Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


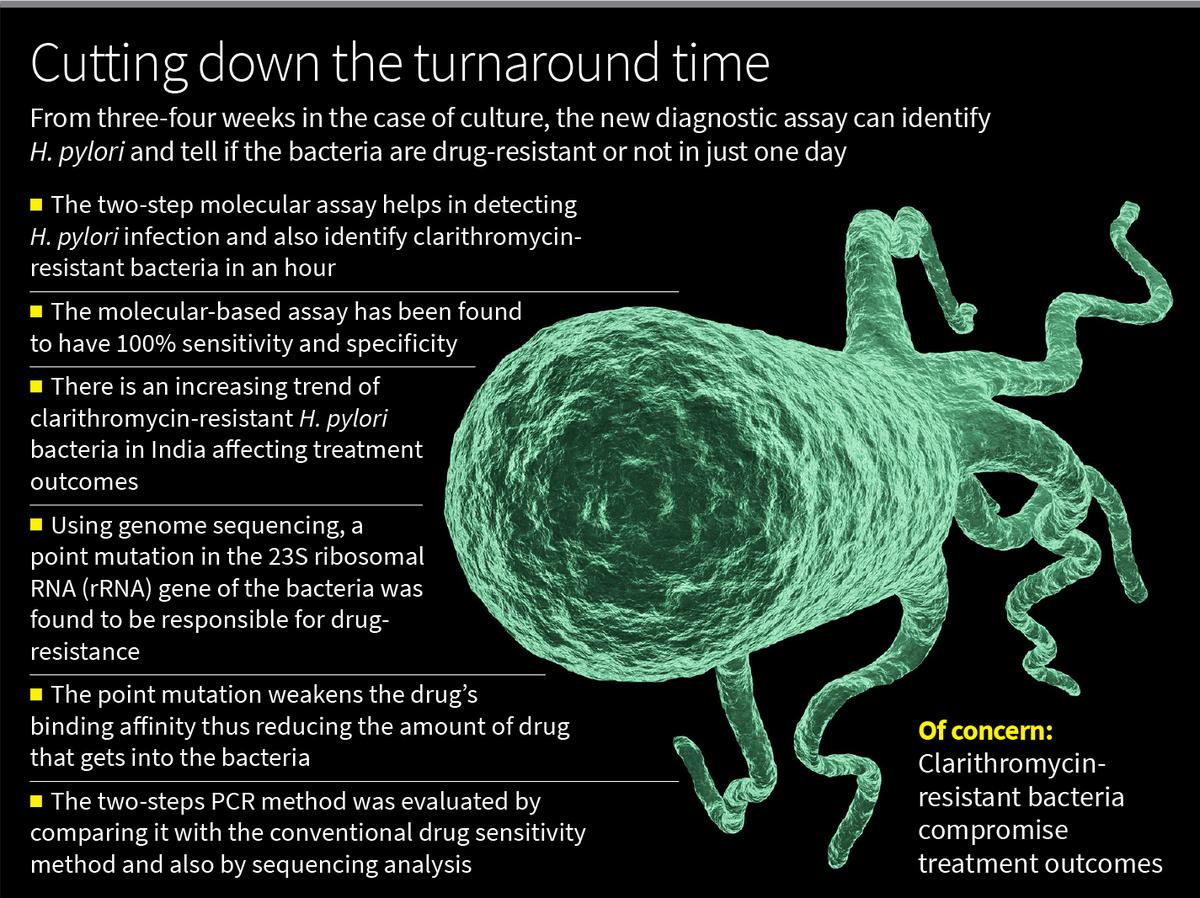
Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: THE HINDU
Context: Researchers at the National Institute of Cholera and Enteric Diseases (ICMR-NICED) in Kolkata, have developed a two-step PCR-based assay that can detect Helicobacter pylori infection and identify clarithromycin-resistant bacteria in six to seven hours, providing significant improvements over the conventional methods.
Key Highlights
pylori Infection and Drug Resistance
Traditional Detection and Drug Sensitivity Testing
Development of a PCR-Based Assay
Significance of PCR-based assay for Public Health
Conclusion
Must Read Articles:
Antibiotics Resistance: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/antibiotics-resistance
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. How does the overuse and misuse of antibiotics contribute to the development of antibiotic resistance in bacteria, and what strategies can be implemented to combat this growing global health threat? |
© 2024 iasgyan. All right reserved