Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now



Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: https://www.telegraphindia.com/opinion/gulp-it-down-editorial-on-centres-minimal-fund-hike-in-midday-meal-schemes/cid/1891517
Context: The Lancet study highlights a dual health challenge in India with a significant increase in obesity among both adults and children over the past 32 years, coexisting with a persistent prevalence of undernutrition, creating a "double burden" on the country's health system.
Details
Obesity
|
Obesity Trends ●Women: There has been a substantial increase in obesity among women, with the prevalence rising from 1.2% in 1990 to 9.8% in 2022. The absolute number of women living with obesity in 2022 reached 44 million. ●Men: Obesity in men also increased by 4.9 percentage points during the same period. In 2022, there were 26 million men living with obesity. ●Childhood Obesity: The study reveals a significant increase in childhood obesity over the 32-year period. In 2022, 3.1% of girls and 3.9% of boys were classified as obese. The absolute numbers indicate a substantial rise, with millions of boys and girls being obese in 2022. |
Underweight
|
Underweight and Thinness Trends ●Overall Prevalence: Despite the rise in obesity, the prevalence of underweight and thinness remains high across genders and age groups. ●Women and Men: 13.7% of women and 12.5% of men were classified as underweight. ●Childhood Thinness: Thinness in children, particularly girls, is a significant concern. ●Indian girls have the highest prevalence of thinness globally, with a rate of 20.3%. ●Indian boys have the second-highest prevalence of thinness globally, with a rate of 21.7%. |
Factors contributing to the higher prevalence of obesity in women compared to men in India
|
●The higher prevalence of obesity in women has significant health implications, as obesity is associated with an increased risk of various health conditions, including diabetes and hypertension. ●Understanding the multifaceted factors contributing to gender-specific obesity trends is crucial for developing effective public health strategies. Interventions should be tailored to address the unique challenges faced by women in maintaining a healthy lifestyle. |
Patterns of obesity and undernutrition in India
|
Effective public health policies must address the socio-economic determinants of health. Strategies may include promoting healthier and more affordable food options, improving access to nutritious meals in rural areas, and raising awareness about balanced diets. |
Consequences of the Double Burden
Individual Health Implications
Economic Burden
Public Health Challenges
Social Inequality and Disparities
Way Forward
|
Malnutrition in India |
|
|
Key Points |
Description |
|
Prevalence |
●According to the latest National Family Health Survey (NFHS-5, 2019-21), 20.3% of girls and 21.7% of boys under five are wasted (indicating low weight for height) - the highest rates globally. Furthermore, 35.5% of children under-five and 13.7% of women are underweight. ●The NFHS-5 data reveals that 28.6% of urban men and 31.7% of urban women are overweight or obese, compared to 18.8% and 19.0% in rural areas, respectively. |
|
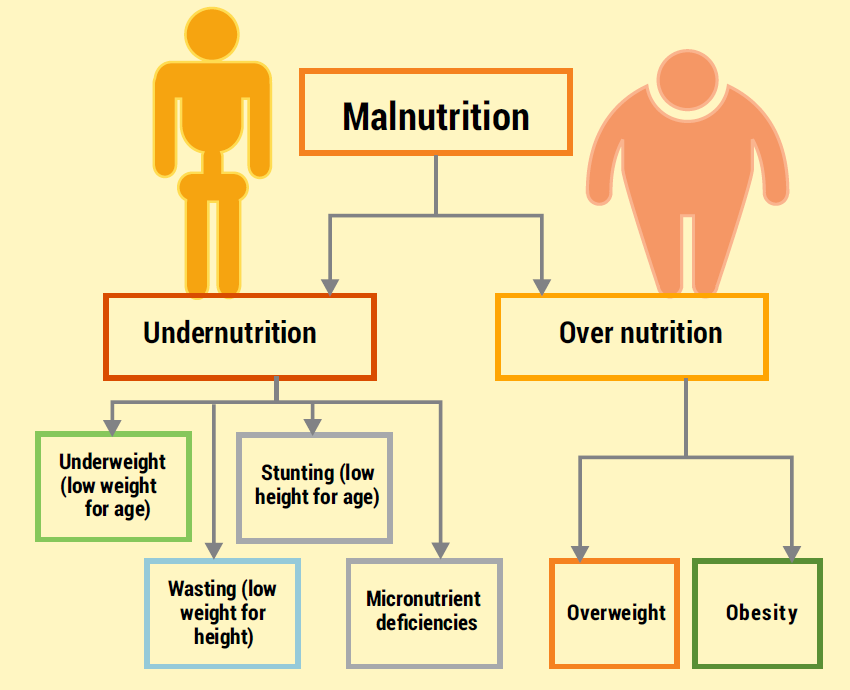
Types of Malnutrition |
●Undernutrition: This includes stunting (low height for age), wasting (low weight for height), and underweight (low weight for age) among children, indicating chronic malnutrition. ●Micronutrient Deficiency: Common deficiencies include iron, vitamin A, and iodine, leading to various health issues. ●Overnutrition: This refers to the rising prevalence of overweight and obesity, particularly in urban areas, driven by factors such as unhealthy dietary habits and sedentary lifestyles. |
|
Causes |
