Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


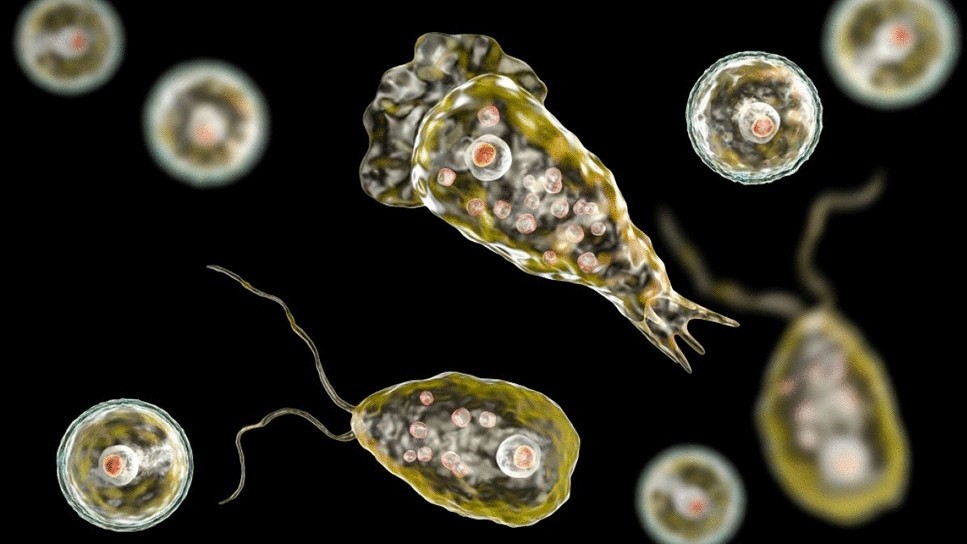
Source: IndianExpress
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
Details
Classification
Morphology
Naegleria fowleri exists in three forms:
Habitat and Transmission
Pathogenesis
Symptoms of Primary Amebic Meningoencephalitis (PAM)
Epidemiology
Sources:
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. Which of the following preventive measures can reduce the risk of Naegleria fowleri infection?
Select the correct answer using the codes given below: (a) 1, 2, and 3 only Answer: (a) |
© 2024 iasgyan. All right reserved