Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


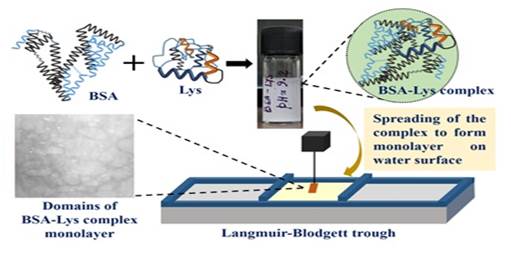
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
|
A thin film is a layer of material ranging from fractions of a nanometer (monolayer) to several micrometers in thickness. The controlled synthesis of materials as thin films (a process referred to as deposition) is a fundamental step in many applications. Advances in thin film deposition techniques during the 20th century have enabled a wide range of technological breakthroughs in areas such as magnetic recording media, electronic semiconductor devices, Integrated passive devices, LEDs, optical coatings (such as antireflective coatings), hard coatings on cutting tools, and for both energy generation (e.g. thin-film solar cells) and storage (thin-film batteries). It is also being applied to pharmaceuticals, via thin-film drug delivery. A stack of thin films is called a multilayer. |
Details
Use case
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1834267
© 2024 iasgyan. All right reserved