Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Copyright infringement is not intended
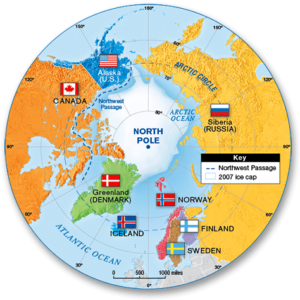
Context: India's Arctic policy titled 'India and the Arctic: building a partnership for sustainable development’ launched.
About India's Arctic policy:
India and Arctic region:
About Arctic Council
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1806993
© 2024 iasgyan. All right reserved