Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


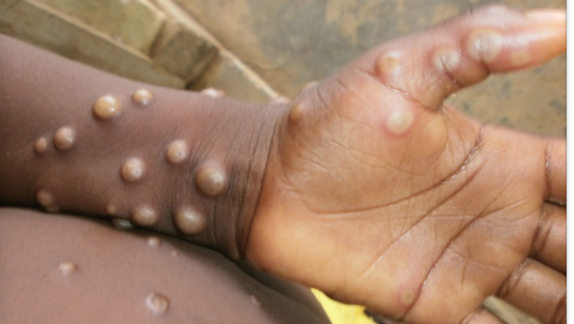
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
Monkey Pox Virus
About
Cause
Symptoms
Transmission
Treatment
© 2024 iasgyan. All right reserved