Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
Details
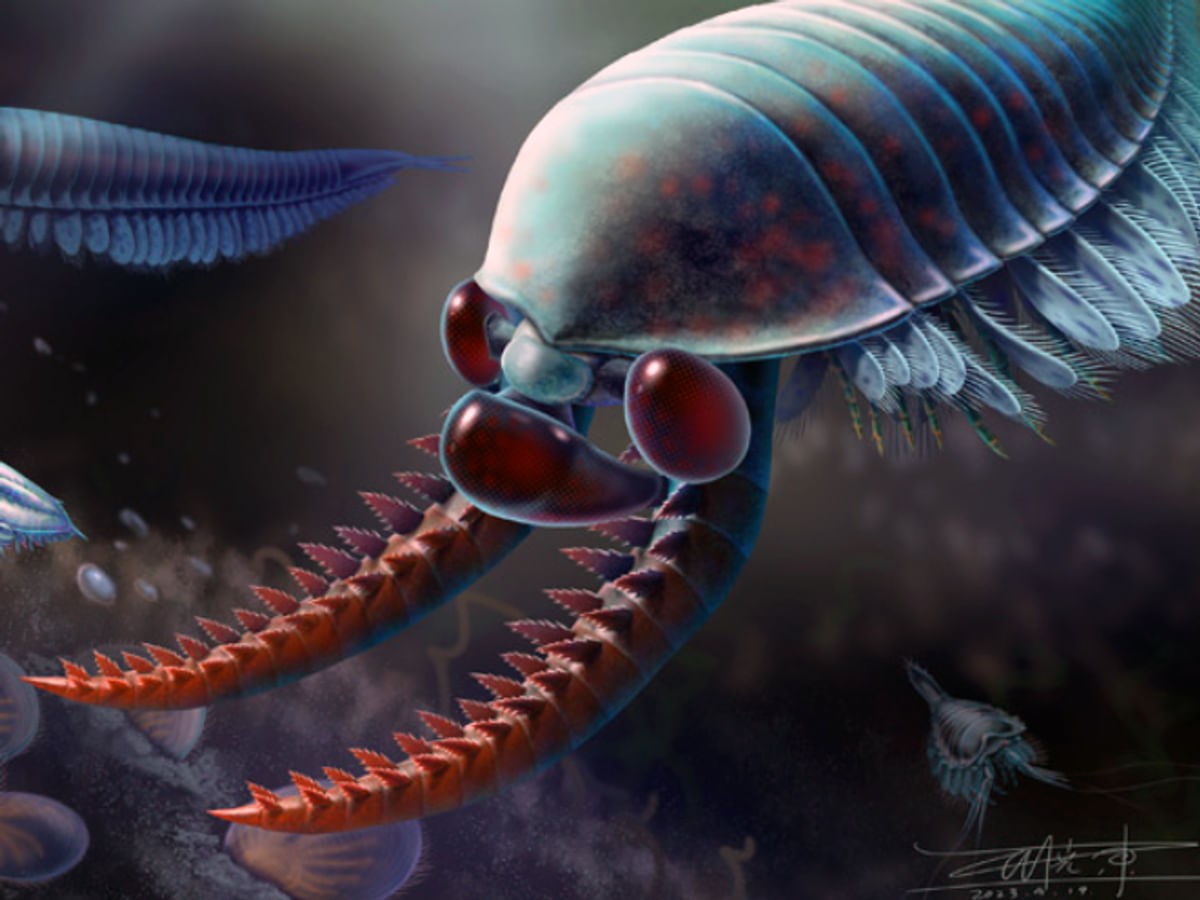
About Kylinxia zhangi
Features
Etymology
Taxonomy
Introduction to Arthropods
Key Characteristics of Arthropods
Arthropods share several key characteristics that define their phylum:
Major Groups of Arthropods
Arthropods are divided into four major groups, each with its own unique characteristics:
Ecological Roles and Importance
Notable Arthropod Facts
Conclusion
This discovery contributes to our understanding of the evolutionary history of arthropods and the development of their distinctive features, such as segmented bodies and jointed limbs. It highlights the importance of well-preserved fossils in unraveling the mysteries of ancient life forms.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. Which of the following is NOT a major group of arthropods? a) Insects b) Myriapods c) Annelids d) Crustaceans Correct Answer: c) |
© 2024 iasgyan. All right reserved