Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: www.fitpaa.com
Context: The World Health Organization (WHO) announced that Egypt has made "unprecedented progress" in its efforts to eliminate hepatitis C, becoming the first country to achieve "gold tier" status on the path to eliminating the disease.
Details
Picture Courtesy: Assunta Hospital Malaysia
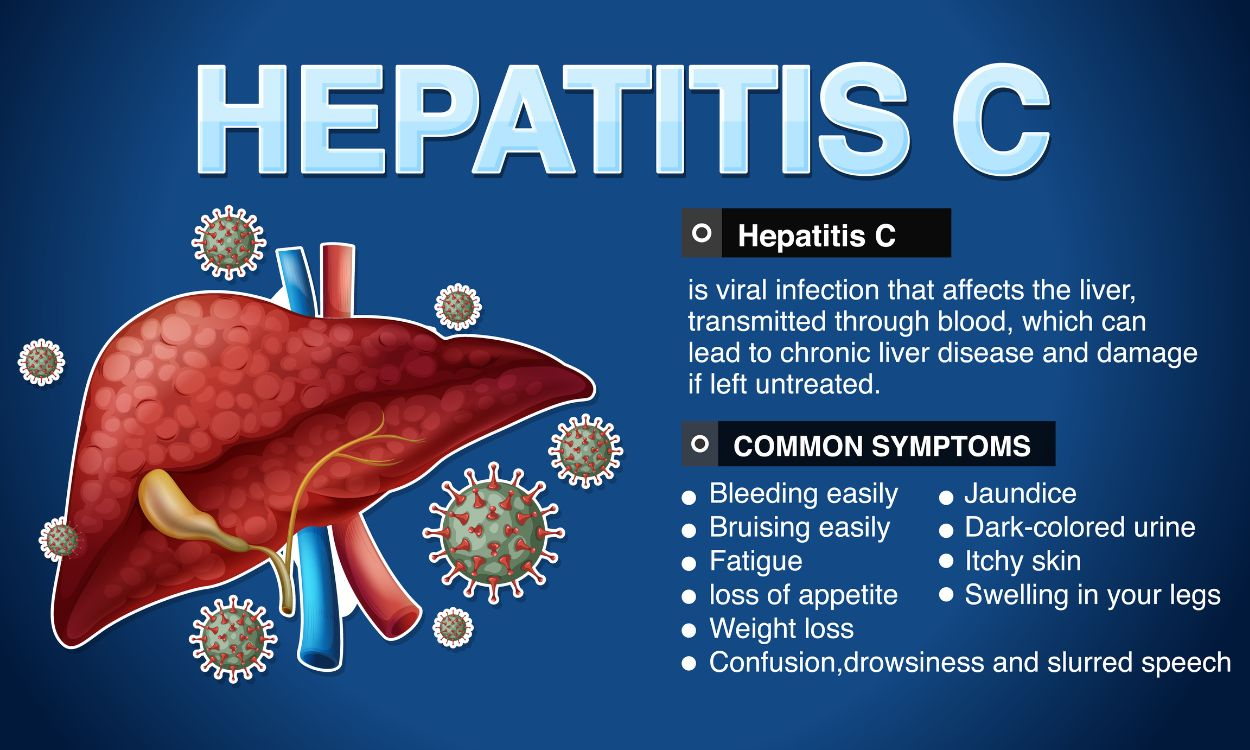
Hepatitis C
|
Prevention ●Do not share needles or other drug paraphernalia. Practice safe sex, and do not engage in unprotected sex with multiple partners. ●Blood and organ donations are screened for HCV to prevent transmission. ●Healthcare workers should follow strict protocols for needle safety to prevent accidental exposures. ●Pregnant women with HCV can work with healthcare providers to reduce the risk of transmission to the baby during childbirth. ●Providing clean needles and syringes to injection drug users can reduce the risk of HCV transmission. |
Must Read Articles:
World Hepatitis Day: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/world-hepatitis-day-12
|
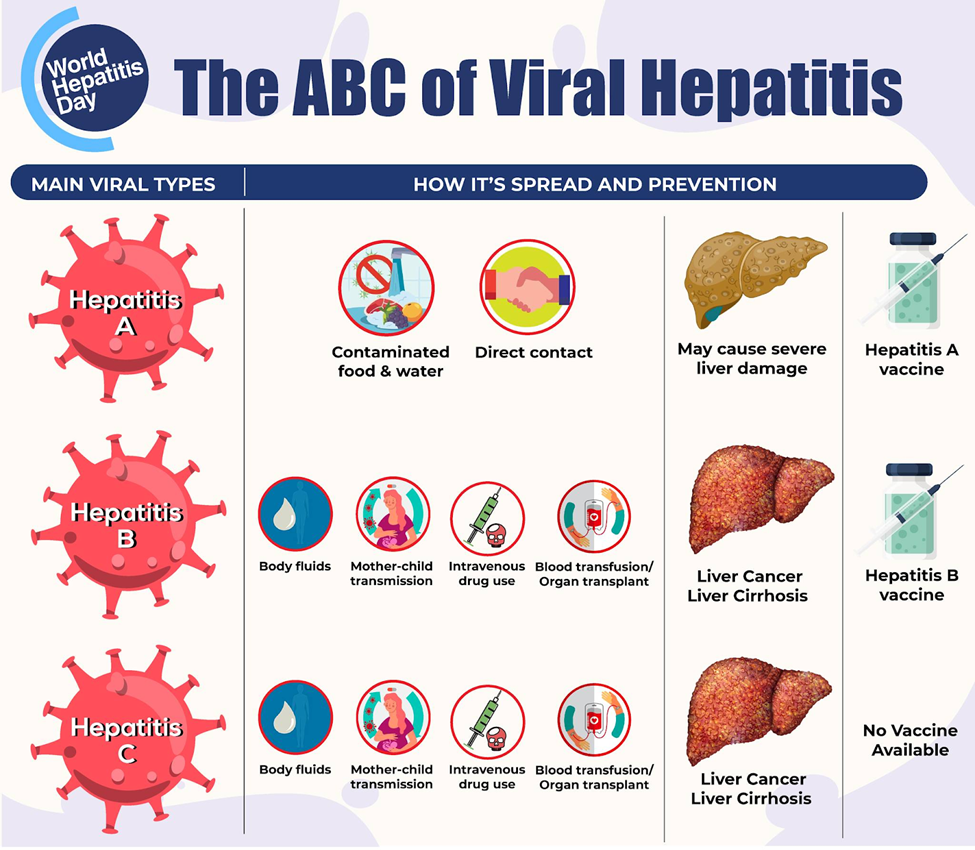
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. Consider the following statements in the context of Hepatitis C: 1. It can be diagnosed through a physical examination. 2. It can be transmitted from a mother to her baby during childbirth. 3. It can lead to liver failure due to scarring of the liver tissue. 