Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


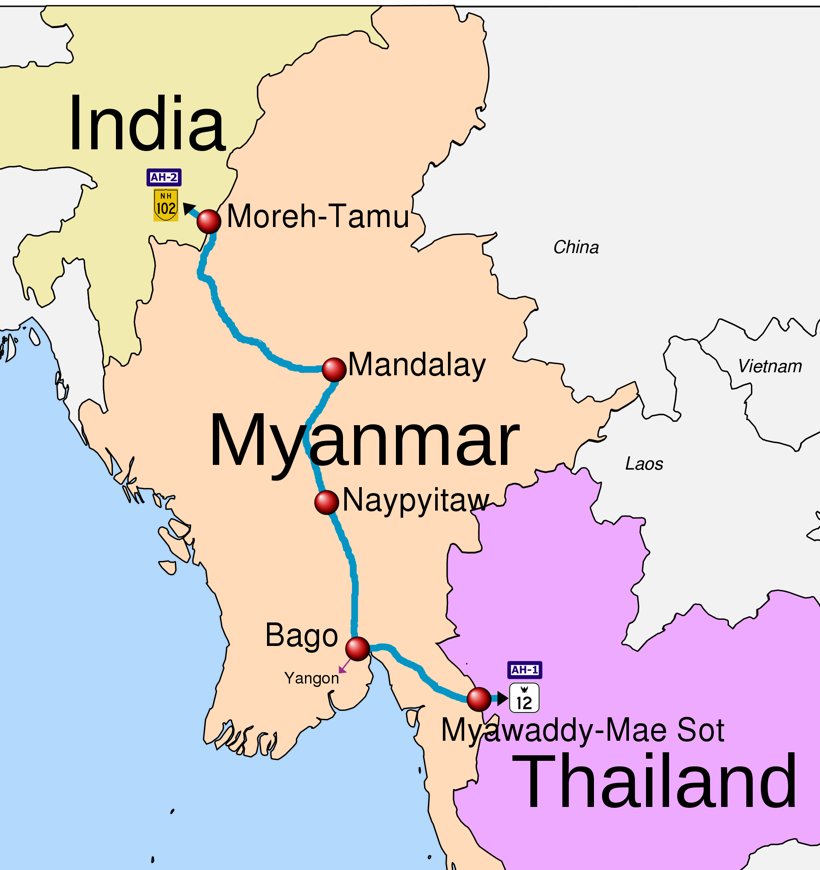
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
Background
About
Significance
Scope
Recent Developments
India’s contribution
Strategic Importance
Benefits
Challenges
Way Forward
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. IMT Highway will improve trade and commerce in the ASEAN–India Free Trade Area, as well as with the rest of Southeast Asia. Elucidate. (150 Words) |
© 2024 iasgyan. All right reserved