Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: https://evolutionofculturaldiversity.anu.edu.au/our-research/peopling-sahul/
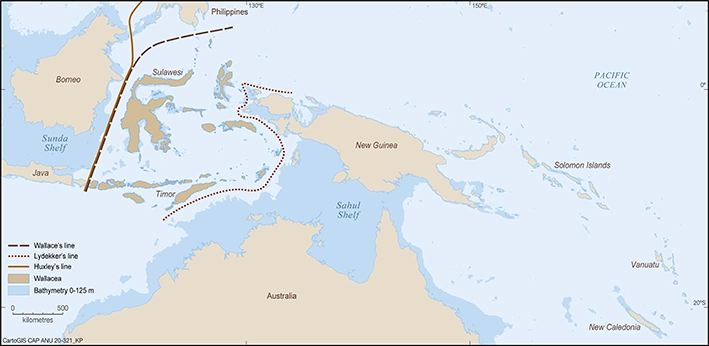
Context: Archaeologists unearthed Sahul, a supercontinent exposed by lower sea levels during the last ice age. This land bridge enabled human migration from Asia to Australia roughly 70,000 years ago.
Details
What is Sahul?
Discovery and Significance
Migration Routes and Archaeological Evidence
The discovery of Sahul is significant for several reasons
Conclusion
Source:
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. Sahul, a term making headlines recently, refers to: A) A newly discovered continent in the Arctic Ocean. B) An ancient supercontinent that once existed where Australia is today. C) A future landmass predicted by geologists. D) A type of unique marine ecosystem. Answer: B |
© 2024 iasgyan. All right reserved