Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now



Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: https://www.euronews.com/2024/02/04/opposition-leaders-reject-senegal-election-delays-as-west-african-bloc-urges-dialogue
Context: The political unrest in Senegal prompts the West African bloc to appeal for unity and address the departure of three countries affected by coups.
Details
|
About the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) |
|
|
Established |
●On May 28, 1975 ●By the Treaty of Lagos signed by 15 member states ●Headquarters: Abuja, Nigeria |
|
Members (Current) |
●15 West African countries: Benin, Burkina Faso, Cabo Verde, Côte d'Ivoire, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Liberia, Mali, Niger, Nigeria, Sierra Leone, Senegal, Togo ●Recently, Burkina Faso, Mali, and Niger announced withdrawal (not yet finalized). |
|
Aim |
●Promote cooperation and integration for economic prosperity and regional stability. ●Addresses challenges like poverty, conflict, and climate change. |
|
Key Objectives |
●Economic Integration: Create a common market, free trade area, and eventually, an economic and monetary union. ●Harmonization: Align policies and programs in areas like trade, investment, agriculture, and energy. ●Development: Promote balanced development across member states, focusing on vulnerable groups. ●Peace & Security: Foster regional peace and security through conflict prevention, resolution, and cooperation. ●Human Rights: Protect and promote human rights in accordance with international and regional standards. |
|
Structure |
●Heads of State and Government: Highest decision-making body, meets annually. ●Council of Ministers: Oversees implementation of policies and programs, and meets twice annually. ●Commission: Executes decisions and manages day-to-day operations. ●Other Institutions: Include the Court of Justice, Parliament, and Investment Bank. ●Each member state has representation in all organs. |
|
Challenges |
●Political instability: Coups and internal conflicts hinder progress. ●Economic disparities: Member states have diverse economic strengths and weaknesses. ●Implementation gaps: Turning policies into action remains a challenge. ●Security threats: Terrorism, piracy, and organized crime pose dangers. |
|
Achievements |
●Trade liberalization: Increased intra-regional trade and economic activity. ●Peacekeeping missions: Stabilized conflict zones and facilitated elections. ●Policy harmonization: Improved regional cooperation and coordination. ●Infrastructure development: Built roads, bridges, and power grids. |
|
Future Vision |
●ECOWAS of the People: Achieve peace, prosperity, and sustainable development for all citizens by 2050. ●Borderless region: Facilitate free movement of people, goods, and services. ●Integrated economy: Create a single economic and monetary union. ●Good governance: Promote democracy, rule of law, and human rights. |
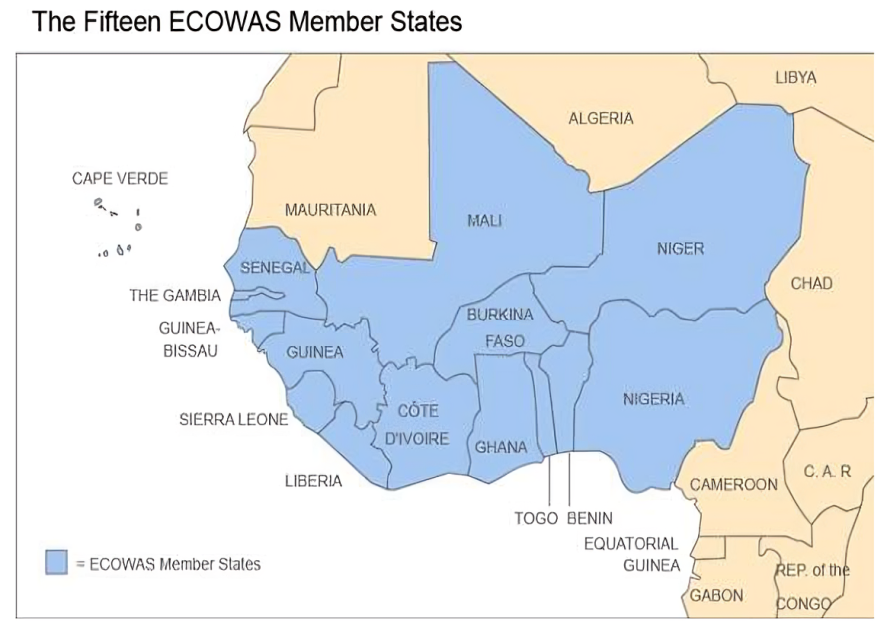
Senegal's Political Crisis
Role of ECOWAS
|
Senegal |
|
|
Geography and Ecology |
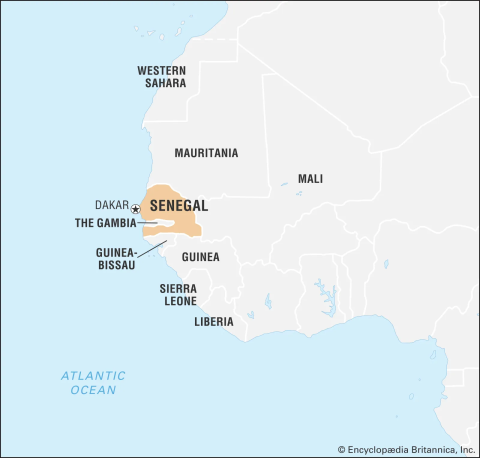
●Senegal is a West African country situated on the Atlantic Ocean coastline. ●Bordered by Mauritania to the north, Mali to the east, Guinea to the southeast, and Guinea-Bissau to the southwest. ●Ecologically diverse: semiarid grassland, oceanfront, tropical rainforest convergence. ●Rich plant and animal life; national symbols: baobab tree and lion. |
|
Historical Background |
●Part of ancient Ghana and Djolof kingdoms; key point on trans-Saharan caravan routes. ●Contested by European powers (England, France, Portugal, Netherlands) before French control in the late 19th century. ●Gained independence in 1960 under Léopold Senghor's leadership. |
|
Economy |
●Traditionally dependent on peanuts; government diversification efforts. ●Economic decline in the 20th century due to external factors (CFA franc devaluation, high debt servicing costs) and internal factors (population growth, unemployment). |
|
Ethnic Composition |
●Almost 40% Wolof population; a stratified society with hereditary nobility and griots (musicians/storytellers). ●Contemporary culture, especially music and arts, draws on Wolof sources; influences from other ethnic groups (Fulani, Serer, Diola, Malinke). |
Conclusion
Must Read Articles:
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. How can India effectively cooperate with West Asian countries to counter the spread of radicalization and extremism, considering the complex socio-political landscape and differing approaches? Answer Structure: ●Introduction: Give a brief background of India-West Asia relations, highlighting the common interests and challenges, and the significance of countering radicalization and extremism for regional stability and security. ●Body: Discuss the main causes and drivers of radicalization and extremism in West Asia, such as sectarianism, political instability, socio-economic grievances, foreign intervention, etc. Also, mention the different approaches adopted by the West Asian countries to deal with this problem, such as military, political, ideological, or developmental. Then, explain how India can effectively cooperate with the West Asian countries to counter this threat, by suggesting some specific measures or initiatives, such as intelligence sharing, counter-terrorism cooperation, dialogue and mediation, cultural and educational exchanges, development assistance, etc. Provide examples or evidence to support your arguments. ●Conclusion: Summarize the main points of your answer, and restate your position on how India can effectively cooperate with West Asian countries to counter radicalization and extremism. You can also mention some challenges or limitations that may hinder this cooperation, and suggest some ways to overcome them. |
© 2024 iasgyan. All right reserved