
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- Amid the recent attacks on ships passing through the Red Sea trade route in West Asia, one ship as on the way to India.
Red Sea Attacks
- The Red Sea attacks have been carried out by Yemen-based Houthi rebels, who have been in a civil war with the Yemeni government for about a decade. They say the attacks are to protest Israel’s military offensive in Gaza.
- While the US-led maritime security coalition has swiftly announced countermeasures, indicating the importance of the route for world trade, the recent shipping crisis in the Red Sea is not the only pain point here.
- Two crucial choke points – the Suez Canal and the Panama Canal – threaten to disrupt over a third of global trade.
What do the ongoing Red Sea and Panama Canal crises mean for world trade?
- A disruption in maritime transport is a crucial concern for the world economy, as over 80 per cent of the global goods trade is carried by sea. The share of trade via sea is much higher for developing countries such as India.
- Currently, two important shipping routes are facing blockages. While the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait that leads to the Suez Canal in the Red Sea region connects Asia to Europe, the 100-year-old Panama Canal connects the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans.
- Both these routes are among the busiest in the world and a blockage results in forcing global shipping lines to take longer alternate routes, pushing up freight rates.
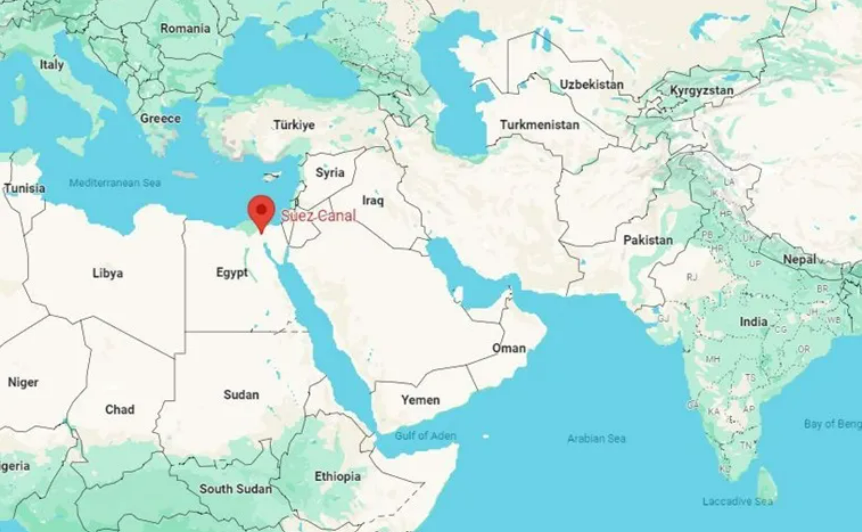
The Suez Canal connects the Mediterranean Sea and the Indian Ocean.
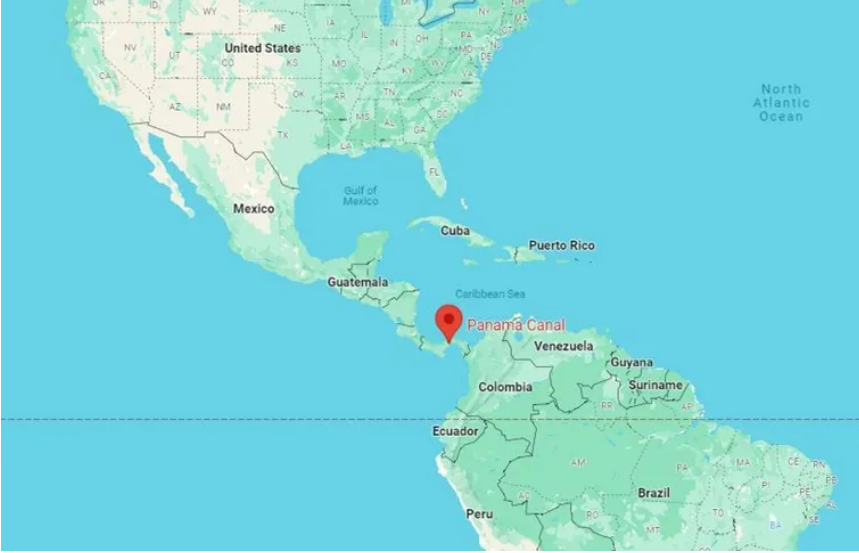
The Panama Canal connects the Pacific and Atlantic Oceans.
