Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


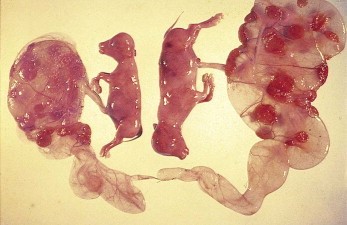
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
Freemartin
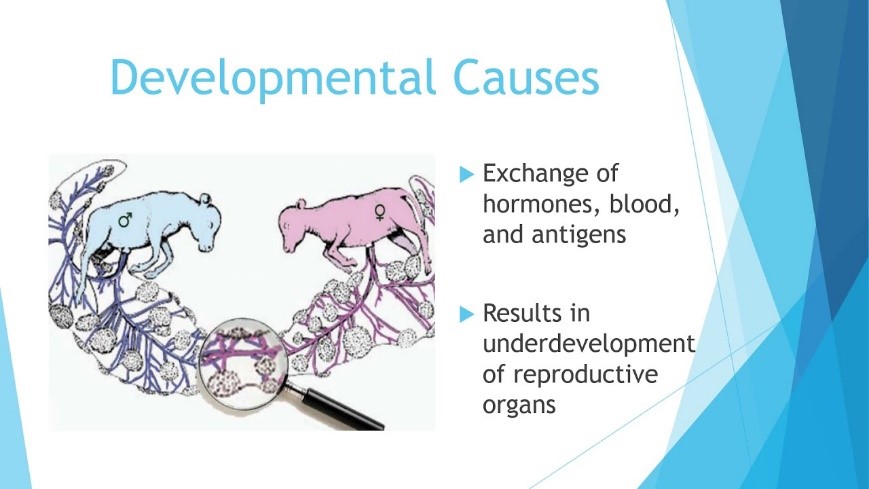
Mechanism
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. Recently, Freemartin was in the news. What is it? 1. An animal that has both male and female sexual organs. 2. A reproductive strategy that involves development of a female gamete without fertilization. 3. Infertile female cattle with masculinized behavior. 4. Multiplication of genetically identical copies of a cultivar by asexual reproduction. Choose the correct code.
Answer Option 3. C |
© 2024 iasgyan. All right reserved