Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
Gulf Stream Could Collapse As Early As 2025, Mini Ice Age On The Way: Study
Details
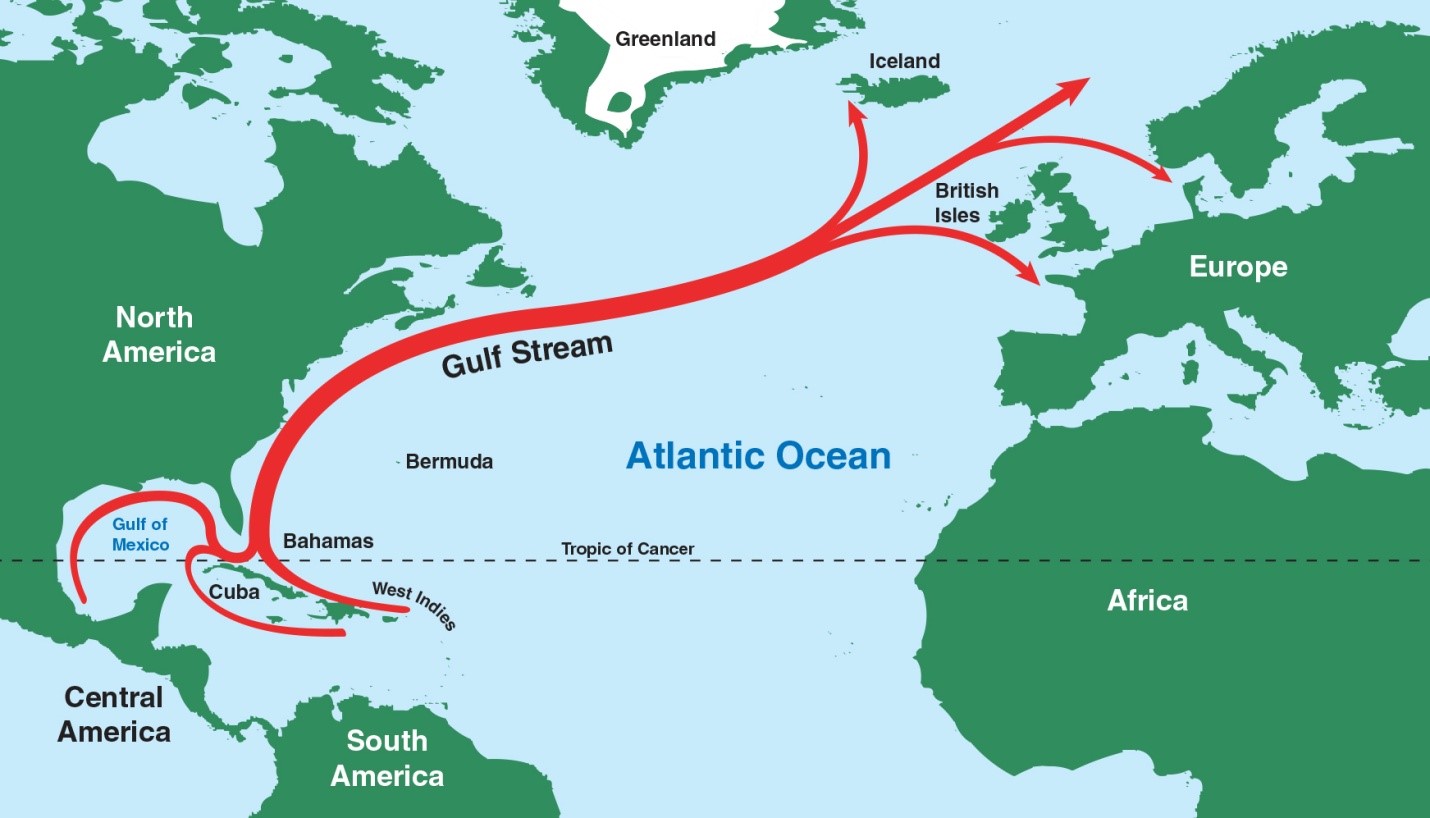
Gulf Stream
Origin and Path
Significance
Climate Influence:
Oceanic Circulation
Marine Life:
Scientific Research and Monitoring:
Economic and Societal Impacts:
Recent study on the Gulf Stream
Collapse if global carbon emissions remain unchecked
Conclusion
The Gulf Stream is a dynamic and influential ocean current that shapes climate, weather, and marine ecosystems across a vast region spanning from North America to Europe. Its complex interactions with the atmosphere, ocean, and marine life make it a subject of extensive scientific research and monitoring. Its role in global climate dynamics is essential for addressing current and future challenges related to climate change and oceanic variability.
|
PRACTICE QUESTIONS The Gulf Stream is a pole ward flowing current in the Atlantic Ocean. Which one of the following statements with regard to this is not correct?
|
© 2024 iasgyan. All right reserved