- The disruption at the Red Sea route, for instance, is estimated to push the prices of Indian agricultural products by 10 to 20 percent, as shipments would be routed through the Cape of Good Hope.
- This comes at a time when much of the West is witnessing higher interest rates to curb inflation. Higher prices could further fuel demand concerns for global and Indian exporters.
Why is trade via the Panama Canal slowing?
- Shipping via the Panama Canal has dropped by over 50% due to drought conditions at the 51-mile stretch. Due to the shortage of water, ships moving from Asia to the US are being forced to use the Suez Canal, which takes six more days compared to the Panama Canal.
- Moreover, Panama is facing its driest rainy season in decades, raising fears of prolonged canal bottlenecks. According to S&P Global, rather than taking longer voyages through alternative routes, LNG vessels are participating in pricey auctions to expedite their transit through the Panama Canal.
- One vessel paid nearly $4 million for an open slot in an auction in early November. The number of Very Large Gas Carriers transiting the Panama Canal is projected to almost halve by February 2024, and there are concerns that those transits will reduce to zero come January, S&P Global further said.
Why are oil flows to India immune to attack in the Red Sea?
- With global shipping majors such as Maersk avoiding transit through the Red Sea, global oil and petroleum product flows through the maritime channel have declined by over 50 per cent in December from their regular levels.
- However, India has not faced a disruption in its Russian oil imports. Russia is perceived as Iran’s ally and as the Houthi rebels are widely believed to be backed by Tehran, its tankers have been passing through.
- The price of benchmark Brent crude, however, jumped over 5 per cent since the attacks and is hovering around the $80-per-barrel mark.
- In a recent report, Goldman Sachs said that it does not expect the disruptions in the Red Sea to significantly impact international oil prices as global oil production is unlikely to be directly affected.

How have the Red Sea attacks impacted freight rates?
- Ever since the attacks along the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait began earlier this month, global shipping firms have begun imposing war risk surcharges over and above the normal freight rates.
- Indian exporters said that freight rates for Indian shipments headed to Europe and Africa could surge as much as 25-30 per cent if the ongoing security concern along the Red Sea trade route continues.
- This is troubling, as the European Union is one of India’s second-largest export destinations. Slowing demand from the region has impacted India’s labor-intensive sectors, such as textiles, gems and jewelry exports.
Strategic importance of Panama Canal
- The Panama Canal is indeed a critical cornerstone of global maritime transportation.
- It serves as a vital link between the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans, enabling ships to avoid the lengthy and hazardous voyage around Cape Horn at the southern tip of South America.
- By providing a shortcut, the canal contributes to the reduction of carbon emissions and helps mitigate the environmental impact of global maritime transportation.
Here are some key reasons why the Panama Canal is crucial for global maritime transportation:
- Vital Strategic Asset:The United States has a vested interest in the secure, efficient, and reliable operation of the Panama Canal. The canal’s strategic significance extends beyond economic benefits and encompasses national security, defense capabilities, diplomatic relations, and logistical resilience.
- Shorter Transit Routes:The canal shortens the distance between ports on the east and west coast of the Americas, facilitating more efficient trade and transportation. Around 72 percent of transiting ships are either going to or coming from U.S. ports.
- Time and Cost Savings:By using the Panama Canal, ships can save considerable time and fuel costs. The shorter transit time reduces the time in transit and enables faster delivery of goods. This benefit is particularly significant for time sensitive cargoes, perishable goods, and industries with just-in-time supply chains.
