Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now
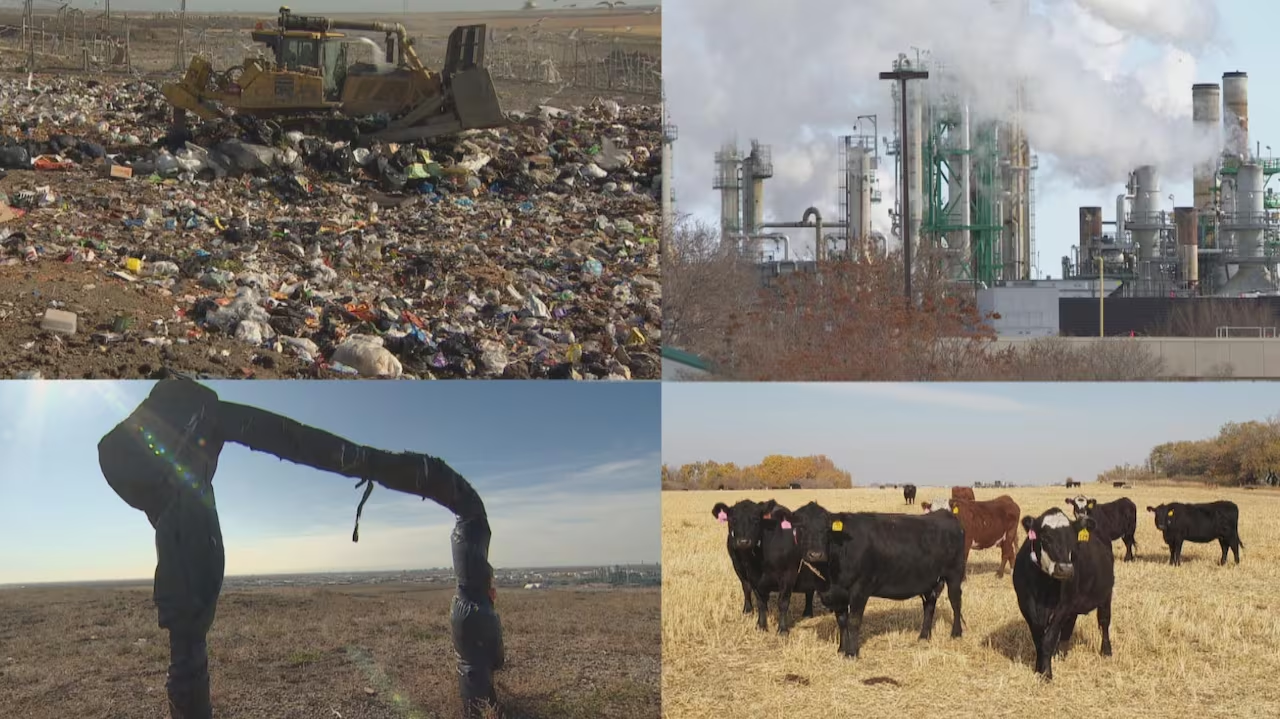



Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: https://www.cbc.ca/news/canada/saskatchewan/methane-emission-reduction-sask-1.6762784
Context: A drilling accident in Kazakhstan produced a fire that lasted a record six months, from June to December 2023. Recently, the leak has been stopped, and efforts are ongoing to permanently seal the well with cement.
Key Highlights
|
Kazakhstan - It is a landlocked country in Eurasia, the ninth largest in the world. Astana is the capital. - Shares borders with Russia, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, and China. The Caspian Sea serves as its western border. - Rich in petroleum, natural gas, minerals; reserves of uranium, chromium, lead, zinc, manganese, copper, coal, iron, gold, diamonds. |
|
About Methane leak
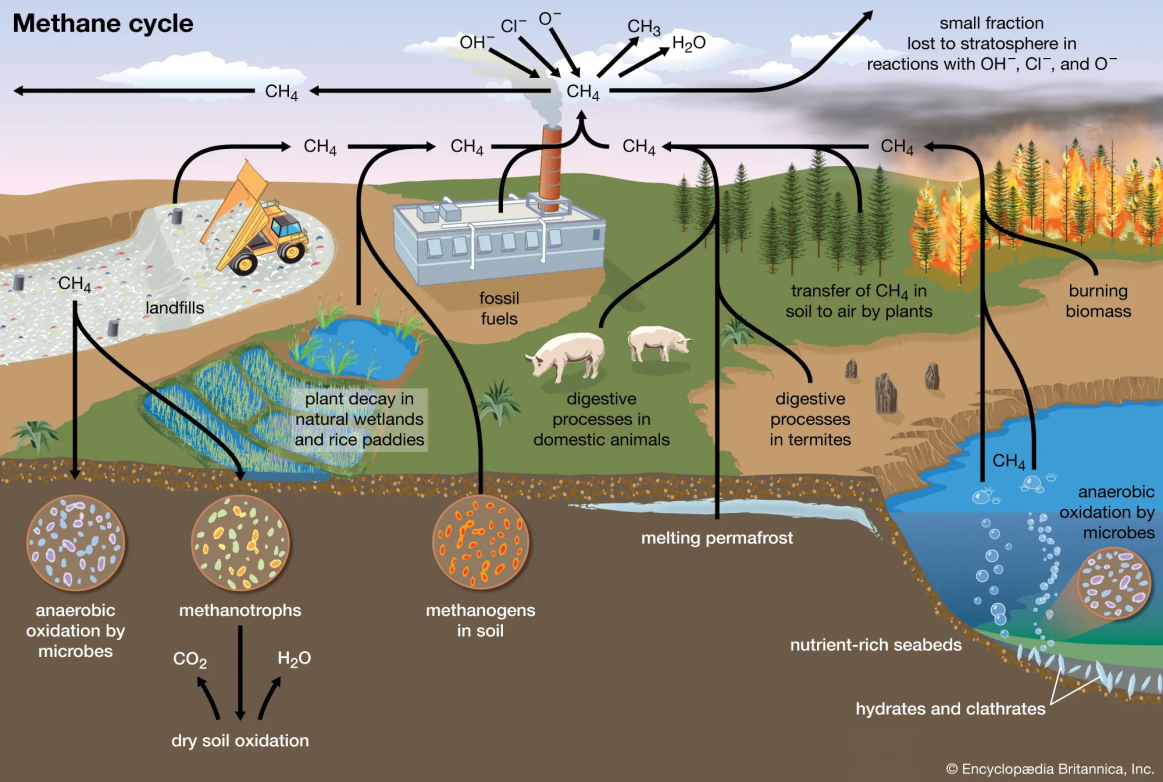
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. Consider the following statements in the context of the Methane: 1. It is a more potent greenhouse gas than carbon dioxide. 2. It is produced during the digestion of food in the stomachs of ruminant animals. 3. It is chemically inert and does not participate in chemical reactions. 4. It has a lower boiling point than water. How many of the above statements are correct? A) Only one B) Only two C) Only three D) All four Answer: C Statement 1 is correct: Methane has a higher global warming potential than carbon dioxide. Statement 2 is correct: Ruminant animals like cows, sheep, and goats produce methane during food digestion in their stomachs. Statement 3 is incorrect: Methane is not chemically inert. It can participate in various reactions, including burning as a fuel source. Statement 4 is correct: Methane boils at a much lower temperature (-161°C) than water (100°C), making it easier to transport as a liquid and vaporize for use as fuel. |
© 2024 iasgyan. All right reserved