Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Copyright infringement not intended
Context - The Union Jal Shakti Minister has chaired a review meeting on Jal Jeevan Mission (JJM).
Details
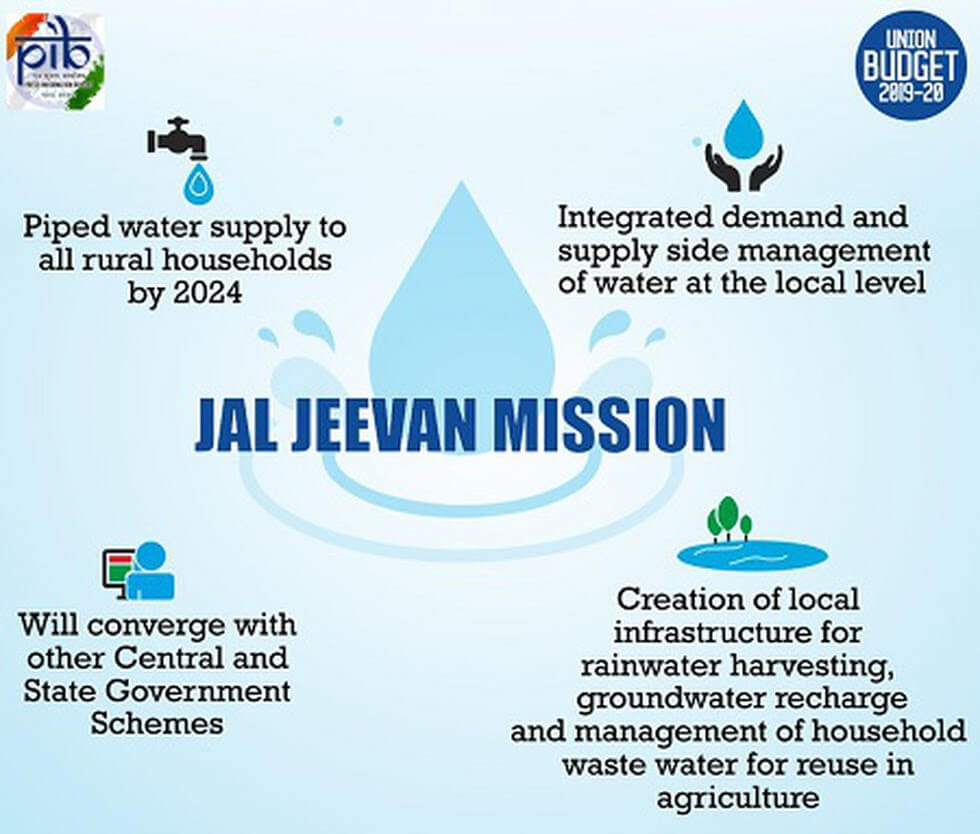
Jal Jeevan Mission
Features
Steps by the Government for water management
Steps need to be taken
Way forward
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1821166
© 2024 iasgyan. All right reserved