Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
GRAPHENE AND ITS APPLICATIONS: https://www.iasgyan.in/blogs/graphene-and-its-applications
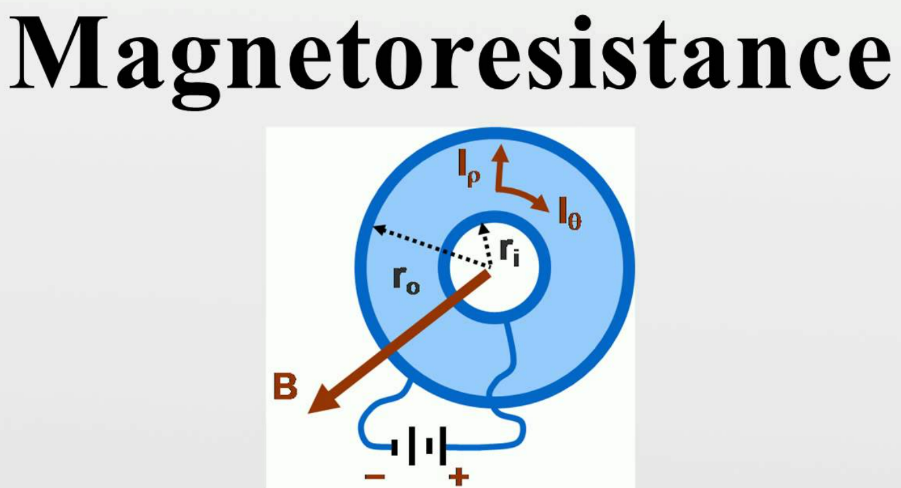
Magnetoresistance
Working Principle of Magnetoresistor
Characteristic of Magnetoresistor
Giant Magnetoresistance (GMR)
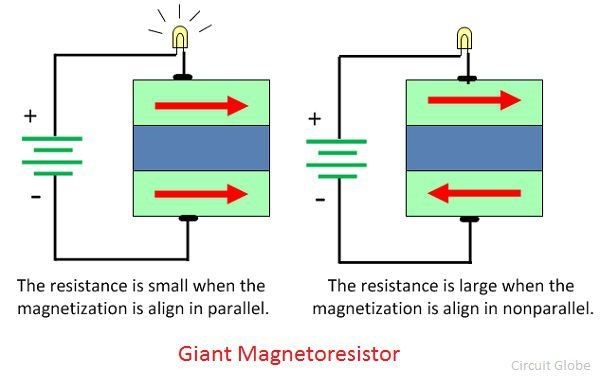
The current heavy will flows if the magnetisation of the electrodes is parallel to each other. The antiparallel arrangement increases the resistance between the layer.
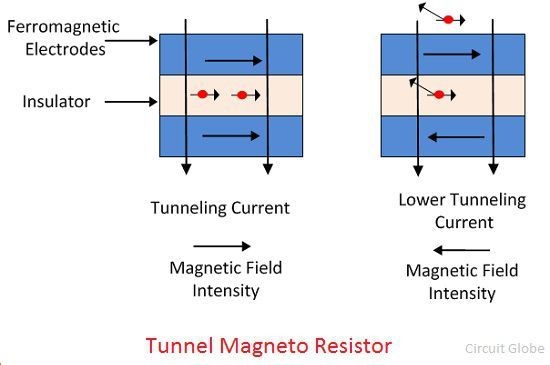
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. What do you understand by the term Magnetoresistance? What are Magnetoresistors and what are their applications? |
© 2024 iasgyan. All right reserved