●Poor Dietary Practices: Limited access to a diverse and nutritious diet due to factors such as poverty, food insecurity, and lack of awareness about healthy eating habits. ●Poverty: Economic constraints restrict access to quality food and healthcare services, exacerbating malnutrition. ●Lack of Healthcare: Limited access to healthcare facilities, including maternal and child healthcare services, contributes to malnutrition, especially in rural areas. ●Poor Sanitation: Inadequate sanitation facilities and hygiene practices increase the risk of infections and diseases that impact nutritional status. |
|
Impact on Health |
●Child Development: Malnutrition during the critical early years of life can lead to stunted growth, impaired cognitive development, and long-term health issues. ●Increased Vulnerability to Diseases: Malnourished individuals have weakened immune systems, making them more susceptible to infections and diseases. ●Maternal Health Issues: Undernourished mothers face higher risks during pregnancy and childbirth, leading to complications for both the mother and child. ●Rising Non-Communicable Diseases: Overnutrition contributes to the increasing burden of non-communicable diseases such as diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular diseases. |
|
Government Initiatives |
●Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS): Government program focusing on maternal and child health, providing supplementary nutrition, healthcare, and early childhood education services. ●National Health Mission (NHM): Aims to improve healthcare infrastructure and provide essential healthcare services, including maternal and child healthcare. ●Midday Meal Scheme: Government initiative providing free meals to school children to improve nutritional intake and encourage school attendance. ●Fortification Programs: Efforts to fortify staple foods with essential micronutrients to address deficiencies on a larger scale. |
|
Challenges |
●Regional Disparities: Malnutrition rates vary across different states and regions, with some areas facing higher prevalence due to socioeconomic disparities and unequal access to resources. ●Lack of Awareness: Limited understanding of the importance of nutrition and healthcare practices, particularly in rural and marginalized communities. ●Infrastructure Issues: Inadequate healthcare infrastructure, including healthcare facilities and trained healthcare professionals, especially in rural and remote areas, hinders effective intervention and treatment of malnutrition. ●Climate-Related Challenges: Climate variability and environmental factors impact agricultural productivity, affecting food availability and exacerbating food insecurity and malnutrition. |
|
Future Strategies |
●Education Programs: Implementing comprehensive nutrition education programs to increase awareness about healthy dietary practices, proper nutrition during different life stages, and the importance of healthcare services. ●Enhanced Healthcare Infrastructure: Investing in improving healthcare infrastructure, including healthcare facilities, equipment, and trained healthcare professionals, particularly in rural and underserved areas. ●Agricultural Reforms: Promoting sustainable agricultural practices, diversification of crops, and improving access to irrigation and agricultural inputs to enhance food production and availability. ●Policy Revisions: Implementing policy reforms addressing socioeconomic factors contributing to malnutrition, such as poverty alleviation measures, social safety nets, and promoting equitable access to resources and opportunities. |
Conclusion
Must Read Articles:
CHILD MALNUTRITION: JOINT CHILD MALNUTRITION ESTIMATES: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/child-malnutrition-joint-child-malnutrition-estimates#:~:text=India%20is%20the%20largest%20country,%25
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. The Indian government provides food subsidies to address food insecurity. However, these programs can sometimes incentivize the consumption of refined carbohydrates over more nutritious options. How to reform subsidy programs to promote both food security and healthy dietary patterns? |
© 2024 iasgyan. All right reserved