Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
Who are the Quds Force?
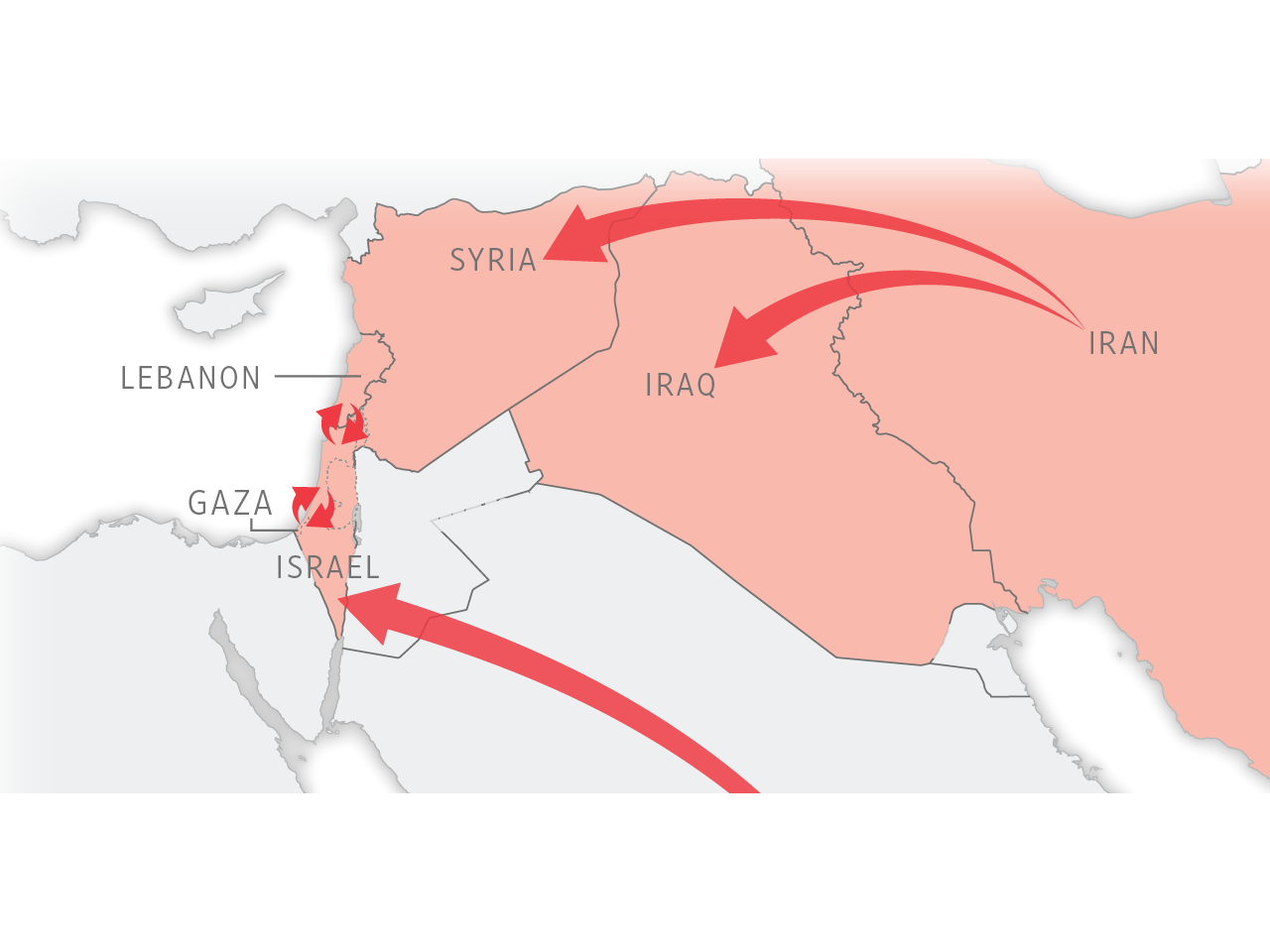
What is Israel’s problem with the Quds Force?
Israel- Iran Issues
Sources:
|
Practice Question The conflict in the Middle East is continuing and it has even increased in recent years. To what extent the escalation and conflict in the Middle East could be attributed to the meddling of Western powers, especially the US? Critically analyze. |
© 2024 iasgyan. All right reserved