Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now



Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
Details
Achievements of PACER
Scientific Expedition to Antarctica
Indian Southern Ocean Expedition in Antarctica
Reconstruction of past Climate
Glaciological and geophysical measurements
Study of Biogeochemical Process
Establishment of atmospheric observatories
Climate variability over Antarctica
Arctic Expedition
Studies in Western Himalayas
Indian Antarctic Program
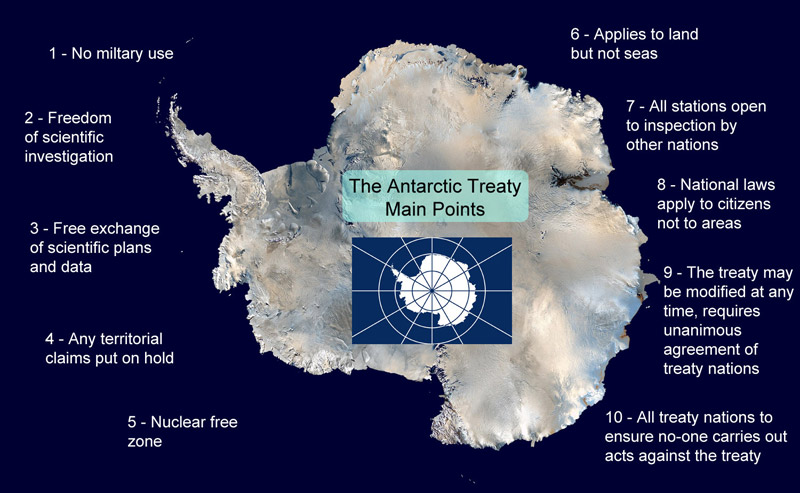
The Antarctic Treaty
India’s Arctic Program
|
Arctic Council · The Arctic Council is a high-level intergovernmental forum that addresses issues faced by the Arctic governments and the indigenous people of the Arctic. · The eight countries with sovereignty over the lands within the Arctic Circle constitute the members of the council: Canada, Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, Russia, Sweden, and the United States. · Outside these, there are some observer states. · The 1996 Ottawa Declaration established the Arctic Council as a forum for promoting cooperation, coordination, and interaction among the Arctic states, with the involvement of the Arctic Indigenous communities and other Arctic inhabitants on issues such as sustainable development and environmental protection. · Observer status is open to non-Arctic states approved by the Council at the Ministerial Meetings that occur once every two years. Observers have no voting rights in the Council. Svalbard Treaty The Svalbard Treaty (originally the Spitsbergen Treaty) recognises the sovereignty of Norway over the Arctic archipelago of Svalbard, at the time called Spitsbergen. The treaty regulates the demilitarisation of the archipelago. The signatories were given equal rights to engage in commercial activities (mainly coal mining) on the islands. Uniquely, the archipelago is an entirely visa-free zone under the terms of the Svalbard Treaty. |
https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1809081
© 2024 iasgyan. All right reserved