Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now



Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
Details
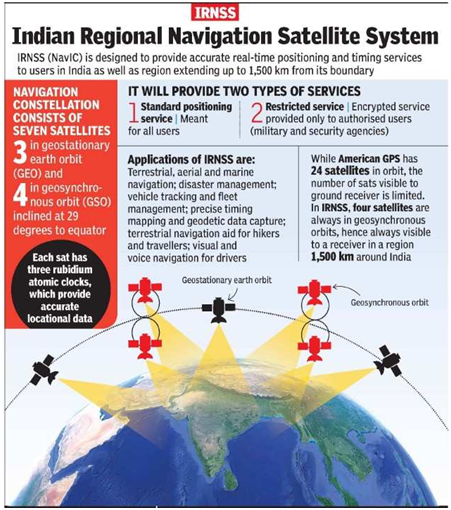
NaviC
Coverage
Satellites
Accuracy
Applications
Examples Redmi Note 9 series from Xiaomi, the Realme 6 series, the OnePlus Nord, etc.
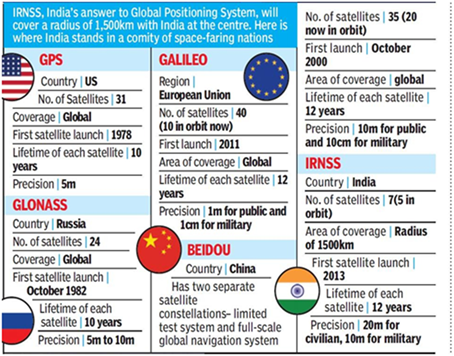
GPS VS NAVIC
About Frequency Bands
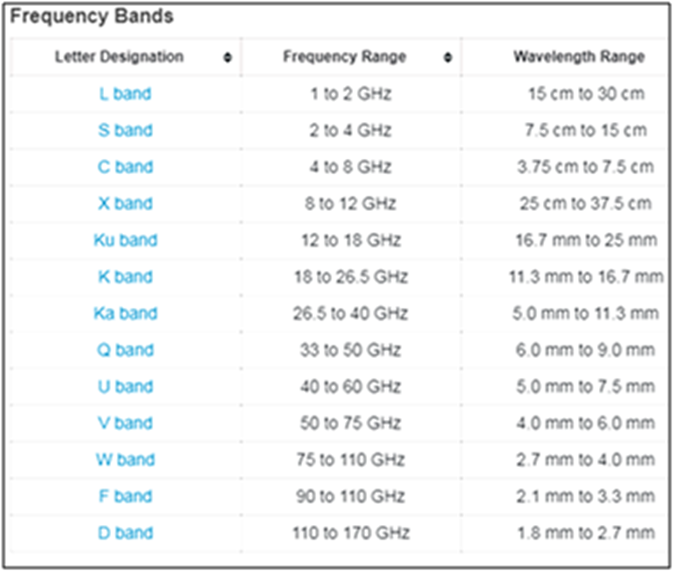
L Band
Applications
.jpg)
Advantages of L Band Frequency over other frequency bands:
S band
Applications
L1
Where is NavIC being used right now?
Significance of NaVIC
© 2024 iasgyan. All right reserved