Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: lsdssindia.org
Context: Pompe disease is a rare genetic disorder that affects the muscles, causing progressive weakness and impacting various bodily functions.
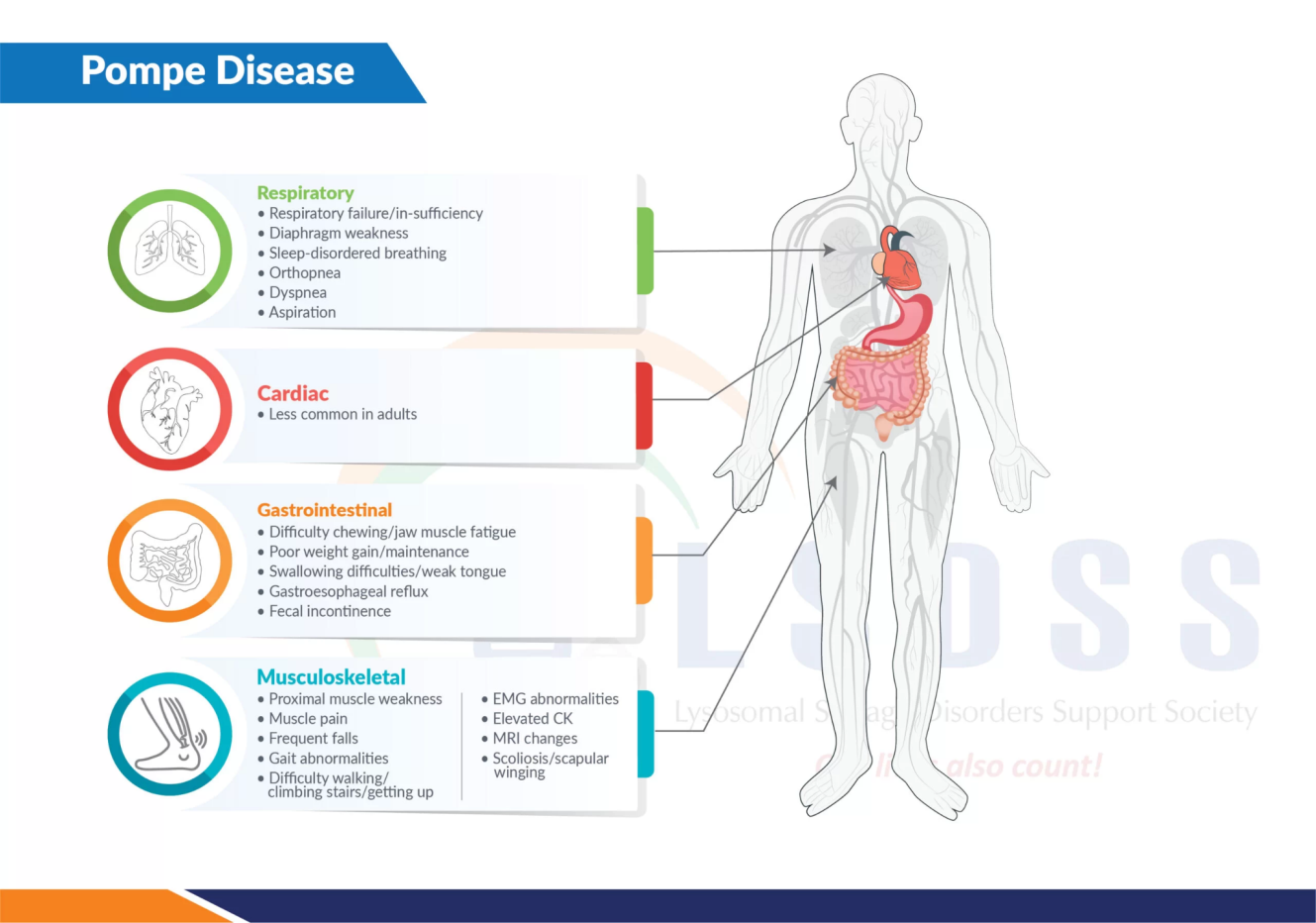
About Pompe disease
Genetic Basis and Enzyme Dysfunction
Clinical Presentation and Variants
Infantile-Onset Pompe Disease
Late-Onset Pompe Disease
Diagnostic Approach
Treatment Options
Challenges and Ongoing Research

Conclusion
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. Case Study: Emma, a 4-month-old infant, presents with poor muscle tone, difficulty feeding, and respiratory problems. After several tests, the doctors diagnosed her with Pompe disease. Which of the following best describes the underlying cause of Pompe disease? A) Deficiency of alpha-glucosidase enzyme B) Mutation in the dystrophin gene C) Absence of hexosaminidase A enzyme D) Mutation in the CFTR gene Correct Answer: A Explanation: Pompe disease, or glycogen storage disease type II, arises from alpha-glucosidase enzyme deficiency, impeding glycogen breakdown in cell lysosomes. The enzyme's role in converting glycogen to glucose is pivotal for waste disposal. Insufficient alpha-glucosidase causes glycogen buildup within lysosomes, predominantly impacting muscle cells. Symptoms manifest early in infancy, exerting effects across bodily systems, notably on skeletal and cardiac muscles due to glycogen accumulation. Progressive muscle weakening ensues, accompanied by severe respiratory complications, posing life-threatening risks. |
© 2024 iasgyan. All right reserved