Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Details
About Earthquake
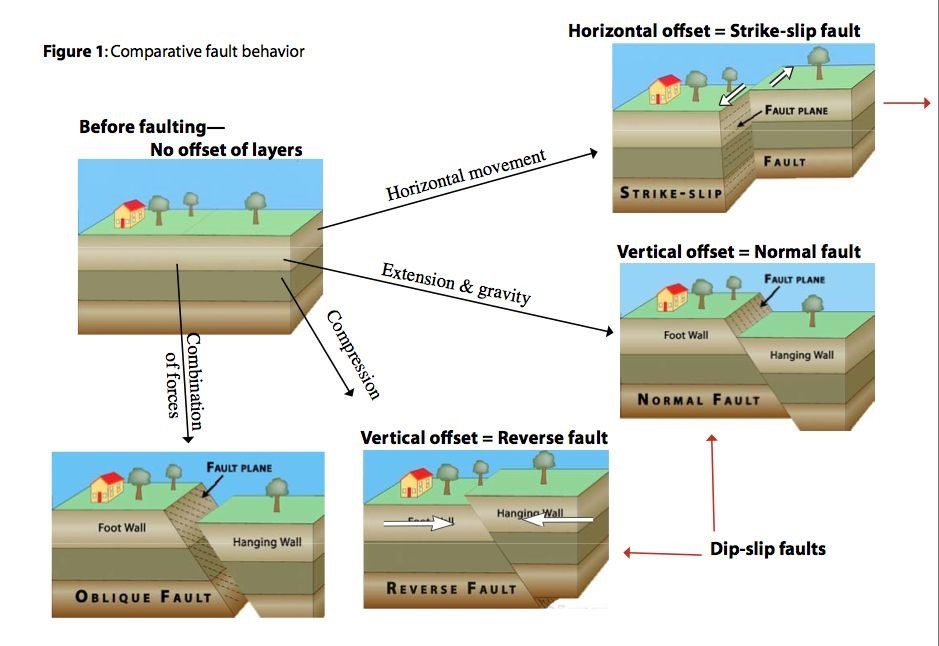
Types of Earthquakes:
Seismic Zones of India:
Seismic Active Zones:
|
Mercalli Scale: a twelve-point scale for expressing the local intensity of an earthquake, ranging from I (virtually imperceptible) to XII (destruction). Richter scale: It is a scale of numbers used to tell the power (or magnitude) of earthquakes. |
Causes of Earthquakes in India
Impact of Earthquakes
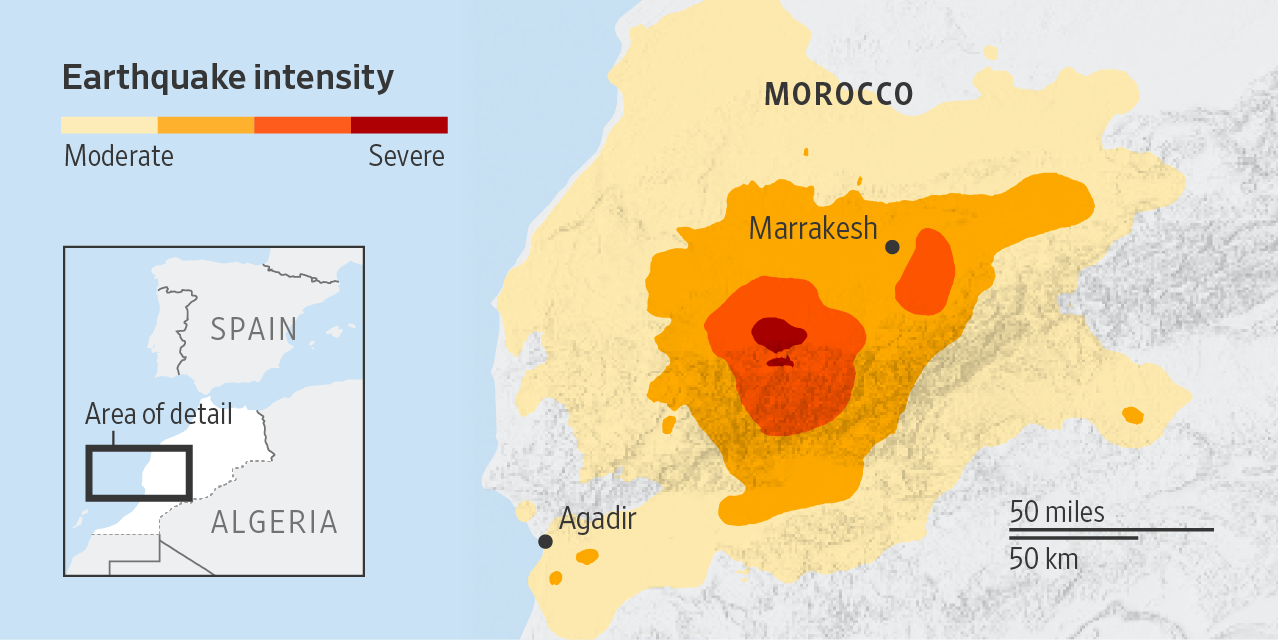
About Morocco
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Discuss about types of Seismic waves and causes of earthquakes in India. |
© 2024 iasgyan. All right reserved