Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
About
The debate around GM Crops
Merits
Reduced input burden
Disease resistant and Sustainability
Environmental Protection
Longer Shelf life
Affordability
Fortification
Decreased Use of Pesticides
Demerits
Gene Transfer
Antibiotic resistance
Carcinogen exposure risk
Lower Level of Biodiversity
Gene Spilling
Exploitation
Widening Gap of Corporate Sizes
New Diseases
Economic Concerns
|
Case Studies Monsanto's INGARD cotton Monsanto sold its INGARD cotton (also known as Bt cotton) to Australian growers with estimates that there would be a 90% drop in sprays. In fact, for the 1996-97 crops there was a 52% decrease. However, Australian farmers generally found themselves worse off financially than they thought they would. Some had to spray just as much as usual, yields were variable and costs higher. More insects survived than had been intended by the developer. Mannion and Morse report On a global level, from 1996 to 2006, GM crops increased farm income by $40.7 billion, occurring in both developed (47%) and developing agricultures (53%). There has been a global yield increase of 377 million tons from 1996 to 2012. |
In a nutshell,
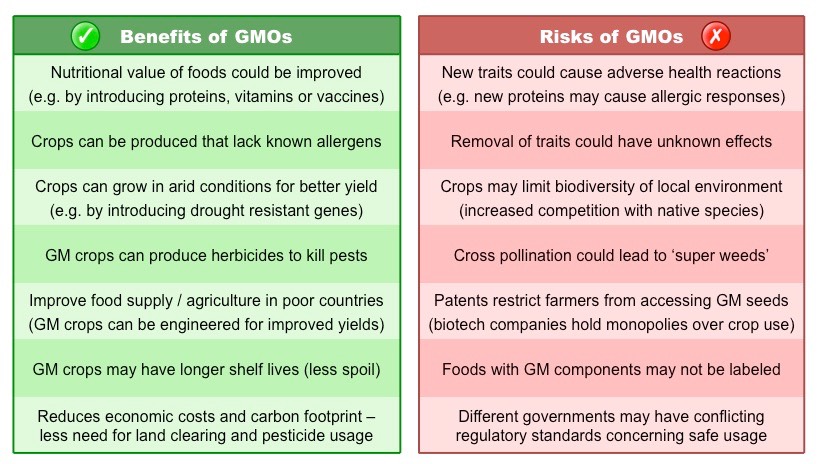
The Case of India
Note: In India, the Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC) under of Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change is the apex body that allows for commercial release of GM crops
Conclusion
© 2024 iasgyan. All right reserved