Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now



Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
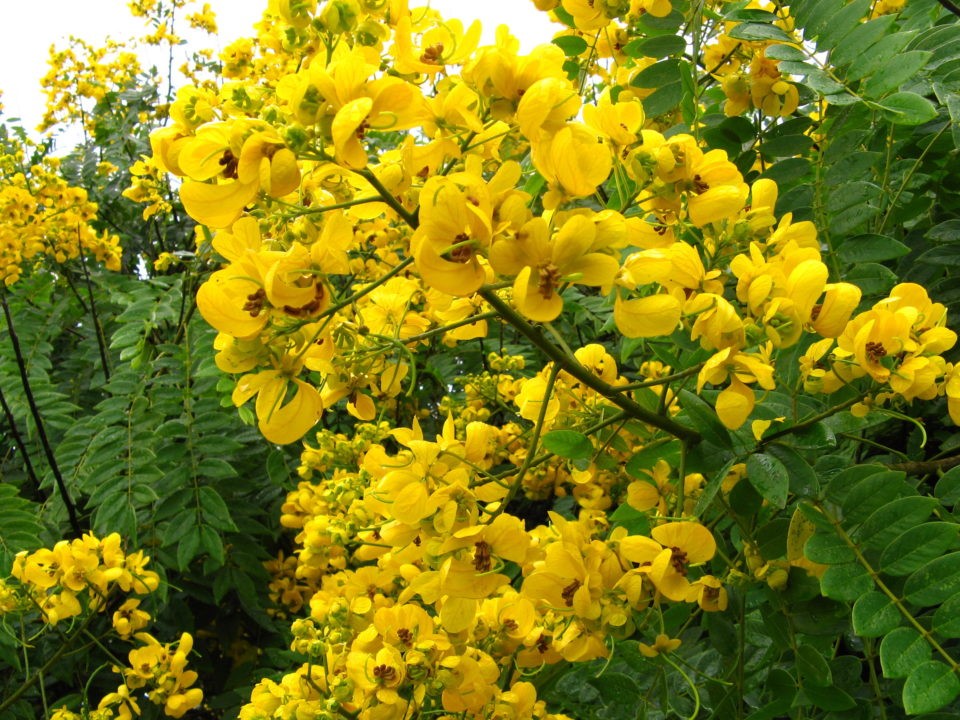
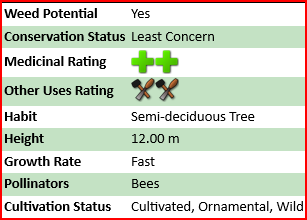
Senna spectabilis
Common Names:
Description:
Range
Habitat
Properties
Senna spectabilis an Invasive species
Ecological Impact:
Uses
Edible Uses
Medicinal
Agroforestry Uses:
Other Uses
|
Invasive Species Definition: Invasive species are organisms introduced into an environment where they are not native, causing ecological or economic harm. Impact on Biodiversity: Invasives can lead to extinctions of native plants and animals, reducing overall biodiversity. They outcompete native species for resources, altering ecosystems. Introduction Mechanisms: Introduced through various means: Ship Ballast Water: Species transported in ship ballast water can be released in new environments. Accidental Release: Unintentional release, often associated with trade and transport. Human Activities: Deliberate introduction for agriculture, horticulture, or as pets. Examples in India: Charru Mussel: Invasive freshwater mussel affecting water bodies. Lantana bushes: Invasive plant species impacting native vegetation. Indian Bullfrog: Exotic amphibian species competing with native frogs. Ecological and Economic Consequences: Invasive species can lead to habitat degradation, loss of native species, and disruption of ecosystem services. Economic impacts include damage to agriculture, fisheries, and infrastructure. Management and Control: Strategies involve early detection, monitoring, and eradication efforts. Biocontrol methods using natural predators or pathogens may be employed. Prevention through strict regulations on trade and transportation. Global Perspective: Invasive species are a global concern, with significant efforts focused on prevention and control. International collaborations address invasive threats to biodiversity. IUCN and Red List: Some invasive species are assessed by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) and may be categorized based on their impact. |
Sathyamangalam Wildlife Sanctuary
Sathyamangalam Wildlife Sanctuary, now known as the Sathyamangalam Tiger Reserve, is one of the significant protected areas in southern India. It is situated in the Erode District of Tamil Nadu, spanning into the Chamarajanagar District of Karnataka and the Malappuram District of Kerala. Below are key details about the Sathyamangalam Tiger Reserve:
Establishment and Recognition:
Geographical Extent:
Flora and Fauna:
Connectivity:
Conservation Initiatives:
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Question: Consider the following statements about Senna spectabilis:
Which of the statements above are correct? A. 1 and 2 only B. 2 and 3 only C. 1, 3, and 4 only D. 1, 2, 3, and 4 Answer: C. 1, 3, and 4 only Explanation:
|
© 2024 iasgyan. All right reserved