
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- The collision of two galaxies likely ignites quasars, the new study published in the journal Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society highlighted.
READ: Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN): https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/active-galactic-nuclei-agn
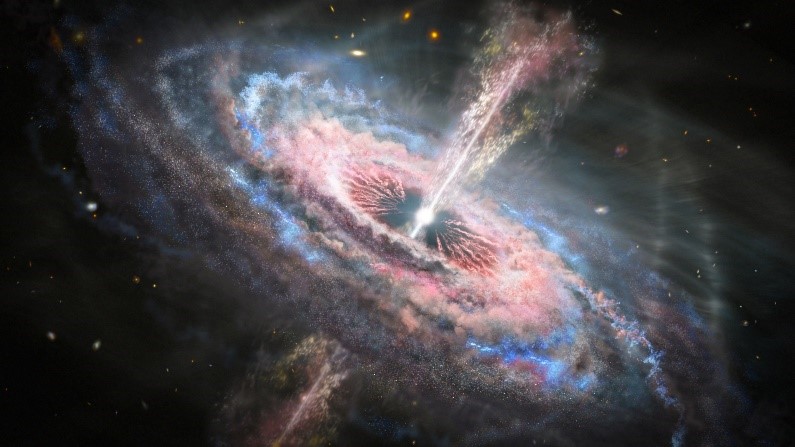
Quasar
- Quasars, short for “Quasi-Stellar Radio Sources”, were first discovered six decades ago.
- They are located in supermassive black holes, which sit in the center of galaxies.
- As a supermassive black hole feed on gas and dust, it releases extraordinary amounts of energy in the form of radiation, resulting in a quasar.
READ ABOUT BLACK HOLE: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/black-hole-13
Origin
- The mechanisms that trigger quasars have been hotly debated. Some studies suggest galaxy mergers are responsible, while others found little evidence to support the theory.
READ: https://www.iasgyan.in/blogs/black-hole
Recent study on the origin of Quasar
- Researchers from the University of Sheffield and Hertfordshire relied on the Isaac Newton Telescope in La Palma in the Canary Islands. They compared 48 galaxies that host quasars with over 100 non-quasar galaxies.
- Galaxies that host a quasar showed morphological features that are consistent with galaxy mergers, the researchers noted.
- When galaxies collide, it pushes the gas from the outer reaches of the galaxies to the centre. And as the supermassive black hole gorges on the gas, it releases ferocious fountains of energy in the form of radiation, leading to the quasar.
- These results present strong evidence that galaxy interactions are the dominant trigger for quasars in the local universe. However, they are unlikely to be the sole factor, the researchers wrote in their study.

Significance of Quasars
- When a quasar is ignited, it can drive the rest of the gas out of the galaxy.
- The radiation from these objects is so intense that intervening gas within the galaxy feels a pressure that moves it away from the quasar in the nucleus, driving “outflows” of material.
- In extreme cases, a significant fraction of the total gas in a galaxy gets displaced. This has drastic consequences on star formation. Also, the collision of the Milky Way galaxy with the Andromeda galaxy could likely trigger a quasar, the scientists predict in their study.
- Quasars are one of the most extreme phenomena in the universe and what we see is likely to represent the future of our own Milky Way galaxy when it collides with the Andromeda galaxy in about five billion years.
READ: MAGNETAR: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/magnetar
BLUE STRAGGLER: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/blue-straggler-20
QUASAR: KEY POINTERS
- Quasar belongs to a family of objects which are together known as the active galactic nuclei (AGN). Of all the objects in AGN, the quasars are the most distant and most energetic objects.
READ: Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN): https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/active-galactic-nuclei-agn
- Quasars are the brightest known objects invisible universe. They are 100 times more luminous than our entire Milky Way which consists of nearly 200-400 billion stars!
- They are so bright that they outshine the entire galaxy they sit in. They emit radio waves, x-rays, and light waves.
- Quasars are the most distant objects ever on record. The most distant quasar discovered called ULAS J1120+0641 is nearly 29 billion light-years away from us.
- Quasars can only be detected using radio telescopes. With a normal optical telescope, a quasar will look like a normal bright star. The difference between a quasar and a star is difficult to identify even with Hubble Space Telescope. A normal star will perhaps be 100 light-years away but a quasar will be millions or billions of light-years away.
- The first quasar that was discovered was in 1950 and was named 3C 273. As of date, nearly 200,000 quasars have been discovered.
