Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Copyright infringement not intended
Context - The Union Government has released the ‘Guidelines on Prevention of Misleading Advertisements and Endorsements for Misleading Advertisements, 2022’.
Details
Key points of the Guidelines
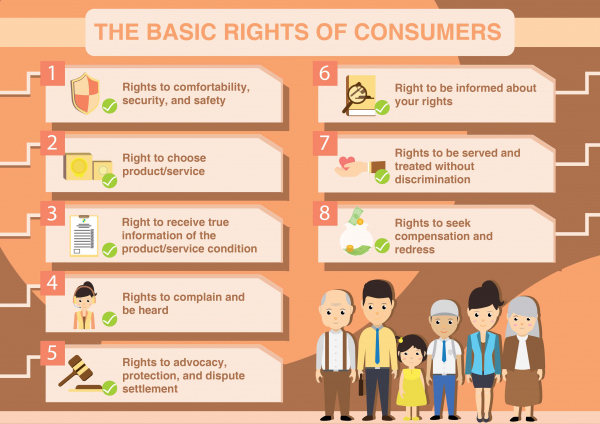
Consumer Protection Act, 2019
Copyright infringement not intended
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1832906
https://t.me/+hJqMV1O0se03Njk9
© 2024 iasgyan. All right reserved