19 outbreak, with disruptions in operations due to lockdowns, inventory pileups, supply chain difficulties, and labor shortages.
- Rise in Immunity Products: There's been a surge in demand for immunity-based products, leading companies to venture into healthcare manufacturing and introduce products like hand sanitizers, disinfectants, and Ayurvedic items.
- Expansion of Distribution Networks: Significant investments are being made in distribution networks, particularly to cater to rural demand, with emphasis on Direct-to-Consumer channels and Go-to-Market strategies.
- Premiumization: Companies are making premium products accessible to rural consumers by offering them at affordable price points.
- Growth of Modern Channels: Modern retail channels, including e-commerce platforms, have seen significant growth, serving as testing grounds for new products and driving sales.
- In-home Consumption Surge: With a decline in out-of-home consumption, there's been an increase in in-home consumption, particularly of ready-to-eat foods and snacks.
- Ayurvedic Products Demand: There's a rising preference for Ayurvedic products rooted in Indian culture, prompting industry players to introduce natural variants.
- Cost-saving Programs: Many companies have implemented cost-saving programs to enhance efficiency post-pandemic.
- Investment in Data Analytics: FMCG companies are heavily investing in data analytics to identify consumer trends and tailor their portfolios accordingly.
Factors in play
- Rural consumption is on the rise due to increasing income and higher aspirations.
- Branded products are in greater demand in rural India.
- The organised sector in the FMCG industry is growing as the share of the unorganised market declines.
- Brand consciousness is increasing, aided by the expansion of modern retail.
- The demand for food services in India is boosted by the growing youth population, especially in urban areas.
- Time constraints lead many urban consumers to opt for food services over cooking at home.
- Online portals are crucial for companies aiming to penetrate rural markets.
- The internet has significantly contributed to expanding companies' reach through cost-effective means.
- India's internet user base is projected to reach 1 billion by 2025.
FMCG Sector Outlook:
- Growth Potential: India's GDP, driven by domestic consumption, is expected to reach $6 trillion by 2030, supported by a young population and high domestic savings.
- Rural Consumption Boost: Increased MSP of crops and direct benefit transfers are expected to boost rural consumption in the short term.
- Shift to Organized Sector: With the decline of the unorganized sector, the organized sector is projected to grow, driven by brand consciousness and modern retail.
- Internet Penetration Impact: Increased internet penetration is expected to exceed a billion users by 2030, influencing consumer aspirations and spending patterns.
- Future of Modern Channels: Modern retail channels, including e-commerce, are expected to drive FMCG growth, with significant revenue contribution from online grocery sales.
- Demographic Trends: India's growing population, with a large working-age demographic, will drive non-discretionary spending across categories.
- Middle-Class Growth: The growth of the upper-middle and high-income segments will drive future consumption patterns, while efforts to reduce poverty will impact household spending.
- Consumer Drivers: Growing brand awareness, convenience, and changing lifestyles will shape the consumer market.
- Government Initiatives: Focus on agriculture, MSMEs, education, healthcare, and infrastructure is expected to positively impact the FMCG sector.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. Discuss the challenges and strategies of the FMCG sector in India, considering recent economic trends and policy shifts. Propose measures for its sustained growth.
|





