Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now



Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: https://hindicurrentaffairs.adda247.com/conservation-plan-for-great-indian-bustards/
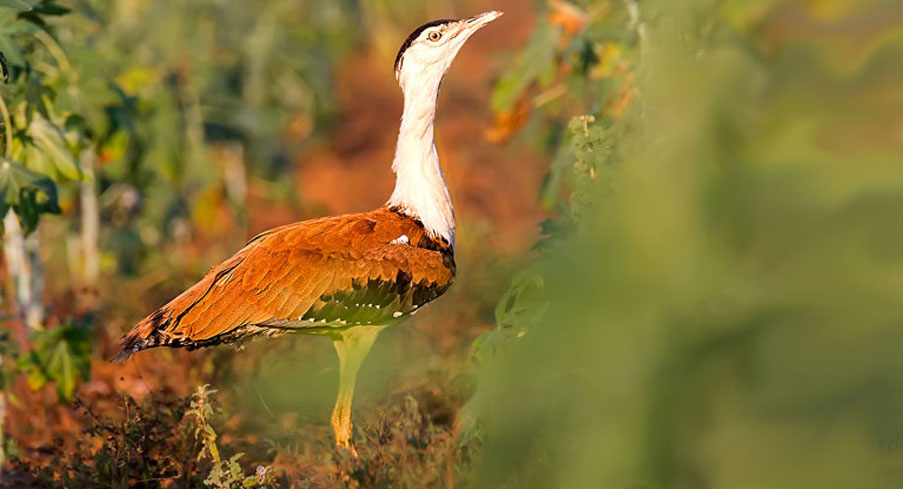
Context: The Supreme Court is overseeing the conservation of the Great Indian Bustard (GIB) through a series of orders and directions aimed at minimising the risks to this critically endangered bird species, particularly overhead electricity lines.
Supreme Court's 2021 Judgement
Challenges Raised in 2024
Supreme Court's Response in 2024
Formation of the Committee
Great Indian Bustard (GIB)
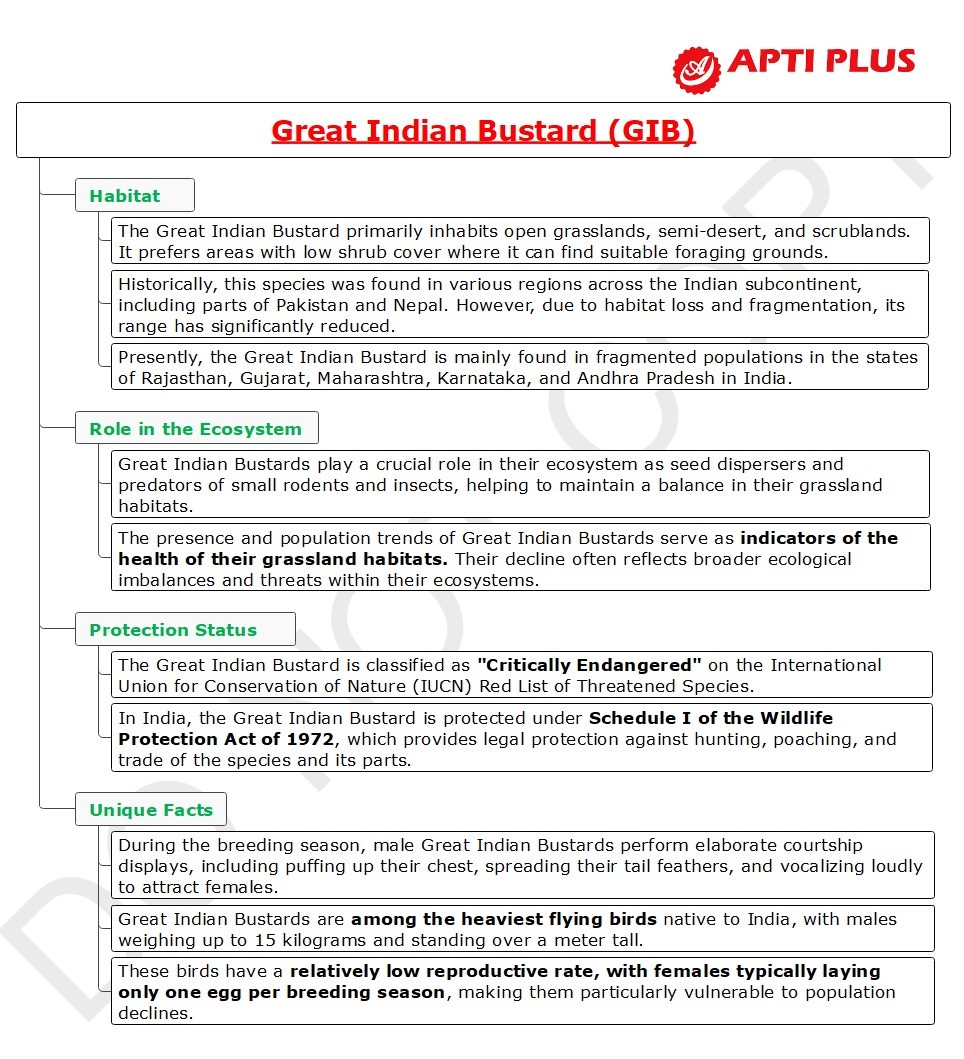
Threats to the Great Indian Bustard
Conservation Efforts
Conclusion
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. Consider the following statements in the context of the Great Indian Bustard: 1. Their ideal habitat includes open grasslands with short shrubs. 2. They are extensively hunted for their meat and feathers. 3. It is classified as Endangered on the IUCN Red List. 4. They prey on small mammals, controlling their populations. How many of the above statements are correct? A) Only one B) Only two C) Only three D) All four Answer: C Explanation: Statement 1 is correct: Their ideal habitat includes open grasslands with short shrubs. These open areas provide them with a clear view of their surroundings, allowing them to spot predators and prey easily. Short grasses are especially preferred during the breeding season, as they offer less obstruction for their courtship displays. Statement 2 is correct: They are extensively hunted for their meat and feathers. Despite being protected under the Wildlife Protection Act of 1972, illegal hunting and poaching continue to be major threats to the Great Indian Bustard population. Statement 3 is incorrect: It is classified as Critically Endangered on the IUCN Red List. This classification reflects the urgent need for conservation efforts to prevent the extinction of the Great Indian Bustard. Habitat loss due to the conversion of grasslands for agriculture and infrastructure development, collisions with power lines, and hunting are all significant threats to the species. Statement 4 is incorrect: The Great Indian Bustard is an omnivore, but its diet primarily consists of insects, reptiles, and seeds. While they may occasionally consume small mammals, they are not major predators and don't play a significant role in controlling mammal populations. Their primary ecological contribution is likely seed dispersal through their droppings, which helps to maintain the health of grassland ecosystems. |
© 2024 iasgyan. All right reserved