- Global Supply Chain:The canal plays a crucial role in global supply chains, supporting the movement of various commodities, including Dry Bulk, Container, Chemical Tankers, LPG carriers, LNG, Vehicle carriers, Refrigerated cargo, General Cargo and Passengers.
Complexities of the Red Sea: Geopolitics and Conflict
- The Red Sea, a vital global trade route, witnesses about 10% of the world’s trade and 20% of its oil transportation. Yemen, situated along this strategic route, has been embroiled in a civil war since 2014, with Houthi tribes controlling the southern part.
The Emergence of Houthi Power:
- The Houthi tribes, in power for nine years, have engaged in conflicts with both the Saudi-backed Yemeni government and Saudi aircraft. Possessing a formidable military with thousands of missiles, drones, rockets, and tanks, they control Hudaydah, a crucial port in southern Yemen.
Houthi-Israel Conflict:
- In a surprising turn of events, the Houthis declared war against Israel on November 2. Initially causing minor damage, they escalated by seizing the Galaxy Leader, an Israeli billionaire’s ship, on November 20. The ship’s ownership discrepancy led to international tensions, further complicated by the geopolitical dynamics of the Red Sea.
Strategic Importance of Yemen’s Coast:
- Yemen’s coastal position of about 300 kilometers plays a crucial role in controlling the Red Sea trade route. The narrow Nero Passage gives the Houthis the ability to disrupt maritime activities, posing a challenge to ships heading to and from Israel.
International Response and Diplomatic Efforts:
- Japan, Britain, and Israel have mobilized diplomatic efforts to secure the release of the seized crews. With Russia and Iran supporting the Houthi faction, the situation has become a new crisis intertwined with the ongoing Israel-Gaza conflict.
Media Coverage and Shifting Public Opinion:
- The Israel-Gaza conflict has garnered extensive media attention, showcasing the brutality of the situation. Social media, particularly platforms like TikTok and X, has become a battleground for information and perspectives.
- The younger generation, influenced by these platforms, questions established narratives, especially regarding U.S. support for Israel.
Soft Power Dynamics and China’s Influence:
- The decline of U.S. soft power is evident, with China adopting a neutral peace-breaking model that challenges traditional carrot-and-stick diplomacy. The Abraham Accords, a recent U.S. peace deal, has faced setbacks, highlighting the changing dynamics of global influence.
- As the world grapples with complex geopolitical issues and the potential for major conflicts, the need for effective leadership to avert catastrophe becomes paramount.
- The power shifts, media influence, and evolving diplomatic strategies shape a new era where the world order established post-World War II may be facing significant challenges.
Escalating Tensions in the Gaza-Israel Conflict:
- The Gaza-Israel conflict, marked by its one-sided brutality, has drawn significant criticism from various quarters. Western media, traditionally aligned with Israeli policies, is experiencing a shift as social media brings forth alternative perspectives, challenging the established narratives.
China’s Soft Power and Changing Global Dynamics:
- China’s neutral peacebroking model, demonstrated in its efforts to reconcile Iran and Saudi Arabia, marks a departure from the traditional U.S. approach. This shift in global dynamics challenges the dominance of the U.S.-led world order.

Conclusion and Global Leadership:
- The world finds itself at a crossroads, with the old world order undergoing seismic shifts. Soft power, diplomatic strategies, and media influence play pivotal roles in shaping global perspectives.
- As the younger generation questions established norms, the need for effective leadership to avert major conflicts becomes increasingly apparent.
- The unfolding events in the Gaza-Israel conflict, coupled with broader geopolitical changes, underscore the complexities of navigating a rapidly evolving global landscape.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. What do the ongoing Red Sea and Panama Canal crises mean for world trade? Also shed light on the Strategic importance of the Panama Canal and the geopolitical significance of the Red Sea.
|






