Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now



Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
Details
Food security
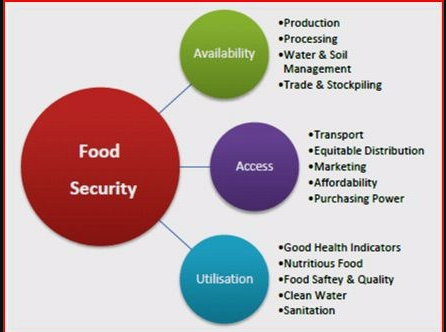
Pillars of Food Security
The three pillars of food security as defined by the World Health Organization (WHO) to be:
Laws
Government steps taken to ensure food security
Challenges of Food Security
The challenges India faces to meet its food security are as follows:
Climate change
Crop Diversification
.
Mismatch between water demand and availability
.
Land fragmentation
Quality seeds and Planting material
Agricultural Marketing
Globalisation
Way Ahead and Conclusion
© 2024 iasgyan. All right reserved