Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now



Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: https://sitn.hms.harvard.edu/flash/2018/looking-trash-can-nuclear-waste-management-united-states/
Context: Nuclear waste management is a critical component of nuclear power generation, and countries like India, which have ambitious nuclear energy programmes, must efficiently address this challenge.
Details

Environmental and Health Impacts
Handling and Management of Nuclear Waste
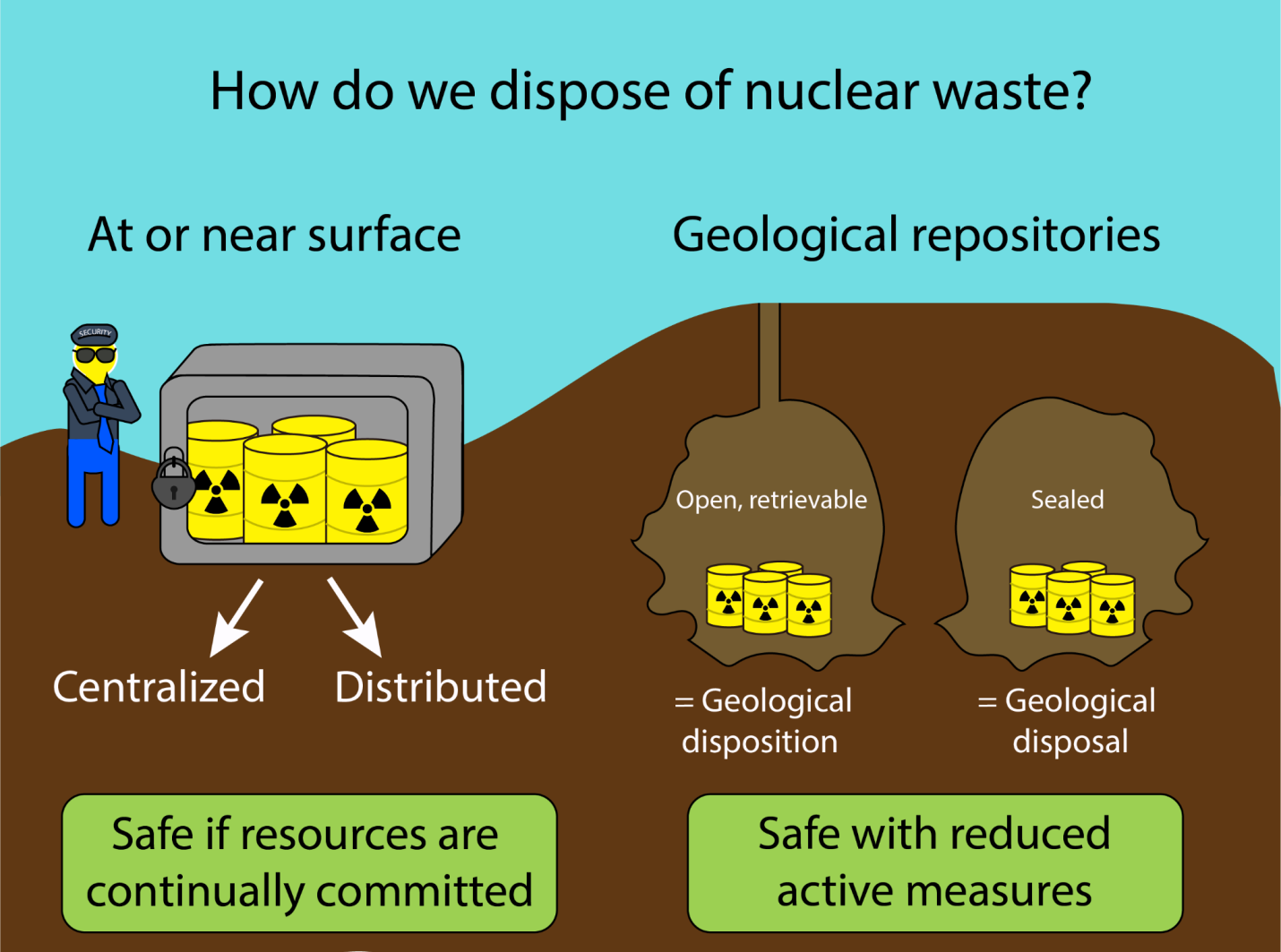
Challenges and Concerns
Way Forward
Must Read Articles:
NUCLEAR POWER IN INDIA: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/nuclear-power-in-india#:~:text=Nuclear%20waste%20is%20a%20major,disposed%20of%20through%20safe%20storage.
NUCLEAR WASTEWATER: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/nuclear-wastewater
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. Evaluate the potential risks and environmental impacts of nuclear accidents, such as core meltdowns or radioactive leaks, and analyse the effectiveness of current safety measures in mitigating these risks. |
© 2024 iasgyan. All right reserved