4. There is currently no vaccine available for Hepatitis C. How many of the above statements is/are correct? A) Only one B) Only two C) Only three D) All four Answer: C Explanation: Statement 1 is incorrect: Hepatitis C cannot be diagnosed through a physical examination alone. A healthcare provider cannot determine the presence of Hepatitis C based on visible symptoms or physical signs. Diagnosis requires specific blood tests that detect the presence of HCV antibodies and viral RNA in the bloodstream. These tests are essential for confirming the infection. Statement 2 is correct: Hepatitis C can be transmitted from an infected mother to her baby during childbirth. This mode of transmission is known as perinatal or vertical transmission. However, with appropriate medical care and antiviral interventions, the risk of transmission from mother to child can be significantly reduced. Statement 3 is correct: Hepatitis C can lead to serious liver complications, including the development of liver fibrosis (scarring of the liver tissue). Over time, this scarring can progress to cirrhosis, a condition where extensive scarring disrupts the liver's function. If left untreated, cirrhosis can lead to liver failure, which is a life-threatening condition. Statement 4 is correct: There is no approved vaccine for Hepatitis C. While there are vaccines available for Hepatitis A and Hepatitis B, there is no specific vaccine to prevent Hepatitis C. Preventative measures primarily focus on avoiding exposure to infected blood, such as not sharing needles and practising safe sex. |
© 2024 iasgyan. All right reserved