Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now



Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
Orion
.jpg)
Artemis program
Details
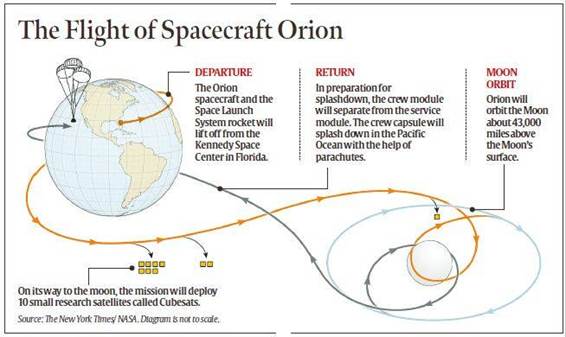
Cubesats
Orion spacecraft
Space Launch System, or SLS
Organizations involved
Artemis Accords
Final Thought
© 2024 iasgyan. All right reserved