Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


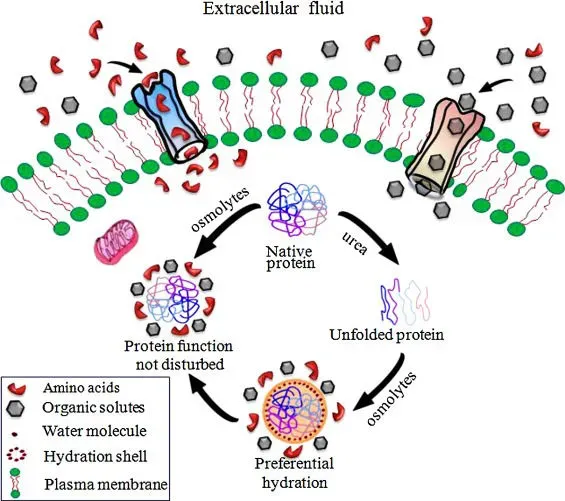
Context:
Details:

About Osmolyte:
Mechanism of Action
Case Study:
READ IN DETAIL ABOUT- About Alzheimer
ALSO READ ABOUT- Parkinson's Disease
Conclusion
Source:
https://dst.gov.in/osmolyte-protein-interaction-study-can-help-treatments-alzheimers-parkinsons#
MUST READ ARTICLES:
Researchers find brain protein in frontotemporal dementia ...
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. With reference to Osmolyte, consider the following statements:
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 and 2 only (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2, and 3 Answer: (b) |
© 2024 iasgyan. All right reserved