Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


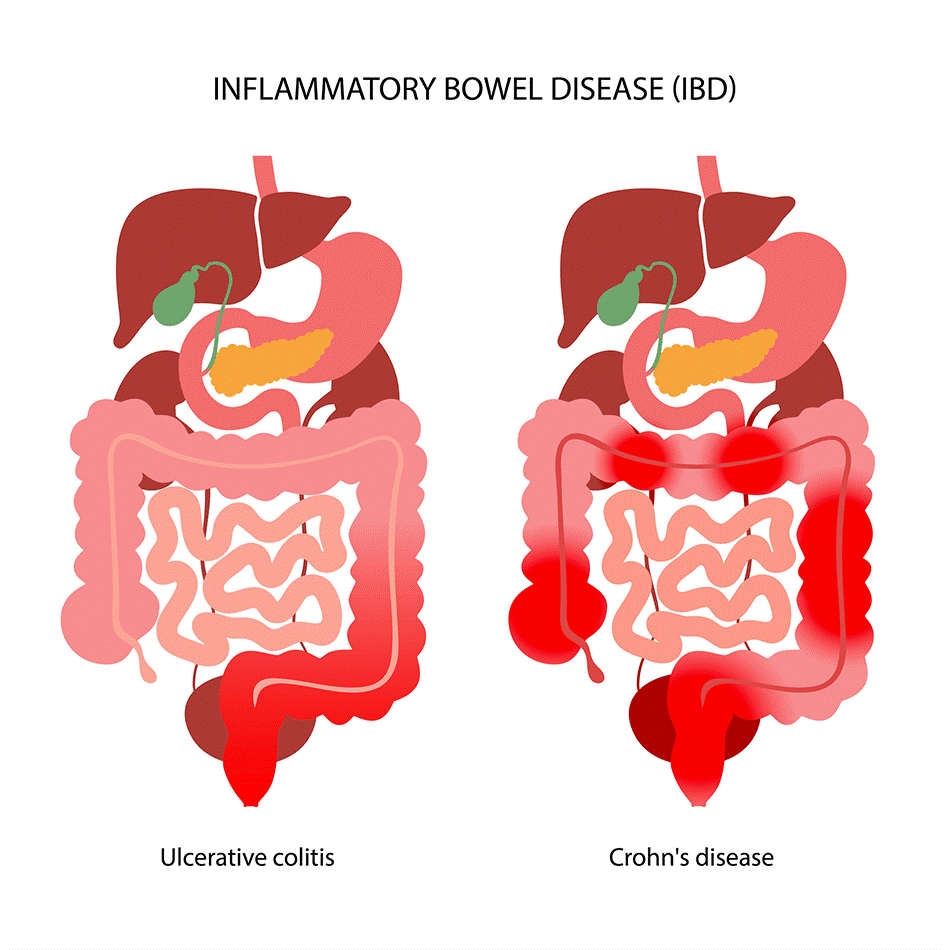
Source: JohnHapkinsMedicine
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
Details
Global Trends
Contributing Factors in India:
About Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
Symptoms of Inflammatory Bowel Disease:
Causes and Risk Factors:
Diagnosis and Delay:
Treatment:
Complications:
Sources:
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. Discuss the epidemiology, risk factors, and impact of chronic diseases on public health. What measures can be taken to address the rising burden of chronic diseases globally? (250 words) |
© 2024 iasgyan. All right reserved