- Because of the staggering distance of the quasars from the earth, they are clearly the most ancient objects known to us. They give an insight into the early years of the formation of our universe.
- A quasar is a compact region found at the central part of a massive galaxy and that this central region is actually surrounding the supermassive black hole that sits at the very center of the galaxy. A supermassive black hole has a mass equivalent to a billion solar masses.
An accretion disc is a circular disc-like structure usually made of gasses and the matter spins around the black hole at a very high speed. As matter starts falling into the black hole from the accretion disc, the friction between matters gradually heats up the matter, leading to energy emission.
The energy or radiation of charged particles prefers to get attached to the magnetic field lines. So, as the disc rotates, these charged particles are shot upward and because of the twisted magnetic field lines, the charged particles from a tight column known as the astrophysical jets or cosmic jets, or quasar jets.
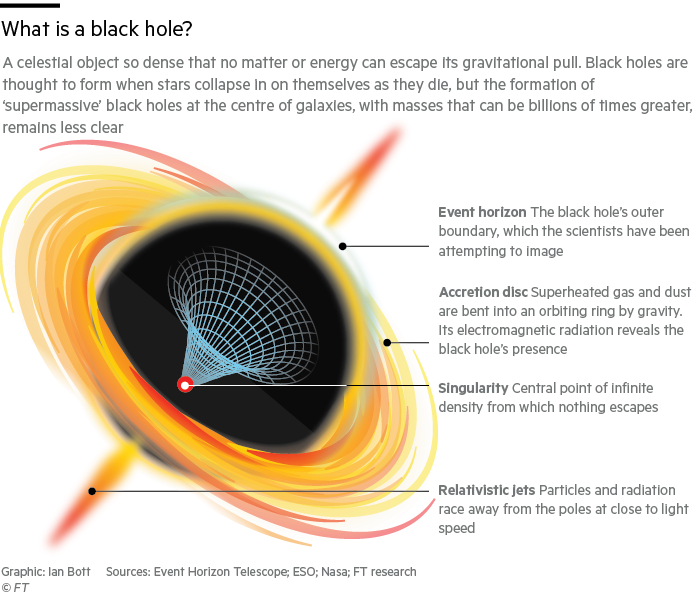
- These quasar jets shoot out to long distances but they don’t really originate from the center of the black hole but are emitted from spinning disc of gas and matter that gradually falls down into the black hole.
- The charged particles inside the quasar jets travel at nearly the speed of light, making them visible from a very long distance.
- This collision of the quasar jets with intergalactic medium gives rise to massive hotspots which are known as DRAGN or Double Radio Source Active Galactic Nucleus. Amazingly a DRAGN can extend to a distance of 1.5 million light-years or more from one end to another end.
- Today’s largest known quasars burn mass every year that is equivalent to the mass of 1000 suns! In terms of earth, these largest quasars eat up mass equivalent to 600 piles of the earth every single day!
- Quasars eventually die. This happens when the supermassive black hole consumes all the matter of the accretion disc and there is nothing left for it to feed on.
- Quasars show high redshift. A redshift is defined as an object’s light spectrum shifting towards the red end of the visible light range. This simply means that an object is moving away from the point from where it is being viewed. Thus, quasars are actually shifting away from Earth.
- It has been found that quasars are drifting away from us at the speed of at least 93,200 miles per second (which is half the speed of light). Some quasars move at 93% of the speed of light.
- Combining the redshift of the quasars with Hubble’s Law, scientists have found that quasars are THE MOST distant objects visible to us in time and space. The closest known quasar known as IC 2497 is 730 million light-years away from us.
- Perhaps our Milky Way once hosted a quasar but now it is dead. Our galaxy may have a quasar when Andromeda Galaxy collides with our Galaxy some 3-5 billion years from now.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. Which of the following statements are incorrect with reference to Quasars?
a) Quasar belongs to a family of objects which are together known as the active galactic nuclei (AGN).
b) Quasars emit radio waves, x-rays, and light waves.
c) The charged particles inside the quasar jets travel at nearly the speed of light.
d) Quasars can only be detected using radio telescopes.
1. a and b only
2. b and c only
3. a, b and d only
4. None of the above.
Correct Answer: Option 4
|

https://www.downtoearth.org.in/news/science-technology/galaxy-mergers-ignite-quasars-the-most-powerful-celestial-objects-study-88971





